Beating insulin resistance through lifestyle changes
... digest and enter the blood stream. The slower a food digests, the easier it is for the body to process and utilize that food, because the insulin response to a low glycemic index food can be ...
... digest and enter the blood stream. The slower a food digests, the easier it is for the body to process and utilize that food, because the insulin response to a low glycemic index food can be ...
Diabetes mellitus (DM), also known as simply diabetes, is a group of
... for surgery, which one is truea. oral hypoglycemic drug should not be stopped b.oral hypoglycemic agent should be stopped few days before surgery and long acting insulin should be started pre and post op c.oral hypoglycemic agent should be stopped few days before surgery and short acting insulin sho ...
... for surgery, which one is truea. oral hypoglycemic drug should not be stopped b.oral hypoglycemic agent should be stopped few days before surgery and long acting insulin should be started pre and post op c.oral hypoglycemic agent should be stopped few days before surgery and short acting insulin sho ...
Presentation
... Threshold of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is 100 mg/dl. Half-maximal insulin response occurs at 150 mg/dl A maximum insulin response occurs at 300 mg/dl ...
... Threshold of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is 100 mg/dl. Half-maximal insulin response occurs at 150 mg/dl A maximum insulin response occurs at 300 mg/dl ...
No Slide Title
... down to acetate & glycerol. Stores amino acids as protein, & can break proteins down to amino acids. ...
... down to acetate & glycerol. Stores amino acids as protein, & can break proteins down to amino acids. ...
Type 2 Diabetes
... • The role of the kidney in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis has come into focus. • Latest development efforts for novel antidiabetic therapies have concentrated on insulin-independent mechanisms like the sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. • The emerging profile o ...
... • The role of the kidney in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis has come into focus. • Latest development efforts for novel antidiabetic therapies have concentrated on insulin-independent mechanisms like the sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. • The emerging profile o ...
- National Lipid Association
... SREBP-1c: Regulates Fatty Acid and Triglyceride Synthesis, Responsive to changes in feeding status via regulation by insulin, glucagon, and PUFA. SREBP-1a: Highly expressed in tumor cell lines, low level expression in normal cells, not responsive to dietary conditions. Can drive both cholesterol ...
... SREBP-1c: Regulates Fatty Acid and Triglyceride Synthesis, Responsive to changes in feeding status via regulation by insulin, glucagon, and PUFA. SREBP-1a: Highly expressed in tumor cell lines, low level expression in normal cells, not responsive to dietary conditions. Can drive both cholesterol ...
Does insulin glargine (Lantus ) cause CANCER?
... Observational studies are ALWAYS untrustworthy as they can’t perfectly match groups at baseline (e.g., in these studies, groups were not the same for many factors that could effect cancer rates, such as weight, age, & BP). ...
... Observational studies are ALWAYS untrustworthy as they can’t perfectly match groups at baseline (e.g., in these studies, groups were not the same for many factors that could effect cancer rates, such as weight, age, & BP). ...
ENERGY METABOLISM
... 2. the need to mobilize fatty acids from adipose tissue, and the synthesis and release of ketone bodies from the liver, to supply energy to all other tissues. ...
... 2. the need to mobilize fatty acids from adipose tissue, and the synthesis and release of ketone bodies from the liver, to supply energy to all other tissues. ...
Insulin - ISpatula
... * The body has multiple overlapping mechanisms to prevent or correct hypoglycemia. - Hormonal changes in reversing hypoglycemia are increase glucagon and epinephrine with decrease release of insulin. *Symptoms of hypoglycemia: Appear when glucose level of 45mg/dl or less The symptoms are divided int ...
... * The body has multiple overlapping mechanisms to prevent or correct hypoglycemia. - Hormonal changes in reversing hypoglycemia are increase glucagon and epinephrine with decrease release of insulin. *Symptoms of hypoglycemia: Appear when glucose level of 45mg/dl or less The symptoms are divided int ...
NEW! D-Chiro-Inositol: Enhances Insulin Function and Blood
... exists in a galactosyl form requiring alphagalactosidase for hydrolysis and absorption. As this enzyme is not found in human digestive secretions, a significant portion of dietary DCI may not be bioavailable. Additionally, some dietary forms of DCI exist as methylated derivatives which may be ineffe ...
... exists in a galactosyl form requiring alphagalactosidase for hydrolysis and absorption. As this enzyme is not found in human digestive secretions, a significant portion of dietary DCI may not be bioavailable. Additionally, some dietary forms of DCI exist as methylated derivatives which may be ineffe ...
Chapter 8 Homeostasis of blood sugar, gas concentrations and
... The adrenals secrete glucocorticoids, which ensure enough energy is provided to the cells by stimulating the conversion on glycogen to glucose. They also increase the rate at which amino acids are removed from cells and transported to the liver for construction. The adrenals (medulla) secrete adrena ...
... The adrenals secrete glucocorticoids, which ensure enough energy is provided to the cells by stimulating the conversion on glycogen to glucose. They also increase the rate at which amino acids are removed from cells and transported to the liver for construction. The adrenals (medulla) secrete adrena ...
Insulin - WordPress.com
... ◦ Glucagon : let glucose out of liver cells - lost of negative feedback too much β-cells of Islet of Langerhans in pancreas insulin α-cells of Islet of Langerhans in pancreas glucagon ...
... ◦ Glucagon : let glucose out of liver cells - lost of negative feedback too much β-cells of Islet of Langerhans in pancreas insulin α-cells of Islet of Langerhans in pancreas glucagon ...
1 - Wk 1-2
... element of insulin’s control of hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipolysis in adipose tissue. When blood sugar levels are diminished, insulin secretion decreases and suppression of α-cells finishes and glucagon is released. Glucagon however does not affect the insulin secreting cells. Secretion of hormon ...
... element of insulin’s control of hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipolysis in adipose tissue. When blood sugar levels are diminished, insulin secretion decreases and suppression of α-cells finishes and glucagon is released. Glucagon however does not affect the insulin secreting cells. Secretion of hormon ...
Diabetes and Renal Disease
... present at time of Dx • Degree of proteinuria correlates with general vascular risk and 20x CKD risk ...
... present at time of Dx • Degree of proteinuria correlates with general vascular risk and 20x CKD risk ...
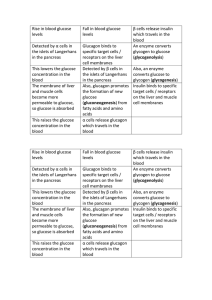
Rise in blood glucose levels
... Also, glucagon promotes the formation of new glucose (gluconeogenesis) from fatty acids and amino acids α cells release glucagon which travels in the blood ...
... Also, glucagon promotes the formation of new glucose (gluconeogenesis) from fatty acids and amino acids α cells release glucagon which travels in the blood ...
Progression to Diabetes: Prediabetes and Insulin
... Studies show that untreated sleep problems, especially sleep apnea, can increase the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Night shift workers may also be at increased risk for these problems. Sleep apnea is a common disorder in which a person's breathing is interrupted during sl ...
... Studies show that untreated sleep problems, especially sleep apnea, can increase the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Night shift workers may also be at increased risk for these problems. Sleep apnea is a common disorder in which a person's breathing is interrupted during sl ...
The effect of the NPO diet order - Canadian Malnutrition Task Force
... Why NPO* is not a healthy diet order for hospitalized patients Although we all fast between meals and when we are asleep at night, our tissues and especially our brain needs glucose to provide energy to function properly. During fasting the required glucose comes from carbohydrate that is stored in ...
... Why NPO* is not a healthy diet order for hospitalized patients Although we all fast between meals and when we are asleep at night, our tissues and especially our brain needs glucose to provide energy to function properly. During fasting the required glucose comes from carbohydrate that is stored in ...
BIO1004 Microbial biotech 2015 for online taster course cut down
... • Insulin regulates uptake of glucose from the blood into cells. • Type I diabetes is caused by lack of insulin high blood sugar. ...
... • Insulin regulates uptake of glucose from the blood into cells. • Type I diabetes is caused by lack of insulin high blood sugar. ...
Opinion Box: Thrifty Genes in Polynesia? Jim Bindon
... to periodic famine. In the case of the Pacific it has been invoked as an adaptive response to caloric restriction associated with voyaging and settlement of the islands (Bindon and Baker, 1997). Metabolic efficiency in storage of excess calories is achieved through over secretion of insulin which in ...
... to periodic famine. In the case of the Pacific it has been invoked as an adaptive response to caloric restriction associated with voyaging and settlement of the islands (Bindon and Baker, 1997). Metabolic efficiency in storage of excess calories is achieved through over secretion of insulin which in ...
Hyperglycemia Syndromes - UT Health Science Center
... uses only those biologically effective molecules which are able to draw water out of the cell. Urea and other molecules measured in the lab (alcohol) move freely between the intra and extravascular spaces and don’t draw water out of the cell. ...
... uses only those biologically effective molecules which are able to draw water out of the cell. Urea and other molecules measured in the lab (alcohol) move freely between the intra and extravascular spaces and don’t draw water out of the cell. ...
All 3 fates of pyruvate from glycolysis provide for the regeneration of
... Gluconeogenesis: Needed to produce glucose for the brain when food isn’t available. Glycogen stores are depleted in 12 to 18 hours. Use other non-carbohydrate sources (glycerol,lactate, some amino acids, & (in plants) acetyl-CoA) ...
... Gluconeogenesis: Needed to produce glucose for the brain when food isn’t available. Glycogen stores are depleted in 12 to 18 hours. Use other non-carbohydrate sources (glycerol,lactate, some amino acids, & (in plants) acetyl-CoA) ...
Setting sail for glucose homeostasis with the AKAP150PP2Banchor
... cAMP fluctuation which is necessary for insulin secretion (Dyachok et al, 2008) was also abolished in AKAP150KO mice. Therefore, AKAP150KO mice exhibit an insulin secretory defect due to multiple impairments including (1) decreased Ca2þ influx and (2) defective cAMP production. Surprisingly, while the ...
... cAMP fluctuation which is necessary for insulin secretion (Dyachok et al, 2008) was also abolished in AKAP150KO mice. Therefore, AKAP150KO mice exhibit an insulin secretory defect due to multiple impairments including (1) decreased Ca2þ influx and (2) defective cAMP production. Surprisingly, while the ...
Determination of Insulin Levels in Human Serum
... Reader can be used to automate some of the steps of a human insulin ELISA. The assay kit instructions indicate that the initial 30-minute and the second 15-minute incubations are both performed with shaking throughout their duration. In our hands the color development step occurred more rapidly than ...
... Reader can be used to automate some of the steps of a human insulin ELISA. The assay kit instructions indicate that the initial 30-minute and the second 15-minute incubations are both performed with shaking throughout their duration. In our hands the color development step occurred more rapidly than ...