Cells
... Selective Permeability Some things can go through, while others cannot. The plasma membrane, with its embedded molecules, controls this. ...
... Selective Permeability Some things can go through, while others cannot. The plasma membrane, with its embedded molecules, controls this. ...
Plasma Membranes
... There are two types of proteins in the plasma membrane; EXTRINSIC PROTEINS – these proteins are found on the outer and inner surfaces of the membrane but do not penetrate the whole membrane. INTRINSIC PROTEINS – these proteins penetrate the whole plasma membrane. The functions of the membrane prote ...
... There are two types of proteins in the plasma membrane; EXTRINSIC PROTEINS – these proteins are found on the outer and inner surfaces of the membrane but do not penetrate the whole membrane. INTRINSIC PROTEINS – these proteins penetrate the whole plasma membrane. The functions of the membrane prote ...
LPS- or Pseudomonas aeruginosa- mediated activation of
... Shaikh, Jolly & Chapkin, 2012), which might hamper the stimulation-induced initiation of the TLR4 signaling cascade via blocking the TLR4-CD14 interaction in lipid rafts. To address this issue in a comprehensive approach we investigated the consequences of a PUFA supplementation on the TLR4 pathway ...
... Shaikh, Jolly & Chapkin, 2012), which might hamper the stimulation-induced initiation of the TLR4 signaling cascade via blocking the TLR4-CD14 interaction in lipid rafts. To address this issue in a comprehensive approach we investigated the consequences of a PUFA supplementation on the TLR4 pathway ...
Structure and Function of Membrane Proteins: Overview
... hydrophobic fatty acid (acyl) tails protected from aqueous environment 2. Polar heads face cytoplasm on one side & blood plasma on the other; polar heads of each leaflet were directed outward toward aqueous environment C. Got right answer, but used several miscalculations; however, mistakes compensa ...
... hydrophobic fatty acid (acyl) tails protected from aqueous environment 2. Polar heads face cytoplasm on one side & blood plasma on the other; polar heads of each leaflet were directed outward toward aqueous environment C. Got right answer, but used several miscalculations; however, mistakes compensa ...
Archaea - The Ancient Oddities
... volcanic vents), but are also found in marshes, soils, oceans, intestines • Unlike Eubacteria, none are known parasites or pathogens (are often mutualists or commensalists) ...
... volcanic vents), but are also found in marshes, soils, oceans, intestines • Unlike Eubacteria, none are known parasites or pathogens (are often mutualists or commensalists) ...
Module 3 Lecture 3 Lysosome and vacuolar membrane
... needs some additional features in its membrane. It is slightly thicker than that of the plasma membrane. It contains substantial amounts of carbohydrate component, particularly sialic acid. In fact, most lysosomal membrane proteins are highly glycosylated, which may help protect them from the lysoso ...
... needs some additional features in its membrane. It is slightly thicker than that of the plasma membrane. It contains substantial amounts of carbohydrate component, particularly sialic acid. In fact, most lysosomal membrane proteins are highly glycosylated, which may help protect them from the lysoso ...
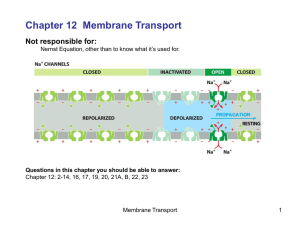
What is “membrane potential”
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
... Not responsible for: Nernst Equation, other than to know what it’s used for. ...
The use of isotope-coded affinity tags (ICAT)
... between the two organelles, proteomic analysis of the Golgirich fraction was performed. Golgi membrane proteins were identified, as well as numerous uncharacterized proteins. However, the presence of contaminating ER proteins in the Golgi-rich fraction prevented the assignment of these uncharacteriz ...
... between the two organelles, proteomic analysis of the Golgirich fraction was performed. Golgi membrane proteins were identified, as well as numerous uncharacterized proteins. However, the presence of contaminating ER proteins in the Golgi-rich fraction prevented the assignment of these uncharacteriz ...
Active transport
... a, The hair cell has an array of pencil-shaped stereocilia on its surface, each linked to its neighbour through a 'tip link'. b, The ion channel that mediates the conversion of sound or movement into electrical signals is located at one (and possibly both) ends of the tip link, which is shown here a ...
... a, The hair cell has an array of pencil-shaped stereocilia on its surface, each linked to its neighbour through a 'tip link'. b, The ion channel that mediates the conversion of sound or movement into electrical signals is located at one (and possibly both) ends of the tip link, which is shown here a ...
Expressing Biologically Active Membrane Proteins in a Cell
... Membrane proteins are difficult targets as compared to soluble proteins because of the challenges associated with their expression, solubilization, and stabilization. Typical studies of membrane proteins rely on proteins produced from cells and solubilized cell membrane using deterge ...
... Membrane proteins are difficult targets as compared to soluble proteins because of the challenges associated with their expression, solubilization, and stabilization. Typical studies of membrane proteins rely on proteins produced from cells and solubilized cell membrane using deterge ...
Small GTPases
... • regulation of the active transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm (TFs, histons from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, tRNA and mRNA vice versa) RanGAP is in the cytoplasm RanGTP is converted here to RanGDP RanGEF is in the nucleus RanGDP is converted here to RanGTP transport from the cyt ...
... • regulation of the active transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm (TFs, histons from the cytoplasm to the nucleus, tRNA and mRNA vice versa) RanGAP is in the cytoplasm RanGTP is converted here to RanGDP RanGEF is in the nucleus RanGDP is converted here to RanGTP transport from the cyt ...
Syllabus, BIOSC 2105: Cell Signaling Spring Term, 2014 Instructor
... 7. How does Ca2+ signaling initiate embryonic development in response to sperm fertilization? What changes occur in the cell and is expression of maternal RNA linked to this calcium signaling event. ...
... 7. How does Ca2+ signaling initiate embryonic development in response to sperm fertilization? What changes occur in the cell and is expression of maternal RNA linked to this calcium signaling event. ...
The term “fluid mosaic model” refers to ______.
... saturated phospholipids in its cell membranes than an organism living at the South Pole. Why? a. In cold climates, more unsaturated fats with kinked tails are needed to maintain the fluidity of the cell membranes. b. In cold climates, more saturated fats with kinked tails are needed to maintain the ...
... saturated phospholipids in its cell membranes than an organism living at the South Pole. Why? a. In cold climates, more unsaturated fats with kinked tails are needed to maintain the fluidity of the cell membranes. b. In cold climates, more saturated fats with kinked tails are needed to maintain the ...
Effects of phosphatidylethanolamine glycation on lipid–protein
... within it [9]. A number of studies have later demonstrated that membrane structure is more complex; their components can form segregated domains of variable size and stability [10,11]. This inhomogeneous organization seems to be intimately related to certain membrane functions [12]. Furthermore, the ...
... within it [9]. A number of studies have later demonstrated that membrane structure is more complex; their components can form segregated domains of variable size and stability [10,11]. This inhomogeneous organization seems to be intimately related to certain membrane functions [12]. Furthermore, the ...
3.3 Cell Membrane TEKS 3E, 4B, 9A
... Cell Membrane The student is expected to: 3E evaluate models according to their limitations in representing biological objects or events; 4B investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules; ...
... Cell Membrane The student is expected to: 3E evaluate models according to their limitations in representing biological objects or events; 4B investigate and explain cellular processes, including homeostasis, energy conversions, transport of molecules, and synthesis of new molecules; ...
Viral hepatitis and fatty liver disease: how an
... growing list of transcription factors with which HBx has been shown to interact [1]. The link between LXR, SREBP1c and steatosis has been noted before with HCV infection. HCV ‘non-structural protein2’ activated SREBP1c and FAS transcription which involved the LXREs and SREs (sterol-response elements ...
... growing list of transcription factors with which HBx has been shown to interact [1]. The link between LXR, SREBP1c and steatosis has been noted before with HCV infection. HCV ‘non-structural protein2’ activated SREBP1c and FAS transcription which involved the LXREs and SREs (sterol-response elements ...
The Estrogen Trinity: Membrane, Cytosolic, and - Rose
... Summary The existence of one of the three mechanisms in a particular cell is not exclusive. In this way, estrogens can elicit diverse cellular effects that may depend on their concentration because most of the estrogen binding sites present different affinities. In general, binding to ion channels a ...
... Summary The existence of one of the three mechanisms in a particular cell is not exclusive. In this way, estrogens can elicit diverse cellular effects that may depend on their concentration because most of the estrogen binding sites present different affinities. In general, binding to ion channels a ...
Presynaptic mechanisms: neurotransmitter release, synaptic vesicle
... In the slow track, vesicles are recruited from the reserve pool that corresponds to synaptic vesicles attached to the actin cytoskeleton via synapsin. These vesicles then translocate to the vicinity of the plasma membrane. They undergo priming through an unknown mechanism in which nSec1 and Munc13, ...
... In the slow track, vesicles are recruited from the reserve pool that corresponds to synaptic vesicles attached to the actin cytoskeleton via synapsin. These vesicles then translocate to the vicinity of the plasma membrane. They undergo priming through an unknown mechanism in which nSec1 and Munc13, ...
Assessment of antimicrobial compounds by microscopy techniques
... Bacterial membranes display a negatively charged exposed leaflet, while in eukaryotic cells the outer leaflet is neutral and most negative lipids are displayed in the inner leaflet [15]. Most cationic AMPPs need electrostatic interactions to bind selectively with anionic membranes. They tend to form ...
... Bacterial membranes display a negatively charged exposed leaflet, while in eukaryotic cells the outer leaflet is neutral and most negative lipids are displayed in the inner leaflet [15]. Most cationic AMPPs need electrostatic interactions to bind selectively with anionic membranes. They tend to form ...
Come in and take your coat off how host cells
... release the genomic information at the right place within the cell to ascertain viral transcription and replication. Both tasks are coordinated in time and space and rely on a number of ‘cues’ provided by interactions of the host cell with the virus structure. The virus particle During transmission, ...
... release the genomic information at the right place within the cell to ascertain viral transcription and replication. Both tasks are coordinated in time and space and rely on a number of ‘cues’ provided by interactions of the host cell with the virus structure. The virus particle During transmission, ...
Presence of methyl sterol and bacteriohopanepolyol
... and the SDS-PAGE analysis of membrane proteins (Fig. 1). The amount of material recovered in I1 varied widely between experiments; in some, band I1 was not observed, and in others it accounted for as much as 40% of the total recovered protein and phospholipid. A substantial increase in band I1 resul ...
... and the SDS-PAGE analysis of membrane proteins (Fig. 1). The amount of material recovered in I1 varied widely between experiments; in some, band I1 was not observed, and in others it accounted for as much as 40% of the total recovered protein and phospholipid. A substantial increase in band I1 resul ...
Supplementary: Effect of Lipid Head Group Interactions in
... and another, away, which is less aligned (peak at 125◦ ). For the 1M NaCl system, the GL1-G1M vector is better aligned to the bilayer normal, compared to the system with 0M NaCl. The better alignment of the GL1-G1M vector with the bilayer normal at 1M NaCl can be rationalized by the increase in popu ...
... and another, away, which is less aligned (peak at 125◦ ). For the 1M NaCl system, the GL1-G1M vector is better aligned to the bilayer normal, compared to the system with 0M NaCl. The better alignment of the GL1-G1M vector with the bilayer normal at 1M NaCl can be rationalized by the increase in popu ...
No Slide Title
... Hydolases found in blood instead Defective or missing GlcNAc-phosphotransferase No P, no binding M6P receptors Some cell types (heptacytes) still sort to lysosome - must be an M6P independent pathway ...
... Hydolases found in blood instead Defective or missing GlcNAc-phosphotransferase No P, no binding M6P receptors Some cell types (heptacytes) still sort to lysosome - must be an M6P independent pathway ...
Chapter 3 - Palm Beach State College
... Hydrophilic regions contact cytoplasm, extracellular fluid Hydrophobic regions pass through lipid of the membrane Some drift in membrane; others are anchored to ...
... Hydrophilic regions contact cytoplasm, extracellular fluid Hydrophobic regions pass through lipid of the membrane Some drift in membrane; others are anchored to ...
Lipid raft
The plasma membranes of cells contain combinations of glycosphingolipids and protein receptors organized in glycolipoprotein microdomains termed lipid rafts. These specialized membrane microdomains compartmentalize cellular processes by serving as organizing centers for the assembly of signaling molecules, influencing membrane fluidity and membrane protein trafficking, and regulating neurotransmission and receptor trafficking. Lipid rafts are more ordered and tightly packed than the surrounding bilayer, but float freely in the membrane bilayer. Although more common in plasma membrane, lipid rafts have also been reported in other parts of the cell, such as Golgi and lysosomes.