U4L24 Carbo Disposal
... – And so causes GS to be dephosphorylated and active – So insulin effectively stimulates GS ...
... – And so causes GS to be dephosphorylated and active – So insulin effectively stimulates GS ...
ppt
... Figure was assumed from textbook: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ...
... Figure was assumed from textbook: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ...
Chapter 9: Digestive System
... Structure and Function of the Pancreas Insulin • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is high • Stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells (liver, muscle, adipose tissue) to lower blood glucose Glucagon • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is low • Stimulates the liver to break glycogen d ...
... Structure and Function of the Pancreas Insulin • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is high • Stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells (liver, muscle, adipose tissue) to lower blood glucose Glucagon • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is low • Stimulates the liver to break glycogen d ...
******* 1 - medicinegroupmcst2
... form of autoimmune (type 1 diabetes) which is diagnosed in individuals who are older than the usual age of onset of type 1 diabetes. Alternate terms that have been used for "LADA" include Late-onset Autoimmune Diabetes of Adulthood, "Slow Onset Type 1" diabetes, and sometimes also "Type 1.5 Ofte ...
... form of autoimmune (type 1 diabetes) which is diagnosed in individuals who are older than the usual age of onset of type 1 diabetes. Alternate terms that have been used for "LADA" include Late-onset Autoimmune Diabetes of Adulthood, "Slow Onset Type 1" diabetes, and sometimes also "Type 1.5 Ofte ...
Document
... Structure and Function of the Pancreas Insulin • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is high • Stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells (liver, muscle, adipose tissue) to lower blood glucose Glucagon • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is low • Stimulates the liver to break glycogen d ...
... Structure and Function of the Pancreas Insulin • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is high • Stimulates the uptake of glucose by cells (liver, muscle, adipose tissue) to lower blood glucose Glucagon • Hormone secreted when blood glucose level is low • Stimulates the liver to break glycogen d ...
DIABETES OVERVIEW AND UPDATE 11/11/11 Barb Bancroft, RN
... Too much cow’s milk… • Decreased risk in babies who are breast fed • Increased risk in drinking cow’s milk—is there a protein that aggravates the immune system and triggers diabetes in genetically susceptible ...
... Too much cow’s milk… • Decreased risk in babies who are breast fed • Increased risk in drinking cow’s milk—is there a protein that aggravates the immune system and triggers diabetes in genetically susceptible ...
1569471263Herbal Drugs Used For Diabetes
... have resistance to the actions of insulin on liver, muscle and fat tissues (the major targets for the beneficial effects of insulin). An environmental influence also plays a major role by enhancing the phenotypic expression of genes that place individuals at risk for diabetes. This is becoming incr ...
... have resistance to the actions of insulin on liver, muscle and fat tissues (the major targets for the beneficial effects of insulin). An environmental influence also plays a major role by enhancing the phenotypic expression of genes that place individuals at risk for diabetes. This is becoming incr ...
Clinical biochemistry (4) Carbohydrate
... 1. By increasing the entry of glucose into muscles and adipose tissue cells. 2. By promoting liver glycogenesis and thus converting glucose to glycogen. 3. By promoting glycolysis which accelerate glucose utilization. 4. By promoting lipid synthesis from glucose in adipose tissue. 5. By promoting am ...
... 1. By increasing the entry of glucose into muscles and adipose tissue cells. 2. By promoting liver glycogenesis and thus converting glucose to glycogen. 3. By promoting glycolysis which accelerate glucose utilization. 4. By promoting lipid synthesis from glucose in adipose tissue. 5. By promoting am ...
Glargine (Lantus) insulin: should it be discontinued/switched in
... per SD for human insulin). With baseline adjustment, there was no significantly increased risk for malignant neoplasms with glargine, until >50 units/day. Swedish, Scottish, British No dose response analyses ...
... per SD for human insulin). With baseline adjustment, there was no significantly increased risk for malignant neoplasms with glargine, until >50 units/day. Swedish, Scottish, British No dose response analyses ...
Looking For The New Lantus: NextGen
... persevering to offer patients a noninjected alternative. And even Goldman’s halved peak sales projection is still worth $1 billion: not another Lantus, maybe, but still a very valuable proposition, especially for smaller players. Smaller players like private Dance Biopharm Inc., for instance. Set u ...
... persevering to offer patients a noninjected alternative. And even Goldman’s halved peak sales projection is still worth $1 billion: not another Lantus, maybe, but still a very valuable proposition, especially for smaller players. Smaller players like private Dance Biopharm Inc., for instance. Set u ...
Diabetes Mellitus
... – Produced by the cells in the islets of Langherans of the pancreas – Facilitates normal glucose range of 3.9 – 6.7 mmol/L ...
... – Produced by the cells in the islets of Langherans of the pancreas – Facilitates normal glucose range of 3.9 – 6.7 mmol/L ...
Glucose - The Stephens Lab
... Motilin is secreted by Mo cells of the SI that increases the MIGRATING MYOELECTRIC COMPLEX component of GI motility and stimulates the production of PEPSIN. Control of motilin secretion is largely unknown, although some studies show that alkaline pH in the duodenum stimulates its release. Interesti ...
... Motilin is secreted by Mo cells of the SI that increases the MIGRATING MYOELECTRIC COMPLEX component of GI motility and stimulates the production of PEPSIN. Control of motilin secretion is largely unknown, although some studies show that alkaline pH in the duodenum stimulates its release. Interesti ...
The Client with Diabetes Mellitus
... encouraged to exercise vigorously to improve glucose control C) Meticulous glucose control with multiple insulin injections per day based on the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial results should be universally prescribed D) None of the above ...
... encouraged to exercise vigorously to improve glucose control C) Meticulous glucose control with multiple insulin injections per day based on the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial results should be universally prescribed D) None of the above ...
Appendix 1 Questionnaires 138
... phrase that is closest to your opinion about each statement. It is important that you answer every statement. Note: The term “health care professionals” in this survey refers to doctors, nurses, and dieticians. ...
... phrase that is closest to your opinion about each statement. It is important that you answer every statement. Note: The term “health care professionals” in this survey refers to doctors, nurses, and dieticians. ...
A Newsletter for Those Who Care for Children
... OBESITY, regardless of age, is the greatest risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Fat cells secrete chemicals that directly sabotage the cells' ability to use insulin. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes not only stimulate the pancreas to produce excessive insulin, but also stimulate the fat cells to ...
... OBESITY, regardless of age, is the greatest risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Fat cells secrete chemicals that directly sabotage the cells' ability to use insulin. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes not only stimulate the pancreas to produce excessive insulin, but also stimulate the fat cells to ...
Diabetes - High Blood Sugar
... plasma glucose (FPG) > 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) and a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with a glucose > 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L). Type 1 Diabetes Other names: Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM), Juvenile Onset Diabetes. Physiology: There is no production of insulin by the body. K ...
... plasma glucose (FPG) > 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) and a 2-hour oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) with a glucose > 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L). Type 1 Diabetes Other names: Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus (IDDM), Juvenile Onset Diabetes. Physiology: There is no production of insulin by the body. K ...
- Caribbean Institute of Nephrology
... • Treating hyperglycaemia aggressively will decrease appearance of each component of diabetic nephropathy in persons without established diabetic nephropathy ...
... • Treating hyperglycaemia aggressively will decrease appearance of each component of diabetic nephropathy in persons without established diabetic nephropathy ...
Chapter 4
... 1. The RDA for carbohydrate is miniscule 2. More Carbohydrate Means Less Fat or Protein 3. Most Americans Need to eat More Fiber B. Does Your Diet Meet Carbohydrate Recommendations? 1. Use Exchange Lists to Estimate Carbohydrate Content 2. The Nutrition Facts on Food Labels Lists the Amounts of Carb ...
... 1. The RDA for carbohydrate is miniscule 2. More Carbohydrate Means Less Fat or Protein 3. Most Americans Need to eat More Fiber B. Does Your Diet Meet Carbohydrate Recommendations? 1. Use Exchange Lists to Estimate Carbohydrate Content 2. The Nutrition Facts on Food Labels Lists the Amounts of Carb ...
Psychological insulin resistance: A guide for practice nurses
... insulin therapy can be instigated at the time of diagnosis. Furthermore, few of the GPs in Lauritzen and Scott’s study approached the subject of insulin therapy with their patients with type 2 diabetes. When reference was made to insulin it was commonly in the context of a ‘threat’ to enforce adhere ...
... insulin therapy can be instigated at the time of diagnosis. Furthermore, few of the GPs in Lauritzen and Scott’s study approached the subject of insulin therapy with their patients with type 2 diabetes. When reference was made to insulin it was commonly in the context of a ‘threat’ to enforce adhere ...
Regulation of blood glucose (Homeostasis)
... last meal and becomes fully active as stores of liver glycogen are depleted. Gluconeogenesis plays an essential role in maintaining blood glucose during both overnight and prolonged fasting. ...
... last meal and becomes fully active as stores of liver glycogen are depleted. Gluconeogenesis plays an essential role in maintaining blood glucose during both overnight and prolonged fasting. ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
... Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is not driven by Na+ symport, the process that intestinal cells use to absorb glucose from the gut.) After a glucose rich meal, blood glucose rises above th ...
... Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is not driven by Na+ symport, the process that intestinal cells use to absorb glucose from the gut.) After a glucose rich meal, blood glucose rises above th ...
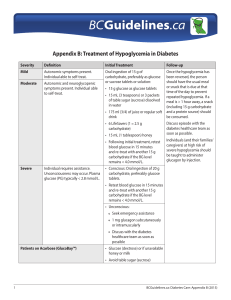
Appendix B: Treatment of Hypoglycemia in Diabetes
... Once the hypoglycemia has been reversed, the person should have the usual meal or snack that is due at that time of the day to prevent repeated hypoglycemia. If a meal is > 1 hour away, a snack (including 15 g carbohydrate and a protein source) should be consumed. ...
... Once the hypoglycemia has been reversed, the person should have the usual meal or snack that is due at that time of the day to prevent repeated hypoglycemia. If a meal is > 1 hour away, a snack (including 15 g carbohydrate and a protein source) should be consumed. ...
Diabetes - nenu.edu.cn
... mitochondrial lipid oxidation in patients who have impaired oxidative capacity and small mitochondria in skeletal muscle. PPARγ co-activator 1 (PGC1), a transcription factor for genes involved in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and ATP synthesis, was decreased in young, lean, insulinresistant off ...
... mitochondrial lipid oxidation in patients who have impaired oxidative capacity and small mitochondria in skeletal muscle. PPARγ co-activator 1 (PGC1), a transcription factor for genes involved in mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation and ATP synthesis, was decreased in young, lean, insulinresistant off ...
Type 1 Diabetes - Carlisle Healthcare
... fat is then broken down back into glucose and some is released back into the bloodstream to keep the blood glucose level normal. Hormones such as insulin are chemicals that are released into the bloodstream and have an action on certain parts of the body. Insulin is made by special cells called beta ...
... fat is then broken down back into glucose and some is released back into the bloodstream to keep the blood glucose level normal. Hormones such as insulin are chemicals that are released into the bloodstream and have an action on certain parts of the body. Insulin is made by special cells called beta ...
Ettinger: Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 7th Edition
... drink excessively in an effort to maintain water balance (hydration). These responses to the simple lack of insulin are natural and instinctive. They are unavoidable. All individuals (people, dogs, cats, etc.) with an insulin deficiency (diabetes mellitus) have the same symptoms: they all eat excess ...
... drink excessively in an effort to maintain water balance (hydration). These responses to the simple lack of insulin are natural and instinctive. They are unavoidable. All individuals (people, dogs, cats, etc.) with an insulin deficiency (diabetes mellitus) have the same symptoms: they all eat excess ...