Life in Athens and Sparta
... Power city-states that became bitter rivals City-States were very different from one another ...
... Power city-states that became bitter rivals City-States were very different from one another ...
Athens or Sparta Comparison - Tamalpais Union High School District
... They could veto rulings made by the council or assembly. Council or Senate, who acted as judges and proposed laws to the citizen’s assembly. The Assembly of all Spartan males could support or veto the council’s recommendations by shouting out their votes. Women did not participate politically. Three ...
... They could veto rulings made by the council or assembly. Council or Senate, who acted as judges and proposed laws to the citizen’s assembly. The Assembly of all Spartan males could support or veto the council’s recommendations by shouting out their votes. Women did not participate politically. Three ...
Chapter 11: Ancient Greece Lesson 4
... Wars led to Greek unification. 1. The city-states realized they needed to put aside their differences and unite in order to defeat a much stronger ...
... Wars led to Greek unification. 1. The city-states realized they needed to put aside their differences and unite in order to defeat a much stronger ...
Peloponnesian War Handout
... To meet the Spartans head on and destroy them in a ground battle To remain inside the walls of their city and use their superior ships to win the war To lay siege to Sparta and eventually starve them out of their city All of the above None of the above 7) What former enemy did Sparta turn to for hel ...
... To meet the Spartans head on and destroy them in a ground battle To remain inside the walls of their city and use their superior ships to win the war To lay siege to Sparta and eventually starve them out of their city All of the above None of the above 7) What former enemy did Sparta turn to for hel ...
Reading Notes 27 - ArchHistoryClasses
... • Sometimes education was continued with a private tutor ...
... • Sometimes education was continued with a private tutor ...
Section 3 Quiz
... 7. What was one result of the Greek victory against the Persians? a. Pericles seized power in Athens. b. Athens formed the Delian League. c. Athenians built a large fleet of ships. d. Spartans battled the Persians at Thermopylae. 8. Why did Pericles approve paying people to serve in government? a. I ...
... 7. What was one result of the Greek victory against the Persians? a. Pericles seized power in Athens. b. Athens formed the Delian League. c. Athenians built a large fleet of ships. d. Spartans battled the Persians at Thermopylae. 8. Why did Pericles approve paying people to serve in government? a. I ...
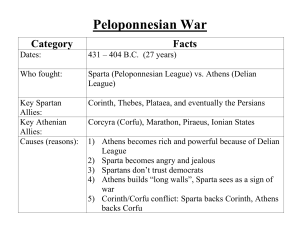
Peloponnesian War - Newton.k12.ma.us
... 1) Sparta had better land force, Athens had better navy 2) Athens brings people together into the city and plague breaks out (430 B.C.) - last four years, 1/4 of Athenian populations dies 3) Athens suffers huge loss at Syracuse (many Athenians die and into slavery; 413 B.C.) 4) Delian League states ...
... 1) Sparta had better land force, Athens had better navy 2) Athens brings people together into the city and plague breaks out (430 B.C.) - last four years, 1/4 of Athenian populations dies 3) Athens suffers huge loss at Syracuse (many Athenians die and into slavery; 413 B.C.) 4) Delian League states ...
New School Rules!!!
... sets of rules, they mirror rules from certain Greek city-states. • Rules #1 were like SPARTA and Rules #2 were like ATHENS. • These are the two most important city-states in Ancient Greece. ...
... sets of rules, they mirror rules from certain Greek city-states. • Rules #1 were like SPARTA and Rules #2 were like ATHENS. • These are the two most important city-states in Ancient Greece. ...
Ancient Greece
... of the Societal and Personal Interactions of the Ancient Hellenistic Cultures ...
... of the Societal and Personal Interactions of the Ancient Hellenistic Cultures ...
the Ch 5 Sec 2 Notes if you missed them.
... • Phalanx—feared by all, formation of soldiers with spears, shields Battle at Marathon • Persian Wars—between Greece and Persian Empire—begin in Ionia • Persian army attacks Athens, is defeated at Marathon in 490 B.C. • The Persians were driven from Greece shortly before the golden age of Athens beg ...
... • Phalanx—feared by all, formation of soldiers with spears, shields Battle at Marathon • Persian Wars—between Greece and Persian Empire—begin in Ionia • Persian army attacks Athens, is defeated at Marathon in 490 B.C. • The Persians were driven from Greece shortly before the golden age of Athens beg ...
Hellenic History
... 3. Which of these events was a great disaster for the Athenians? a. Sicilian expedition b. the discovery of a silver mine at Laurion c. the construction of the long walls d. the battle of Salamis 4. What kingdom, ruled by Croesus, was destroyed when he attacked the Persians in 547? a. Media b. Crisa ...
... 3. Which of these events was a great disaster for the Athenians? a. Sicilian expedition b. the discovery of a silver mine at Laurion c. the construction of the long walls d. the battle of Salamis 4. What kingdom, ruled by Croesus, was destroyed when he attacked the Persians in 547? a. Media b. Crisa ...
The Ancient Greeks
... Spartan Males All babies examined by city elders at birth, weak ones were abandoned Age 7, boys sent to live with army, begin training; little food, clothing, were encouraged to steal Age 20, allowed to marry but had to live with army until 30; remained on active duty until age 60 ...
... Spartan Males All babies examined by city elders at birth, weak ones were abandoned Age 7, boys sent to live with army, begin training; little food, clothing, were encouraged to steal Age 20, allowed to marry but had to live with army until 30; remained on active duty until age 60 ...
The Rise of Greek Cities - Our Lady of the Wayside
... Citizen: a person who has certain rights and ...
... Citizen: a person who has certain rights and ...
sparta - SchoolNotes.com
... Free males; parents were Athenian; property owners; age 18 or older ...
... Free males; parents were Athenian; property owners; age 18 or older ...
Chapter 27 Life in Two City-States: Athens and Sparta What were
... Athens and Sparta? • The economy of Athens relied on trade with other city-states and several foreign lands. The Spartan economy relied on farming and conquest. Sparta depended on slaves and other noncitizens to provide for many of its needs. • In Athens, boys were educated to be good citizens. Educ ...
... Athens and Sparta? • The economy of Athens relied on trade with other city-states and several foreign lands. The Spartan economy relied on farming and conquest. Sparta depended on slaves and other noncitizens to provide for many of its needs. • In Athens, boys were educated to be good citizens. Educ ...
The Hellenic Age of Ancient Greece
... What age were Spartan soldiers given citizenship? The _______________________ was the training camp for all Spartans. What did the soldiers have to endure to become better soldiers? 1. _____________________________________. 2. _____________________________________. 3. _______________________________ ...
... What age were Spartan soldiers given citizenship? The _______________________ was the training camp for all Spartans. What did the soldiers have to endure to become better soldiers? 1. _____________________________________. 2. _____________________________________. 3. _______________________________ ...
Accommodated GCS
... conquered Ionia. o Persian troops were defeated by the Greeks at the battle of Marathon. o Athenians found rich silver mines and used the money to build a fleet of triremes. o The Persian Wars ended when the Greeks defeated the Persian navy at Salamis. Greeks united in a defensive league under the ...
... conquered Ionia. o Persian troops were defeated by the Greeks at the battle of Marathon. o Athenians found rich silver mines and used the money to build a fleet of triremes. o The Persian Wars ended when the Greeks defeated the Persian navy at Salamis. Greeks united in a defensive league under the ...
Warring City-States
... sites; schools; accommodations (like homes where the tourists can stay with some of the locals or homes for sale); transportation; and ...
... sites; schools; accommodations (like homes where the tourists can stay with some of the locals or homes for sale); transportation; and ...
Athens VS Sparta
... • Harsh laws demanded citizens to dedicate themselves to the state • There was a strict devotion to a military ...
... • Harsh laws demanded citizens to dedicate themselves to the state • There was a strict devotion to a military ...
Ancient Greek World 500-440BC (part 2 and 3)
... Ancient Greek World 500-440BC (part 2 and 3) In your preparation for the assessment task you should have notes on the following: The Delian League; what were its aims, how was it organised? Activities of the Delian League up to the Battle of the Eurymedon River Role and contribution of Cimon a ...
... Ancient Greek World 500-440BC (part 2 and 3) In your preparation for the assessment task you should have notes on the following: The Delian League; what were its aims, how was it organised? Activities of the Delian League up to the Battle of the Eurymedon River Role and contribution of Cimon a ...
Ancient Greece Study Guide
... 19. Sparta boys began receiving military training at age seven. After decades of military service, they became citizens at the age of 30. ...
... 19. Sparta boys began receiving military training at age seven. After decades of military service, they became citizens at the age of 30. ...
Athens – Birthplace of Democracy
... individual freedom and creativity, Spartans focused on building up their military, strength and a maintaining a skilled, disciplined army. - To reach these goals, all male citizens of Sparta became full-time soldiers and every aspect of their life was dictated by the city-state. - Sparta was ruled b ...
... individual freedom and creativity, Spartans focused on building up their military, strength and a maintaining a skilled, disciplined army. - To reach these goals, all male citizens of Sparta became full-time soldiers and every aspect of their life was dictated by the city-state. - Sparta was ruled b ...
Sparta

Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, Spártā; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, Spártē) or Lacedaemon (/ˌlæsəˈdiːmən/; Λακεδαίμων, Lakedaímōn) was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece.Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the overall leader of the combined Greek forces during the Greco-Persian Wars. Between 431 and 404 BC, Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War, from which it emerged victorious, though at great cost of lives lost. Sparta's defeat by Thebes in the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended Sparta's prominent role in Greece. However, it maintained its political independence until the Roman conquest of Greece in 146 BC. It then underwent a long period of decline, especially in the Middle Ages, when many Spartans moved to live in Mystras. Modern Sparta is the capital of the Greek regional unit of Laconia and a center for the processing of goods such as citrus and olives.Sparta was unique in ancient Greece for its social system and constitution, which completely focused on military training and excellence. Its inhabitants were classified as Spartiates (Spartan citizens, who enjoyed full rights), mothakes (non-Spartan free men raised as Spartans), perioikoi (freedmen), and helots (state-owned serfs, enslaved non-Spartan local population). Spartiates underwent the rigorous agoge training and education regimen, and Spartan phalanges were widely considered to be among the best in battle. Spartan women enjoyed considerably more rights and equality to men than elsewhere in the classical world.Sparta was the subject of fascination in its own day, as well as in the West following the revival of classical learning. This love or admiration of Sparta is known as Laconism or Laconophilia. At its peak around 500 BC the size of the city would have been some 20,000 – 35,000 free residents, plus numerous helots and perioikoi (“dwellers around”). At 40,000 – 50,000 it was one of the largest Greek cities; however, according to Thucydides, the population of Athens in 431 BC was 360,000 – 610,000, making it unlikely that Athens was smaller than Sparta in 5th century BC.