Insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs
... Islet of Langerhans Alpha cell: 20%, glucagon Beta cell: 75%, insulin Delta cell: 5%, somatostatin D1 cell: VIP PP cell: pancreatic polypeptide ...
... Islet of Langerhans Alpha cell: 20%, glucagon Beta cell: 75%, insulin Delta cell: 5%, somatostatin D1 cell: VIP PP cell: pancreatic polypeptide ...
Exercise in children and adolescents with diabetes
... is usually transient, lasting typically 30–60 minutes, and can be followed by hypoglycemia in the hours after finishing the exercise. Aerobic activities tend to lower blood glucose both during (usually within 20–60 minutes after the onset) and after the Exercise. ...
... is usually transient, lasting typically 30–60 minutes, and can be followed by hypoglycemia in the hours after finishing the exercise. Aerobic activities tend to lower blood glucose both during (usually within 20–60 minutes after the onset) and after the Exercise. ...
LESSON 3.6 WORKBOOK Obesity and Metabolic diseases:
... Diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and is the leading cause of kidney failure and blindness in adults. The reason for these impairments varies by tissue, but the common cause is that extra glucose left in the blood binds to proteins, disrupting their functions. If unregula ...
... Diabetes is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke, and is the leading cause of kidney failure and blindness in adults. The reason for these impairments varies by tissue, but the common cause is that extra glucose left in the blood binds to proteins, disrupting their functions. If unregula ...
DIABETUS MELLITUS: ETIOLOGY, PATHOGENESIS
... oral versus i.v. administration has shown that the incretin effect contributes to 70–90% of the insulin response to oral glucose. This effect is partially achieved by gastrointestinal hormones that are released during meal ingestion and augment glucose-stimulated insulin secretion; the two most impo ...
... oral versus i.v. administration has shown that the incretin effect contributes to 70–90% of the insulin response to oral glucose. This effect is partially achieved by gastrointestinal hormones that are released during meal ingestion and augment glucose-stimulated insulin secretion; the two most impo ...
REVERSE TYPE 2 DIABETES AND TAKE BACK YOUR LIFE
... The type of diet we practice has much to do with this epidemic, if not everything to do with it, for example, the bad oils we use, high levels of carbohydrates, sweeteners and so on. The basic underlying disorder is known to be the derangement of the blood sugar control system by badly engineered fa ...
... The type of diet we practice has much to do with this epidemic, if not everything to do with it, for example, the bad oils we use, high levels of carbohydrates, sweeteners and so on. The basic underlying disorder is known to be the derangement of the blood sugar control system by badly engineered fa ...
1. What is Diabetes? Ans: Our body needs glucose to give us energy
... reaction in body cells that break down glucose from the blood to release energy. In the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system of the body by mistake targets insulinproducing beta cells in the pancreas, till these cells are destroyed and stop producing insulin. Body cannot break down (metabolise ...
... reaction in body cells that break down glucose from the blood to release energy. In the case of type 1 diabetes, the immune system of the body by mistake targets insulinproducing beta cells in the pancreas, till these cells are destroyed and stop producing insulin. Body cannot break down (metabolise ...
DiabetesType2_Chai
... The only antidiabetic drug that has been conclusively shown to prevent the cardiovascular complications of diabetes ...
... The only antidiabetic drug that has been conclusively shown to prevent the cardiovascular complications of diabetes ...
Abstract - WHO archives
... Title: Selecting Natural Animal Insulin Improves Access to Cost-Effective Therapy of Diabetic Patients in the Public Sector of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Problem Statement: Prevalence of diabetes in urban communities of developing countries is expected to triple within the next 25 years. Rising prevale ...
... Title: Selecting Natural Animal Insulin Improves Access to Cost-Effective Therapy of Diabetic Patients in the Public Sector of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania Problem Statement: Prevalence of diabetes in urban communities of developing countries is expected to triple within the next 25 years. Rising prevale ...
Advances around technologies investigating mitochondrial function
... The mitochondrion is an intracellular organelle that plays a central role in the metabolism. Here are the Krebs cycle enzymes and the electron transfer chain (ETC) enzymes, which transduce energy substrates into a usable form of energy, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and heat. Mitochondrion literally ...
... The mitochondrion is an intracellular organelle that plays a central role in the metabolism. Here are the Krebs cycle enzymes and the electron transfer chain (ETC) enzymes, which transduce energy substrates into a usable form of energy, adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and heat. Mitochondrion literally ...
Diabetes slides
... and genetic tendency are two possibilities. There’s a change in the pancreatic function and the cells that normally produce insulin are destroyed. The body’s own immune system may think the pancreas is a foreign body! This form often appears at a time of physical stress or during illness when the bo ...
... and genetic tendency are two possibilities. There’s a change in the pancreatic function and the cells that normally produce insulin are destroyed. The body’s own immune system may think the pancreas is a foreign body! This form often appears at a time of physical stress or during illness when the bo ...
Hormones in intermediary metabolism
... Thyroid hormones actions • ↑ protein synthesis, but ↑↑ protein catabolism – result is proteocatabolic • Increased breakdown of muscle proteins • Stimulation of synthesis: Na+/K+ pump, respiratory chain enzymes, ... • The pro-growth importance: T3 and T4 support metabolism, which is necessary for pr ...
... Thyroid hormones actions • ↑ protein synthesis, but ↑↑ protein catabolism – result is proteocatabolic • Increased breakdown of muscle proteins • Stimulation of synthesis: Na+/K+ pump, respiratory chain enzymes, ... • The pro-growth importance: T3 and T4 support metabolism, which is necessary for pr ...
diabetes - Ravenwood
... and insulin at 1:30 p.m., a BG test before her carbohydrate snack and insulin at LEAP (our local after-school program), a BG test before her dinner and insulin, a BG test before bed, and a BG test at 2 a.m. that my husband or I get to wake up to do. Obviously, she cannot escape this disease and type ...
... and insulin at 1:30 p.m., a BG test before her carbohydrate snack and insulin at LEAP (our local after-school program), a BG test before her dinner and insulin, a BG test before bed, and a BG test at 2 a.m. that my husband or I get to wake up to do. Obviously, she cannot escape this disease and type ...
Emergency Diabetes Management in Athletic Training
... In 2010 the figures were 25.8 million and 8.3%. The prevalence rate for adults age 20 and older in 2012 was 12.3%, compared to 11.3% in 2010. New Cases: The incidence of diabetes in 2012 was 1.7 million new diagnoses/year; in 2010 it was 1.9 million. Deaths: Diabetes remains the 7th leading caus ...
... In 2010 the figures were 25.8 million and 8.3%. The prevalence rate for adults age 20 and older in 2012 was 12.3%, compared to 11.3% in 2010. New Cases: The incidence of diabetes in 2012 was 1.7 million new diagnoses/year; in 2010 it was 1.9 million. Deaths: Diabetes remains the 7th leading caus ...
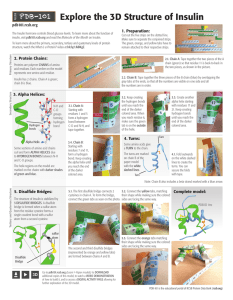
Explore the 3D Structure of Insulin
... additional copies of this model, to watch a VIDEO DEMONSTRATION of how to build it, and to access a DIGITAL ACTIVITY PAGE allowing for further exploration of the 3D model. PDB-101 is the educational portal of RCSB Protein Data Bank (rcsb.org) ...
... additional copies of this model, to watch a VIDEO DEMONSTRATION of how to build it, and to access a DIGITAL ACTIVITY PAGE allowing for further exploration of the 3D model. PDB-101 is the educational portal of RCSB Protein Data Bank (rcsb.org) ...
printed handout sheets
... 19. Catecholamines signal via -receptors, G-proteins and adenyl cyclase, but inhibit the storage granule docking system via -receptors. The inhibitory effect normally prevails. 20. Free fatty acids have a biphasic action: a short term stimulation of insulin release through ATP generation, followed ...
... 19. Catecholamines signal via -receptors, G-proteins and adenyl cyclase, but inhibit the storage granule docking system via -receptors. The inhibitory effect normally prevails. 20. Free fatty acids have a biphasic action: a short term stimulation of insulin release through ATP generation, followed ...
CRITERIOS PARA CLASIFICAR LAS HORMONAS
... • The gland produces three hormones: • 1) 3,5,3’,5’-tetraiodothyronine T4 • 2) 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine T3 • 3) Calcitonin • T4 & T3 are produced by follicular cells by the iodination of tyrosine. Most adults secrete about 80 ug of T4 and 40ug of T3 per day. The thyroxine is bound in peptide linkage ...
... • The gland produces three hormones: • 1) 3,5,3’,5’-tetraiodothyronine T4 • 2) 3,5,3’-triiodothyronine T3 • 3) Calcitonin • T4 & T3 are produced by follicular cells by the iodination of tyrosine. Most adults secrete about 80 ug of T4 and 40ug of T3 per day. The thyroxine is bound in peptide linkage ...
GLYCEMIC CONTROL TO REDUCE ADRENAL STRESS
... We have frequently been told that eating more complex carbohydrates than protein is healthy. However, it has been proven that an excess of carbohydrates to protein results in excess levels of insulin. Excess levels of insulin cause adrenal stress, including hypoglycemia. In order to normalize blood ...
... We have frequently been told that eating more complex carbohydrates than protein is healthy. However, it has been proven that an excess of carbohydrates to protein results in excess levels of insulin. Excess levels of insulin cause adrenal stress, including hypoglycemia. In order to normalize blood ...
Diabetes mellitus
... casual is defined as any time of day without regard to time since last meal or 2. An overnight fasting glucose(FPG) ≥ 7.0mmol/L ,Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 hours or ...
... casual is defined as any time of day without regard to time since last meal or 2. An overnight fasting glucose(FPG) ≥ 7.0mmol/L ,Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 hours or ...
B. Oral hypoglycemic drugs
... (1) Insulin-dependent patients with diabetes mellitus (type 1 diabetes mellitus) (2) Insulin-independent patients: failure to other ...
... (1) Insulin-dependent patients with diabetes mellitus (type 1 diabetes mellitus) (2) Insulin-independent patients: failure to other ...