Review of Suzanne Somers` The Sexy Years
... it is not the most optimal regimen currently available. Following are some important points that need to be taken into account when deciding on treatment after reading the book: ...
... it is not the most optimal regimen currently available. Following are some important points that need to be taken into account when deciding on treatment after reading the book: ...
Eating and Pooing Activities
... What is the purpose of the sphincter in the oesophagus? To prevent reflux of food/stomach contents Is the lower oesophageal sphincter relaxed or contracted during vomiting? Relaxed Name two substances which aid food breakdown in the stomach HCL and pepsin enzymes Where does food in the stomach trave ...
... What is the purpose of the sphincter in the oesophagus? To prevent reflux of food/stomach contents Is the lower oesophageal sphincter relaxed or contracted during vomiting? Relaxed Name two substances which aid food breakdown in the stomach HCL and pepsin enzymes Where does food in the stomach trave ...
Lesson 12. Hormones
... regulation of metabolism. Iodine is necessary for the production of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as goitre. The thyronines act on nearly every cell in the body ...
... regulation of metabolism. Iodine is necessary for the production of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine). A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as goitre. The thyronines act on nearly every cell in the body ...
Classification of Diabetes Mellitus
... The function of β-cells is to maintain energy homeostasis in the organism. The energy receptors of these cells take in the minimal deflections in the modification of blood content of calorigenic molecules. Glucose, amino acids, ketone bodies, and fatty acids are the example of calorigenic molecules ...
... The function of β-cells is to maintain energy homeostasis in the organism. The energy receptors of these cells take in the minimal deflections in the modification of blood content of calorigenic molecules. Glucose, amino acids, ketone bodies, and fatty acids are the example of calorigenic molecules ...
MannKind Corporation - Analyst Reports
... appropriately. In an effort to metabolize glucose, the pancreas initially produces higher concentration of insulin. The pancreas gradually loses its ability to produce the higher level of insulin needed and becomes non-functional. Type 1 diabetes develops when the body’s immune system destroys pancr ...
... appropriately. In an effort to metabolize glucose, the pancreas initially produces higher concentration of insulin. The pancreas gradually loses its ability to produce the higher level of insulin needed and becomes non-functional. Type 1 diabetes develops when the body’s immune system destroys pancr ...
Diabetes and Eating Disorders
... ie: Binge eating disorder, variants of bulimia – binge/purge less often, meet criteria for anorexia but is normal WT or have regular menses, purging after eating small amounts of food, chewing/spitting, milder subthreshold variants. Most people with ED & Type 1 Diabetes will be in the ED-NOS cat ...
... ie: Binge eating disorder, variants of bulimia – binge/purge less often, meet criteria for anorexia but is normal WT or have regular menses, purging after eating small amounts of food, chewing/spitting, milder subthreshold variants. Most people with ED & Type 1 Diabetes will be in the ED-NOS cat ...
phys chapter 78 [2-9
... phospholipids and cholesterol, which are discharged into blood in lipoproteins (along with excess triglycerides) o High lipid concentration (especially high cholesterol) promotes development of atherosclerosis Insulin lack causes excessive amounts of acetoacetic acid to be formed in liver because in ...
... phospholipids and cholesterol, which are discharged into blood in lipoproteins (along with excess triglycerides) o High lipid concentration (especially high cholesterol) promotes development of atherosclerosis Insulin lack causes excessive amounts of acetoacetic acid to be formed in liver because in ...
Regulation of protein synthesis by insulin
... and consequent stimulation of eEF2. Question marks denote steps that remain incompletely understood: see the text for further details. IR, insulin receptor; IRS, IR substrate. ...
... and consequent stimulation of eEF2. Question marks denote steps that remain incompletely understood: see the text for further details. IR, insulin receptor; IRS, IR substrate. ...
Short-chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
... and childhood is hyperinsulinism. So far mutations in four different genes have been identified as causing hyperinsulinism. These are gain-of-function mutations of the enzymes glucokinase and glutamate dehydrogenase and defects in the genes encoding the SUR1 or KIR6.2 subunits of the KATP channel in ...
... and childhood is hyperinsulinism. So far mutations in four different genes have been identified as causing hyperinsulinism. These are gain-of-function mutations of the enzymes glucokinase and glutamate dehydrogenase and defects in the genes encoding the SUR1 or KIR6.2 subunits of the KATP channel in ...
Freescale and Insulet Partner to Help Improve Diabetes Care
... interaction with the pod. The PDM includes a built-in blood glucose monitor—which Freescale also helped integrate—that replaces the traditional finger pricks to test blood glucose levels. A bolus calculator for extra insulin doses, a food library to help manage what you eat, and full data management ...
... interaction with the pod. The PDM includes a built-in blood glucose monitor—which Freescale also helped integrate—that replaces the traditional finger pricks to test blood glucose levels. A bolus calculator for extra insulin doses, a food library to help manage what you eat, and full data management ...
Exercise Management
... ineffective in lowering blood glucose and may further contribute to insulin resistance. Eventually the beta cells may become exhausted and fail to produce adequate amounts of insulin. The mechanisms underlying insulin resistance remain unclear but probably involve defects in the binding of insul ...
... ineffective in lowering blood glucose and may further contribute to insulin resistance. Eventually the beta cells may become exhausted and fail to produce adequate amounts of insulin. The mechanisms underlying insulin resistance remain unclear but probably involve defects in the binding of insul ...
Glycogen Metabolism, Electron Transport/Oxidative Phosphorylation
... • What would happen if it were disrupted or “tricked”? Electron Chain Inhibitors or “de-couplers” are used as poisons • Cyanide: takes the place of oxygen on cytochrome C oxidase, preventing the reduction of O2 to H2O • leads to “suffocation” where the victim is breathing but cannot use the oxygen t ...
... • What would happen if it were disrupted or “tricked”? Electron Chain Inhibitors or “de-couplers” are used as poisons • Cyanide: takes the place of oxygen on cytochrome C oxidase, preventing the reduction of O2 to H2O • leads to “suffocation” where the victim is breathing but cannot use the oxygen t ...
PL05_Glucdisp
... • The stimulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin creates an ‘energy demand’ – Glycogenesis is anabolic – The activation of glucose prior to incorporation into glycogen requires ATP – This drops the cellular [ATP] and increases the [ADP] & [AMP] ...
... • The stimulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin creates an ‘energy demand’ – Glycogenesis is anabolic – The activation of glucose prior to incorporation into glycogen requires ATP – This drops the cellular [ATP] and increases the [ADP] & [AMP] ...
Insulin and Metabolic Pathways in Endometrial Cancer
... Metabolite Profiling and Endometrial Cancer •Hyperinsulinemia is associated with increased risk of endometrial cancer suggesting this pathway is important for endometrial tumorigenesis but: • Complex relationship with IGF-I for both risk and prognosis • Predictive value of hyperinsulinemia is likel ...
... Metabolite Profiling and Endometrial Cancer •Hyperinsulinemia is associated with increased risk of endometrial cancer suggesting this pathway is important for endometrial tumorigenesis but: • Complex relationship with IGF-I for both risk and prognosis • Predictive value of hyperinsulinemia is likel ...
Diabetes mellitus
... with close dietary management, exercise, and use of appropriate medications (insulin only in the case of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Oral medications may be used in the case of type 2 diabetes, as well as insulin). Patient education, understanding, and participation is vital since the complications of ...
... with close dietary management, exercise, and use of appropriate medications (insulin only in the case of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Oral medications may be used in the case of type 2 diabetes, as well as insulin). Patient education, understanding, and participation is vital since the complications of ...
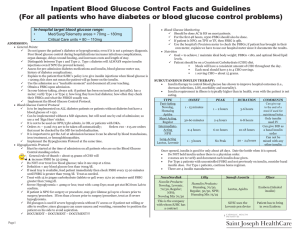
Inpatient Blood Glucose Control Facts and Guidelines (For all
... If patient does not eat meal, nutritional bolus should not be given. 50% of starting dose is nutritional insulin, divided in thirds to be given at each meal. This insulin can be given from before to the end of the meal. If regular insulin is used, it is given 30 minutes before meal. B ...
... If patient does not eat meal, nutritional bolus should not be given. 50% of starting dose is nutritional insulin, divided in thirds to be given at each meal. This insulin can be given from before to the end of the meal. If regular insulin is used, it is given 30 minutes before meal. B ...
Q26to35
... E. The aldolase involved in liver fructose metabolism is slow in comparison to the rate of fructose trapping this is what causes the ATP depletion ...
... E. The aldolase involved in liver fructose metabolism is slow in comparison to the rate of fructose trapping this is what causes the ATP depletion ...
A (Very) - Diabetes in Control
... • Insulin mRNA - 20% of total mRNA (100-200,000 insulin mRNA molecules/cell. • Insulin - 10% of the total protein. • Insulin - 50% or more of the total protein synthesis when maximally stimulated - 1.3 x 106 molecules of insulin/min (and 3.9 million molecules of reactive oxygen species/H2O2 generate ...
... • Insulin mRNA - 20% of total mRNA (100-200,000 insulin mRNA molecules/cell. • Insulin - 10% of the total protein. • Insulin - 50% or more of the total protein synthesis when maximally stimulated - 1.3 x 106 molecules of insulin/min (and 3.9 million molecules of reactive oxygen species/H2O2 generate ...
REGULATION OF BODY WEIGHT
... ONE OF A LARGER FAMILY OF “G PROTEINS” G PROTEINS BIND GDP AND GTP G PROTEINS HAVE GTPase ACTIVITY AMONG THEIR FUNCTIONS ARE: SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION VESICLE TRAFFICKING TRANSLATION TARGETING (SIGNAL RECOGNITION) (NOTE THAT THE GTPase ACTS AS AN “ENERGASE” AND NOT A HYDROLASE IN THESE) ...
... ONE OF A LARGER FAMILY OF “G PROTEINS” G PROTEINS BIND GDP AND GTP G PROTEINS HAVE GTPase ACTIVITY AMONG THEIR FUNCTIONS ARE: SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION VESICLE TRAFFICKING TRANSLATION TARGETING (SIGNAL RECOGNITION) (NOTE THAT THE GTPase ACTS AS AN “ENERGASE” AND NOT A HYDROLASE IN THESE) ...
Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in Cancer
... Thus, IGF1R mAbs could result in harm via the elevation of ligands stimulating the insulin receptor while leaving the insulin receptor uninhibited. Indeed, we have shown that sole inhibition of IGF1R results in enhanced signaling through the insulin receptor (10). These data support the argument tha ...
... Thus, IGF1R mAbs could result in harm via the elevation of ligands stimulating the insulin receptor while leaving the insulin receptor uninhibited. Indeed, we have shown that sole inhibition of IGF1R results in enhanced signaling through the insulin receptor (10). These data support the argument tha ...
Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling in Cancer
... Thus, IGF1R mAbs could result in harm via the elevation of ligands stimulating the insulin receptor while leaving the insulin receptor uninhibited. Indeed, we have shown that sole inhibition of IGF1R results in enhanced signaling through the insulin receptor (10). These data support the argument tha ...
... Thus, IGF1R mAbs could result in harm via the elevation of ligands stimulating the insulin receptor while leaving the insulin receptor uninhibited. Indeed, we have shown that sole inhibition of IGF1R results in enhanced signaling through the insulin receptor (10). These data support the argument tha ...
Anaesthetic management of patients with DM
... Macrovascular complications (as measured by rates of coronary artery, cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular disease) are also similar for type 1 and 2 diabetics. In type 2 patients, at least, abnormally high concentrations of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and, therefore, impaired fibri ...
... Macrovascular complications (as measured by rates of coronary artery, cerebrovascular and peripheral vascular disease) are also similar for type 1 and 2 diabetics. In type 2 patients, at least, abnormally high concentrations of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and, therefore, impaired fibri ...
Breast Health Lecture - Angel Chiropractic Health Center
... Insulin Resistance (AKA “Syndrome X”): When the cells become insensitive to the insulin message. Blood sugar is not properly managed and the pancreas is required to secrete more and more insulin. When insulin levels become very high they influence gene expression, altering cellular function and ...
... Insulin Resistance (AKA “Syndrome X”): When the cells become insensitive to the insulin message. Blood sugar is not properly managed and the pancreas is required to secrete more and more insulin. When insulin levels become very high they influence gene expression, altering cellular function and ...
Practical Applications of Insulin Pump Therapy in Type 2 Diabetes
... portantly the macrovascular complications of the disease begin during this asymptomatic phase before diagnosis occurs. The consequences of insulin resistance at the tissue level include reduced glucose uptake into peripheral sites (i.e., fat and muscle, Exhibit 4). Combined with excessive glucose ou ...
... portantly the macrovascular complications of the disease begin during this asymptomatic phase before diagnosis occurs. The consequences of insulin resistance at the tissue level include reduced glucose uptake into peripheral sites (i.e., fat and muscle, Exhibit 4). Combined with excessive glucose ou ...