Blood Glucose Concentration
... 1. Remove glucose from blood [primary and unique effect of insulin] ...
... 1. Remove glucose from blood [primary and unique effect of insulin] ...
Substrate Breakdown
... Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas Helps to maintain blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (The formation of new glucose) in the liver Secreted in response to a decrease in blood glucose levels. Most of its actions are through a ...
... Glucagon is a hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas Helps to maintain blood glucose levels by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis (The formation of new glucose) in the liver Secreted in response to a decrease in blood glucose levels. Most of its actions are through a ...
My Review of Management of Type 1 Diabetes, Myself as Patient
... After diagnosis, I fully embraced my new lifestyle. I managed to reduce my A1C from 12.4% to 4.6% only 3 months after diagnosis. That’s an average blood glucose of 79 mg/dL and almost on the side of too low. I kept hearing about CGMs and finally explored them during the summer of 2015. A CGM is a sm ...
... After diagnosis, I fully embraced my new lifestyle. I managed to reduce my A1C from 12.4% to 4.6% only 3 months after diagnosis. That’s an average blood glucose of 79 mg/dL and almost on the side of too low. I kept hearing about CGMs and finally explored them during the summer of 2015. A CGM is a sm ...
diabetes in cats
... Generally, diabetes is a disorder of the older, often overweight cat, similar to the Type 2 human patient. Risk factors include body weight > 7 kg, older age (> 10 years), male gender, neutered. He ...
... Generally, diabetes is a disorder of the older, often overweight cat, similar to the Type 2 human patient. Risk factors include body weight > 7 kg, older age (> 10 years), male gender, neutered. He ...
Name: Date: Animal Nutrition Study Guide – Chapter 41 Be able to
... 7. What is the difference between a gastrovascular cavity and a complete digestive tract or alimentary canal? What are the adaptations of an alimentary canal, and how are they advantageous to digestion? 8. Make a table summarizing key digestive hormones and enzymes, what they digest/regulate, and wh ...
... 7. What is the difference between a gastrovascular cavity and a complete digestive tract or alimentary canal? What are the adaptations of an alimentary canal, and how are they advantageous to digestion? 8. Make a table summarizing key digestive hormones and enzymes, what they digest/regulate, and wh ...
Top Research Highlights
... T1D. New insights into the workings of the immune system—and how it interacts with components delivered ...
... T1D. New insights into the workings of the immune system—and how it interacts with components delivered ...
Information
... Ensuring blood glucose balance is critical for anyone seeking to restore or maintain good health, and is particularly indicated for the following conditions:* • Metabolic Syndrome /Insulin resistance management – The group of symptoms including high blood pressure and increased cardiovascular risk, ...
... Ensuring blood glucose balance is critical for anyone seeking to restore or maintain good health, and is particularly indicated for the following conditions:* • Metabolic Syndrome /Insulin resistance management – The group of symptoms including high blood pressure and increased cardiovascular risk, ...
Biology 12 Digestive System The digestive process can be divided
... 2. This signals the glucose channels to open and glucose can diffuse into the cell. 3. Glucose can be used to produce ATP to provide energy for cellular functions. 4. Some glucose can be stored as glycogen. This glycogen can be reconverted back to glucose if the cell is low on glucose and needs ATP. ...
... 2. This signals the glucose channels to open and glucose can diffuse into the cell. 3. Glucose can be used to produce ATP to provide energy for cellular functions. 4. Some glucose can be stored as glycogen. This glycogen can be reconverted back to glucose if the cell is low on glucose and needs ATP. ...
Exercise and Blood Sugar
... Trial and error for increased activity – may need to lower insulin dose or eat extra carbohydrate ...
... Trial and error for increased activity – may need to lower insulin dose or eat extra carbohydrate ...
Digestive System Notes
... Jaundice is most readily detected by looking at portions of the body that are normally white, such as the sclera, or the palms of the hands. ...
... Jaundice is most readily detected by looking at portions of the body that are normally white, such as the sclera, or the palms of the hands. ...
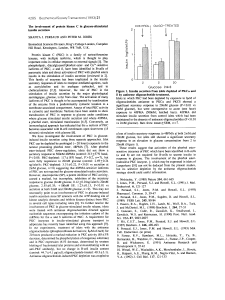
The involvement of protein kinase C in glucose
... Biomedical Sciences Division, King’s College London, Campden Hill Road, Kensington, London, W8 7AH, U.K. Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine/threonine kinases, with multiple isoforms, which is thought to play important roles in cellular responses to external signals [l]. The phospholipid-, ...
... Biomedical Sciences Division, King’s College London, Campden Hill Road, Kensington, London, W8 7AH, U.K. Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine/threonine kinases, with multiple isoforms, which is thought to play important roles in cellular responses to external signals [l]. The phospholipid-, ...
Lecture 4
... Note different sites of activation by insulin 3. Formation of Glycogen (Fig, 12-2 – Metab) Glucose-6-Phosphatase (only in Liver) – WHY? Optional pathways for G-6-P 4. Enzymatic Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism Synthesis – Glycogen Synthase (Fig 12-4 Metab.) Degradation – Glycogen Phosphorylase (Fig ...
... Note different sites of activation by insulin 3. Formation of Glycogen (Fig, 12-2 – Metab) Glucose-6-Phosphatase (only in Liver) – WHY? Optional pathways for G-6-P 4. Enzymatic Regulation of Glycogen Metabolism Synthesis – Glycogen Synthase (Fig 12-4 Metab.) Degradation – Glycogen Phosphorylase (Fig ...
a new therapeutic lead to suppress hepatic glucose production
... We view studying rare diseases with metabolic complications, like lipodystrophy, could also be a window into understanding the pathophysiology of more common diseases, such as Type 2 diabetes (T2D). The liver is the most important organ in mammals for glucose homeostasis. Upon meal ingestion, insuli ...
... We view studying rare diseases with metabolic complications, like lipodystrophy, could also be a window into understanding the pathophysiology of more common diseases, such as Type 2 diabetes (T2D). The liver is the most important organ in mammals for glucose homeostasis. Upon meal ingestion, insuli ...
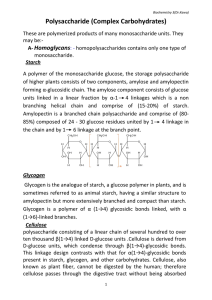
Biochemistry 3(Dr.Kawa) Polysaccharide (Complex Carbohydrates
... Types of Diabetes mellitus (DM) The classical symptoms of diabetes is polyuria, polydipsia and polyphagia Type 1 diabetes (Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus) (IDDM): is characterized by loss of the insulin-producing beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas leading to a deficiency of ...
... Types of Diabetes mellitus (DM) The classical symptoms of diabetes is polyuria, polydipsia and polyphagia Type 1 diabetes (Insulin dependent diabetes mellitus) (IDDM): is characterized by loss of the insulin-producing beta cells of the islets of Langerhans in the pancreas leading to a deficiency of ...
Managing Diabetes during the Muslim fasting month of Ramadan
... Target blood sugar levels in diabetes are achieved through manipulation of diet, exercise and medication. A change in any one of these three things can skew blood sugar levels and create complications associated with hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Fasting during the month of Ramadan is a religious a ...
... Target blood sugar levels in diabetes are achieved through manipulation of diet, exercise and medication. A change in any one of these three things can skew blood sugar levels and create complications associated with hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Fasting during the month of Ramadan is a religious a ...
Second-Messenger Gated Ion Channels
... Mutations in regulatory genes cause hypoglycemia. Here they use Kir6.2-/- mice to study the role of KATP channels in insulin secretion. ...
... Mutations in regulatory genes cause hypoglycemia. Here they use Kir6.2-/- mice to study the role of KATP channels in insulin secretion. ...
NovioSense Tear Glucose Sensor
... ideal sensor and can replace the painfull fingerprick. As diabetes continuous to become ever more prevalent, the need for improved technology is clear. At the moment, there is no solution available on the market to monitor glucose levels in realtime and wireless and non-invasive manner For millions ...
... ideal sensor and can replace the painfull fingerprick. As diabetes continuous to become ever more prevalent, the need for improved technology is clear. At the moment, there is no solution available on the market to monitor glucose levels in realtime and wireless and non-invasive manner For millions ...
52. Akram INSULIN_et al
... lipid and protein metabolism. Insulin exerts anabolic and anticatabolic influences on the body metabolism. In a normal individual, about half of the individual glucose is utilized to meet the energy needs of the body (mainly through glycolysis). The other half is converted to fat (40%) and glycogen ...
... lipid and protein metabolism. Insulin exerts anabolic and anticatabolic influences on the body metabolism. In a normal individual, about half of the individual glucose is utilized to meet the energy needs of the body (mainly through glycolysis). The other half is converted to fat (40%) and glycogen ...
Diabetes mellitus: classification, etiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis of
... The pathogenesis of type II diabetes is a violation of insulin secretion and reduce or decrease the sensitivity of insulin receptors in insulin-dependent tissues. With type II is a sharp \ menshenie insulin secretion in the first phase of secretion, ie because of reduced sensitivity glucoreceptors B ...
... The pathogenesis of type II diabetes is a violation of insulin secretion and reduce or decrease the sensitivity of insulin receptors in insulin-dependent tissues. With type II is a sharp \ menshenie insulin secretion in the first phase of secretion, ie because of reduced sensitivity glucoreceptors B ...
diabetes mellitus
... • insulin facilitates glucose movement into cells • Red blood cells, healing wounds, the brain, and the adrenal medulla require glucose approximately @ 2 mg/kg/min. • Daily requirement of glucose for 70 Kg man is 200gm/day(90-100g stored as glycogen) ...
... • insulin facilitates glucose movement into cells • Red blood cells, healing wounds, the brain, and the adrenal medulla require glucose approximately @ 2 mg/kg/min. • Daily requirement of glucose for 70 Kg man is 200gm/day(90-100g stored as glycogen) ...
insulin deficiency
... Resistance to the action of insulin is a prime cause of the hyperglycemia in most patients with type 2 diabetes. The thiazolidinediones are a group of drugs that improve sensitivity to insulin in several tissues by binding to PPAR-γ receptors, leading to increased expression of glucose transporters. ...
... Resistance to the action of insulin is a prime cause of the hyperglycemia in most patients with type 2 diabetes. The thiazolidinediones are a group of drugs that improve sensitivity to insulin in several tissues by binding to PPAR-γ receptors, leading to increased expression of glucose transporters. ...
ch 4 quiz 15 - Amy E. Hammerstedt
... Extra Credit: ½ point each. The by-products of incomplete ________ breakdown are known as ketone bodies. a. amino acids b. fat c. glucose d.cholesterol Epinephrine can stimulate ________ to quickly flood your blood with glucose. a. lipolysis b. lipogenesis c. glycogenesis d. glycogenolysis Which par ...
... Extra Credit: ½ point each. The by-products of incomplete ________ breakdown are known as ketone bodies. a. amino acids b. fat c. glucose d.cholesterol Epinephrine can stimulate ________ to quickly flood your blood with glucose. a. lipolysis b. lipogenesis c. glycogenesis d. glycogenolysis Which par ...
Introduction
... aggregation. Increased Von Willebrand factor activity and thromboxane A2 production occur during episodes of hyperglycemia and may contribute to the increased risk of clot formation seen in hospitalized patients with hyperglycemia. Diabetic patients carry a much greater risk of cardiovascular dise ...
... aggregation. Increased Von Willebrand factor activity and thromboxane A2 production occur during episodes of hyperglycemia and may contribute to the increased risk of clot formation seen in hospitalized patients with hyperglycemia. Diabetic patients carry a much greater risk of cardiovascular dise ...
signs and symptoms
... Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus is also known as Type I Diabetes, this being the more current name used to differentiate between the several types of diabetes. Additional name used in the past was- Juvenile Diabetes. Type I diabetes is a chronic disease, in which a person no longer has the hormo ...
... Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus is also known as Type I Diabetes, this being the more current name used to differentiate between the several types of diabetes. Additional name used in the past was- Juvenile Diabetes. Type I diabetes is a chronic disease, in which a person no longer has the hormo ...
The Ohio Northern University Raabe College of Pharmacy
... Michael Moranville, Ohio Northern University Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate Diabetes mellitus (DM) affects about 190 million people worldwide, and is predicted to rise to 330 million by 2025. However, about 50 percent of diabetics remain undiagnosed and untreated. The United Kingdom Prospectieve Diabe ...
... Michael Moranville, Ohio Northern University Doctor of Pharmacy Candidate Diabetes mellitus (DM) affects about 190 million people worldwide, and is predicted to rise to 330 million by 2025. However, about 50 percent of diabetics remain undiagnosed and untreated. The United Kingdom Prospectieve Diabe ...