Chapter 7 Reading Guide
... Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. ...
... Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 2. Pleiotropy occurs when a gene produces multiple phenotypic expressions. Pleiotropy results when the protein encoded by a gene enters several different biochemical pathways or affects more than one body part or process. 3. Each gene encodes one protein, but many different proteins may interact in ...
... 2. Pleiotropy occurs when a gene produces multiple phenotypic expressions. Pleiotropy results when the protein encoded by a gene enters several different biochemical pathways or affects more than one body part or process. 3. Each gene encodes one protein, but many different proteins may interact in ...
The Nutritional Value of Milk Proteins
... profiles and good digestibility. In addition, they contain high levels of the amino acids which are deficient in vegetable proteins. Because of this, milk proteins are excellent “complementary” proteins. Utilization of Proteins and Amino Acids All proteins contain amino acids, the protein “building ...
... profiles and good digestibility. In addition, they contain high levels of the amino acids which are deficient in vegetable proteins. Because of this, milk proteins are excellent “complementary” proteins. Utilization of Proteins and Amino Acids All proteins contain amino acids, the protein “building ...
Robustness of the model
... forming organelle by coiled-coil scaffolds. Through our refined sequence alignment, we have shown that the present-day coiled-coil scaffold proteins were already present in the opisthokont ancestor. Independent evidence for the capabilities of coiled-coil proteins comes from synthetic biology. Coile ...
... forming organelle by coiled-coil scaffolds. Through our refined sequence alignment, we have shown that the present-day coiled-coil scaffold proteins were already present in the opisthokont ancestor. Independent evidence for the capabilities of coiled-coil proteins comes from synthetic biology. Coile ...
Document
... compositions of Amino Acids and side-chain groups, to Train Neural Networks The positive entries are labeled with a 1 and the negative entries are labeled with a –1. Using a Matlab Script, a random 20% of the positive data-set is set aside and used as a test set against the other ...
... compositions of Amino Acids and side-chain groups, to Train Neural Networks The positive entries are labeled with a 1 and the negative entries are labeled with a –1. Using a Matlab Script, a random 20% of the positive data-set is set aside and used as a test set against the other ...
The Science of Proteins in Milk (including A1 vs A2 Milk)
... present review of available scientific literature, a cause-effect relationship between BCM7 and etiology or cause of any suggested non-communicable diseases cannot be established.” Report to New Zealand Food Safety Authority (2004): “I do not believe there is sufficient evidence to warrant the gover ...
... present review of available scientific literature, a cause-effect relationship between BCM7 and etiology or cause of any suggested non-communicable diseases cannot be established.” Report to New Zealand Food Safety Authority (2004): “I do not believe there is sufficient evidence to warrant the gover ...
Amino Acid Instruction Sheet
... those building blocks create (for example, bricks could make a building, rocks could make a mountain, and pages could make a book). 2. Ask students what they know of or remember about protein (Note: students who participated in the Venom! lab activity may have more information than those who have no ...
... those building blocks create (for example, bricks could make a building, rocks could make a mountain, and pages could make a book). 2. Ask students what they know of or remember about protein (Note: students who participated in the Venom! lab activity may have more information than those who have no ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... Because the genetic code is triplet, there are three forward reading frames on a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic genes have gaps, called introns, which must be removed from the mRNA before the protein is made. The number of introns, and their length, varies with different genes. Errors in removing introns ...
... Because the genetic code is triplet, there are three forward reading frames on a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic genes have gaps, called introns, which must be removed from the mRNA before the protein is made. The number of introns, and their length, varies with different genes. Errors in removing introns ...
Ch. 11 Cell Communication Review Name Date Per _____ Multiple
... D. The signal transduction pathways of local regulators do not involve second messengers; pathways triggered by hormones do involve second messengers. E. Local regulators often open ligand-gated channels and affect ion concentration in a cell; hormones bind with intracellular receptors and affect ge ...
... D. The signal transduction pathways of local regulators do not involve second messengers; pathways triggered by hormones do involve second messengers. E. Local regulators often open ligand-gated channels and affect ion concentration in a cell; hormones bind with intracellular receptors and affect ge ...
Map of the Human β-Globin Gene – In Brief
... Because the genetic code is triplet, there are three forward reading frames on a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic genes have gaps, called introns, which must be removed from the mRNA before the protein is made. The number of introns, and their length, varies with different genes. Errors in removing introns ...
... Because the genetic code is triplet, there are three forward reading frames on a strand of DNA. Eukaryotic genes have gaps, called introns, which must be removed from the mRNA before the protein is made. The number of introns, and their length, varies with different genes. Errors in removing introns ...
Protein modification in eukaryotic cell-free systems
... The remarkable range of functions carried out by membrane proteins as well as soluble proteins results from only 20 building blocks - the 20 canonical amino acids together with a limited amount of additional chemistries arising from post-translational modifications and cofactors. A huge number of ap ...
... The remarkable range of functions carried out by membrane proteins as well as soluble proteins results from only 20 building blocks - the 20 canonical amino acids together with a limited amount of additional chemistries arising from post-translational modifications and cofactors. A huge number of ap ...
Ch 10
... • Middle range time effect • PKA activates the enzyme that releases glucose from storage ...
... • Middle range time effect • PKA activates the enzyme that releases glucose from storage ...
Aims - Excellence Gateway
... Levels of Organisation, Identify the Organelle, Nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Golgi Body, Lysosome, Mitochondria. Can be shown as a slide show and students to take notes, or can be hand-outs for the students. ...
... Levels of Organisation, Identify the Organelle, Nucleus, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Ribosomes, Golgi Body, Lysosome, Mitochondria. Can be shown as a slide show and students to take notes, or can be hand-outs for the students. ...
File
... Cancer cells have lost their ability to regulate mitosis, resulting in uncontrolled cell division. ...
... Cancer cells have lost their ability to regulate mitosis, resulting in uncontrolled cell division. ...
Signal networks and pathways
... • B. The ras gene produces a G-protein that lacks GTPase activity, thus impacting 3A. • C. Pertussis toxin inactivates the process that downregulates adenylate cyclase activity with respect to G-proteins of the Gi subfamily, with a few exceptions such as Gz, thus impacting 3C. • D. G-proteins of the ...
... • B. The ras gene produces a G-protein that lacks GTPase activity, thus impacting 3A. • C. Pertussis toxin inactivates the process that downregulates adenylate cyclase activity with respect to G-proteins of the Gi subfamily, with a few exceptions such as Gz, thus impacting 3C. • D. G-proteins of the ...
Goal 2.01 Quiz 2
... polysaccharides bonded together. D. Monosaccharides are made up of one amino acid, and polysaccharides are made up of two or more amino acids. ...
... polysaccharides bonded together. D. Monosaccharides are made up of one amino acid, and polysaccharides are made up of two or more amino acids. ...
Protein Creation Pathway Tutorial
... 5. In general, what are small parts of the cell called?___________________________________ ...
... 5. In general, what are small parts of the cell called?___________________________________ ...
Leukaemia Section t(3;11)(p21;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Unknown; likely to be poor, both as it carries a MLL rearrangements and as occurs in t-ANLL. ...
... Unknown; likely to be poor, both as it carries a MLL rearrangements and as occurs in t-ANLL. ...
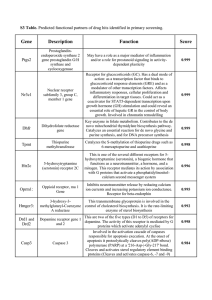
Gene Description Function Score
... differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodelling ...
... differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodelling ...
slides
... predict protein structure for Arabidopsis and rice proteins. Based on sequence similarity, we have identified ;15,000 orthologous/paralogous protein family clusters among these species and used codon-based models to predict positive selection in protein evolution within 175 of these sequence cluster ...
... predict protein structure for Arabidopsis and rice proteins. Based on sequence similarity, we have identified ;15,000 orthologous/paralogous protein family clusters among these species and used codon-based models to predict positive selection in protein evolution within 175 of these sequence cluster ...
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
... that specifies either a start codon, a particular amino acid, or a stop codon • Transfer RNA (tRNA) is another type of RNA – it is found free-floating in the cytoplasm and is responsible for carrying one amino acid – Remember amino acids are the building blocks of proteins ...
... that specifies either a start codon, a particular amino acid, or a stop codon • Transfer RNA (tRNA) is another type of RNA – it is found free-floating in the cytoplasm and is responsible for carrying one amino acid – Remember amino acids are the building blocks of proteins ...
Structure and Function of Membranes
... • Fluidity regulated by different kinds of fatty acid (FA) tails: • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal membranes, keeps FA tails from twisting together ...
... • Fluidity regulated by different kinds of fatty acid (FA) tails: • More unsaturated FA, membrane stays fluid at lower temp (winter) • More saturated FA, membrane is more stable at high temperatures (summer) • Cholesterol embedded in animal membranes, keeps FA tails from twisting together ...
LABORATORY TESTS THAT REFLECT NUTRITION
... LABORATORY TESTS THAT REFLECT NUTRITION There are numerous biochemical tests that have nutritional implications. These are a few of the laboratory tests that can be utilized by nurses and dietitians to assess a patient’s nutritional status. Remember, however, that all of these tests provide a wide v ...
... LABORATORY TESTS THAT REFLECT NUTRITION There are numerous biochemical tests that have nutritional implications. These are a few of the laboratory tests that can be utilized by nurses and dietitians to assess a patient’s nutritional status. Remember, however, that all of these tests provide a wide v ...
- ITA Heidelberg
... the chain onto itself, called a -sheet. Both polypeptides are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape into which these macromolecules fold due to disul de bonds and the hydrophobic interaction. In a fourth type of structure, several protein subunits comb ...
... the chain onto itself, called a -sheet. Both polypeptides are stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape into which these macromolecules fold due to disul de bonds and the hydrophobic interaction. In a fourth type of structure, several protein subunits comb ...
Understanding protein lists from comparative proteomics studies
... “I’ve attached a spreadsheet of our proteomics results comparing 5 Vehicle and 5 Aldosterone treated patients. We’ve included only those proteins whose summed spectral counts are >30 in one treatment group. Would it be possible to get the GO annotations for these? The Uniprot name is listed in colum ...
... “I’ve attached a spreadsheet of our proteomics results comparing 5 Vehicle and 5 Aldosterone treated patients. We’ve included only those proteins whose summed spectral counts are >30 in one treatment group. Would it be possible to get the GO annotations for these? The Uniprot name is listed in colum ...
Protein moonlighting

Protein moonlighting (or gene sharing) is a phenomenon by which a protein can perform more than one function. Ancestral moonlighting proteins originally possessed a single function but through evolution, acquired additional functions. Many proteins that moonlight are enzymes; others are receptors, ion channels or chaperones. The most common primary function of moonlighting proteins is enzymatic catalysis, but these enzymes have acquired secondary non-enzymatic roles. Some examples of functions of moonlighting proteins secondary to catalysis include signal transduction, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, motility, and structural.Protein moonlighting may occur widely in nature. Protein moonlighting through gene sharing differs from the use of a single gene to generate different proteins by alternative RNA splicing, DNA rearrangement, or post-translational processing. It is also different from multifunctionality of the protein, in which the protein has multiple domains, each serving a different function. Protein moonlighting by gene sharing means that a gene may acquire and maintain a second function without gene duplication and without loss of the primary function. Such genes are under two or more entirely different selective constraints.Various techniques have been used to reveal moonlighting functions in proteins. The detection of a protein in unexpected locations within cells, cell types, or tissues may suggest that a protein has a moonlighting function. Furthermore, sequence or structure homology of a protein may be used to infer both primary function as well as secondary moonlighting functions of a protein.The most well-studied examples of gene sharing are crystallins. These proteins, when expressed at low levels in many tissues function as enzymes, but when expressed at high levels in eye tissue, become densely packed and thus form lenses. While the recognition of gene sharing is relatively recent—the term was coined in 1988, after crystallins in chickens and ducks were found to be identical to separately identified enzymes—recent studies have found many examples throughout the living world. Joram Piatigorsky has suggested that many or all proteins exhibit gene sharing to some extent, and that gene sharing is a key aspect of molecular evolution. The genes encoding crystallins must maintain sequences for catalytic function and transparency maintenance function.Inappropriate moonlighting is a contributing factor in some genetic diseases, and moonlighting provides a possible mechanism by which bacteria may become resistant to antibiotics.