The Structure of Cell Walls of Phycomycetes
... placed up to 7 cm. from the anode. For Pythium butleri two main amido black and anaphthol positive spots were detected with respective R ~ v a l u e sof 0.08 and 0.12. The material with the lower RFgave two glycoprotein spots running 8 and 28 cm. on similar electrograms, and the material from the se ...
... placed up to 7 cm. from the anode. For Pythium butleri two main amido black and anaphthol positive spots were detected with respective R ~ v a l u e sof 0.08 and 0.12. The material with the lower RFgave two glycoprotein spots running 8 and 28 cm. on similar electrograms, and the material from the se ...
Sequence identity and homology
... homologous”. Also sometimes defined as “Similar due to descent from a common ancestor.” Homology is either/or-there is no such thing as “percent homology”! Homologous is not a synonym for “similar”! It is, however, possible for only a part of two sequences to be homologous, for instance one domain i ...
... homologous”. Also sometimes defined as “Similar due to descent from a common ancestor.” Homology is either/or-there is no such thing as “percent homology”! Homologous is not a synonym for “similar”! It is, however, possible for only a part of two sequences to be homologous, for instance one domain i ...
Molecular Definition of Distinct Cytoskeletal Structures
... o f nascent phagosomes is different when macrophages ingest IgG- or complement-opsonized particles (13), and we confirmed these data here (Fig. 1): during FclK-mediated phagocytosis, lameUipodia protrude from the macrophage surface and form a phagosome that is tightly apposed to the particle, wherea ...
... o f nascent phagosomes is different when macrophages ingest IgG- or complement-opsonized particles (13), and we confirmed these data here (Fig. 1): during FclK-mediated phagocytosis, lameUipodia protrude from the macrophage surface and form a phagosome that is tightly apposed to the particle, wherea ...
CycD1, a Putative G1 Cyclin from Antirrhinum majus
... plants. Plant D cyclins also contain a functional Rb binding motif, and Rb is a possible substrate (Ach et al., 1997; Huntley et al., 1998; Nakagami et al., 1999, 2002). In Arabidopsis thaliana, there are at least 10 D cyclin genes forming several structurally distinct groups (Arabidopsis Genome Ini ...
... plants. Plant D cyclins also contain a functional Rb binding motif, and Rb is a possible substrate (Ach et al., 1997; Huntley et al., 1998; Nakagami et al., 1999, 2002). In Arabidopsis thaliana, there are at least 10 D cyclin genes forming several structurally distinct groups (Arabidopsis Genome Ini ...
Cyclin Dependent Kinases and Cell Cycle Control
... Two major approaches were used, the first being the cloning of the human cdc2 gene achieved by Melanie Lee (Lee and Nurse, 1987). Initially Melanie had tried to clone a human homologue of cdc2 on the basis of structural similarity. These approaches identified protein kinases, but as there are at lea ...
... Two major approaches were used, the first being the cloning of the human cdc2 gene achieved by Melanie Lee (Lee and Nurse, 1987). Initially Melanie had tried to clone a human homologue of cdc2 on the basis of structural similarity. These approaches identified protein kinases, but as there are at lea ...
YSK1 is activated by the Golgi matrix protein GM130 and plays a
... et al., 2001). In mammals, over 30 Ste20 kinases exist classified into two subgroups. These are the p21-activated kinases and the germinal center kinases (Dan et al., 2001), and it is this latter group that is of interest here. Germinal center kinases possess an NH2-terminal kinase domain and a COOH ...
... et al., 2001). In mammals, over 30 Ste20 kinases exist classified into two subgroups. These are the p21-activated kinases and the germinal center kinases (Dan et al., 2001), and it is this latter group that is of interest here. Germinal center kinases possess an NH2-terminal kinase domain and a COOH ...
eIF-3 - Universidad Autónoma de San Luis Potosí
... The release factors are present at much lower levels than initiation or elongation factors;~600 molecules of each per cell (1 RF per 10 ribosomes). ...
... The release factors are present at much lower levels than initiation or elongation factors;~600 molecules of each per cell (1 RF per 10 ribosomes). ...
SAPS(1) USER COMMANDS SAPS(1) NAME saps
... saps [ -dtv ] [ -T ] [ -s species ] [ -H ] [ -a XY... ] [ -b libfname ] [ -l lstfname ] [ -p ] seqfname(s) DESCRIPTION SAPS evaluates by statistical criteria a wide variety of protein sequence properties. Properties considered include compositional biases; clusters and runs of charge and other amino ...
... saps [ -dtv ] [ -T ] [ -s species ] [ -H ] [ -a XY... ] [ -b libfname ] [ -l lstfname ] [ -p ] seqfname(s) DESCRIPTION SAPS evaluates by statistical criteria a wide variety of protein sequence properties. Properties considered include compositional biases; clusters and runs of charge and other amino ...
Protein Synthesis and Quality Control at the Endoplasmic Reticulum
... that ion movement through the pore is prevented during translocation not by a ribosome–translocon seal, but rather by the structure of the translocon itself. Specifically, they proposed that the translocon pore was only large enough to accommodate an unfolded nascent polypeptide and that ion movment ...
... that ion movement through the pore is prevented during translocation not by a ribosome–translocon seal, but rather by the structure of the translocon itself. Specifically, they proposed that the translocon pore was only large enough to accommodate an unfolded nascent polypeptide and that ion movment ...
Nuclear function for the actin-binding cytoskeletal protein
... In the last few years, it has been shown that, besides the nuclear intermedier filamentforming lamins, several cytoskeletal components are also present in the nucleus including actin, motor proteins and crosslinking proteins (Simon and Wilson 2011). However, the existence of a structure mechanically ...
... In the last few years, it has been shown that, besides the nuclear intermedier filamentforming lamins, several cytoskeletal components are also present in the nucleus including actin, motor proteins and crosslinking proteins (Simon and Wilson 2011). However, the existence of a structure mechanically ...
A role for the DNA-damage checkpoint kinase Chk1 in the virulence
... Sgarlata and Perez-Martin, 2005a). To determine the kinase activity associated with Cdk1 during b-factor-dependent filament formation, we took advantage of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe protein Suc1, which is known to bind specifically to mitotic CDKs with high affinity (Ducommun and Beach, 1990) an ...
... Sgarlata and Perez-Martin, 2005a). To determine the kinase activity associated with Cdk1 during b-factor-dependent filament formation, we took advantage of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe protein Suc1, which is known to bind specifically to mitotic CDKs with high affinity (Ducommun and Beach, 1990) an ...
Adaptation and Protein Quality Control Under Metalloid
... on eukaryotic organisms. 2. Arsenite induces protein aggregation Aim. Arsenite exposure induces formation of protein aggregates. Three questions will be considered: (1) Why does arsenite induce protein aggregation? (2) What are the physiological consequences? (3) How does the cell respond in order t ...
... on eukaryotic organisms. 2. Arsenite induces protein aggregation Aim. Arsenite exposure induces formation of protein aggregates. Three questions will be considered: (1) Why does arsenite induce protein aggregation? (2) What are the physiological consequences? (3) How does the cell respond in order t ...
C2006/F2402 `07
... B. Suppose the kidney cells have receptors for LDL, transferrin, & EGF. You isolate several kinds of vesicles from the cells, and suppose the vesicles carry ENaC. B-1. If you isolate uncoated endocytic vesicles that carry ENaC, the vesicles could also contain (LDL receptors) (transferrin receptors) ...
... B. Suppose the kidney cells have receptors for LDL, transferrin, & EGF. You isolate several kinds of vesicles from the cells, and suppose the vesicles carry ENaC. B-1. If you isolate uncoated endocytic vesicles that carry ENaC, the vesicles could also contain (LDL receptors) (transferrin receptors) ...
Drosophila ventral furrow morphogenesis: a
... stimulates the small GTPase, Rho, to exchange its bound GDP for GTP, thereby activating Rho. A dominant negative form of Rho also produces ventral furrow defects. In tissue culture cells, Rho has been shown to stimulate stress fiber formation (Hall, 1998). These results indicate that the actin cytos ...
... stimulates the small GTPase, Rho, to exchange its bound GDP for GTP, thereby activating Rho. A dominant negative form of Rho also produces ventral furrow defects. In tissue culture cells, Rho has been shown to stimulate stress fiber formation (Hall, 1998). These results indicate that the actin cytos ...
Stitching proteins into membranes, not sew simple
... an N-terminal domain consisting of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR, approximately 200 amino acids) could be controlled by the addition of methotrexate (MTX). In the absence of MTX, ‘loosely folded’ DHFR could be efficiently transported into the ER lumen, driven by a hydrophobic domain; while in the pr ...
... an N-terminal domain consisting of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR, approximately 200 amino acids) could be controlled by the addition of methotrexate (MTX). In the absence of MTX, ‘loosely folded’ DHFR could be efficiently transported into the ER lumen, driven by a hydrophobic domain; while in the pr ...
The trans-Golgi network GRIP-domain proteins form α
... golgins specifically associated with the TGN (trans-Golgi network) have recently been identified [6,7] based on the presence of a modestly conserved, 45-residue Golgi targeting sequence located at the C-terminus, called the GRIP domain [8–10]. The importance of the TGN golgins is highlighted by the ...
... golgins specifically associated with the TGN (trans-Golgi network) have recently been identified [6,7] based on the presence of a modestly conserved, 45-residue Golgi targeting sequence located at the C-terminus, called the GRIP domain [8–10]. The importance of the TGN golgins is highlighted by the ...
Roles of F-box Proteins in Plant Hormone Responses
... shown to form a functional E3-type Ub ligase complex. Moreover, plants that are deficient in other components of SCF complexes also show impaired JA responses [16, 53]. Thus, SCF COI1 is a central component of all JAdependent responses, the activity of which is presumably modulated by several Ub pro ...
... shown to form a functional E3-type Ub ligase complex. Moreover, plants that are deficient in other components of SCF complexes also show impaired JA responses [16, 53]. Thus, SCF COI1 is a central component of all JAdependent responses, the activity of which is presumably modulated by several Ub pro ...
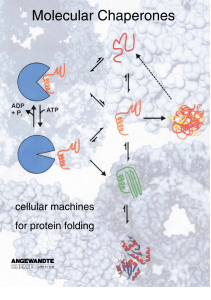
Molecular Chaperones - Cellular Machines for Protein Folding
... and groES genes encode proteins of 57 kDa and 10 kDa size, respectively, which are both required for the viability of E. coli.[25] Thus, at least one essential E. coli protein cannot fold without assistance from the GroE chaperone. 2.1.1. Structure of the GroE Chaperone The most striking feature of ...
... and groES genes encode proteins of 57 kDa and 10 kDa size, respectively, which are both required for the viability of E. coli.[25] Thus, at least one essential E. coli protein cannot fold without assistance from the GroE chaperone. 2.1.1. Structure of the GroE Chaperone The most striking feature of ...
G Protein Subunits Synthesized in Sf9 Cells
... Most interest in G proteins has been focused on their a subunits, since these proteins bind and hydrolyze GTP and most obviously regulate the activity of the best-studied effectors (cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase and adenylylcyclase). Much less is known about the structure and function of by. The Py s ...
... Most interest in G proteins has been focused on their a subunits, since these proteins bind and hydrolyze GTP and most obviously regulate the activity of the best-studied effectors (cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase and adenylylcyclase). Much less is known about the structure and function of by. The Py s ...
CycD1, a Putative G1 Cyclin from Antirrhinum majus, Accelerates
... plants. Plant D cyclins also contain a functional Rb binding motif, and Rb is a possible substrate (Ach et al., 1997; Huntley et al., 1998; Nakagami et al., 1999, 2002). In Arabidopsis thaliana, there are at least 10 D cyclin genes forming several structurally distinct groups (Arabidopsis Genome Ini ...
... plants. Plant D cyclins also contain a functional Rb binding motif, and Rb is a possible substrate (Ach et al., 1997; Huntley et al., 1998; Nakagami et al., 1999, 2002). In Arabidopsis thaliana, there are at least 10 D cyclin genes forming several structurally distinct groups (Arabidopsis Genome Ini ...
The Role of Lipid Domains in Bacterial Cell Processes
... In the past, bacterial cells were thought of as vessels without internal organization, with proteins, mRNA, chromosomes and other soluble compounds dispersed somewhat randomly inside of a membrane-enveloped cytoplasm. This view has gradually changed, thanks mainly to recent advancements in imaging t ...
... In the past, bacterial cells were thought of as vessels without internal organization, with proteins, mRNA, chromosomes and other soluble compounds dispersed somewhat randomly inside of a membrane-enveloped cytoplasm. This view has gradually changed, thanks mainly to recent advancements in imaging t ...
glycosphingolipid degradation - Limes-Institut-Bonn
... The enzymatic degradation of ganglioside GM2, the main storage material in Tay-Sachs disease, requires B-hexosaminidase A and a lysosomal ganglioside-binding protein, the GM2 activatorz6. The GM2 activator binds ganglioside GM2, as well as related gangliosides, and forms watersoluble complexes (most ...
... The enzymatic degradation of ganglioside GM2, the main storage material in Tay-Sachs disease, requires B-hexosaminidase A and a lysosomal ganglioside-binding protein, the GM2 activatorz6. The GM2 activator binds ganglioside GM2, as well as related gangliosides, and forms watersoluble complexes (most ...
Membrane nanodomains in plants: capturing form, function, and
... The plasma membrane is the interface between the cell and the external environment. Plasma membrane lipids provide scaffolds for proteins and protein complexes that are involved in cell to cell communication, signal transduction, immune responses, and transport of small molecules. In animals, fungi, ...
... The plasma membrane is the interface between the cell and the external environment. Plasma membrane lipids provide scaffolds for proteins and protein complexes that are involved in cell to cell communication, signal transduction, immune responses, and transport of small molecules. In animals, fungi, ...
SpoIIQ Anchors Membrane Proteins on Both Sides of
... Shortly after polar division, the mother cell engulfs the forespore in a phagocytic-like process generating a cell-within-acell. As a result of engulfment, the forespore is surrounded by two membranes: its own referred to as the inner forespore membrane and one derived from the mother cell called th ...
... Shortly after polar division, the mother cell engulfs the forespore in a phagocytic-like process generating a cell-within-acell. As a result of engulfment, the forespore is surrounded by two membranes: its own referred to as the inner forespore membrane and one derived from the mother cell called th ...
Synthesis of Substituted Alkanethiols Intended for Protein Immobilization -Chelate Associated Photochemistry (CAP)
... number of other everyday essentials. Organic chemical reactions occur continuously in nature, creating molecules and complexes, often referred as biosynthesis (reactions within a living organism). The coupling of amino acids with each other to form peptides and proteins is one of many examples. Rese ...
... number of other everyday essentials. Organic chemical reactions occur continuously in nature, creating molecules and complexes, often referred as biosynthesis (reactions within a living organism). The coupling of amino acids with each other to form peptides and proteins is one of many examples. Rese ...
Protein phosphorylation

Protein phosphorylation is a post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or modifying its function. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, and tyrosine in eukaryotes, and histidine in prokaryotes, which play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, many other amino acids can also be phosphorylated, including arginine, lysine, and cysteine. Protein phosphorylation was first reported in 1906 by Phoebus Levene at the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research with the discovery of phosphorylated vitellin. However, it was nearly 50 years until the enzymatic phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinases was discovered.