Regents Review - Ancient Greece
... wife of a Mycenaean king • Destroyed Troy with “Trojan Horse” – Greeks built a “gift” for the Trojans – The Greeks hid inside and at night when the horse was taken inside, the Greeks came out and destroyed Troy ...
... wife of a Mycenaean king • Destroyed Troy with “Trojan Horse” – Greeks built a “gift” for the Trojans – The Greeks hid inside and at night when the horse was taken inside, the Greeks came out and destroyed Troy ...
The City States
... Memorized Homer & other poets Age 18 – Males become citizens Took oath at Temple of Zeus Make Athens a better place Be honorable in battle Follow the constitution Respect their religion Persian Wars 545 BC Persians conquer Ionia (Greek city-states in Asia Minor) 525 BC Ionia revolts Ask Greeks o ...
... Memorized Homer & other poets Age 18 – Males become citizens Took oath at Temple of Zeus Make Athens a better place Be honorable in battle Follow the constitution Respect their religion Persian Wars 545 BC Persians conquer Ionia (Greek city-states in Asia Minor) 525 BC Ionia revolts Ask Greeks o ...
Archaic Greece and Classical Greece: the Introduction to Greek
... led another massive attack on the Greeks, one at the Pass of Thermopylae, which the Greeks lost, but the Spartans achieved immortality with three hundred hoplites supposedly detaining the Persians long enough for the rest of the Greek army to go on the offensive.3 Athens was defeated then, but in a ...
... led another massive attack on the Greeks, one at the Pass of Thermopylae, which the Greeks lost, but the Spartans achieved immortality with three hundred hoplites supposedly detaining the Persians long enough for the rest of the Greek army to go on the offensive.3 Athens was defeated then, but in a ...
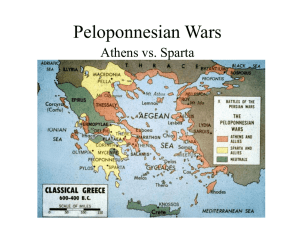
Peloponnesian War - Mr. Reustle's Social Studies
... Created after the Persian Wars Greek city-states unite 200 city-states join (Sparta says no) Defensive alliance Athens becomes leader Used the navy to control the Aegean Sea ...
... Created after the Persian Wars Greek city-states unite 200 city-states join (Sparta says no) Defensive alliance Athens becomes leader Used the navy to control the Aegean Sea ...
greek city states g6 gle11
... Athens was ruled by an Oligarchy-few people have ruling power Solon set up first Athenian Constitution Citizenship was offered to everyone 508b.c. first democratic government setup (favoring the people) Became citizens at age 18 490b.c. the word “Nike” was first used (Greek goddess of victory upon d ...
... Athens was ruled by an Oligarchy-few people have ruling power Solon set up first Athenian Constitution Citizenship was offered to everyone 508b.c. first democratic government setup (favoring the people) Became citizens at age 18 490b.c. the word “Nike” was first used (Greek goddess of victory upon d ...
Ancient Greece Test Review
... 24. What do Spartan men spend all of their time doing? ____________________________________________________ 25. Describe what happens to boys when they are born in Sparta? What if they don’t make the cut? ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
... 24. What do Spartan men spend all of their time doing? ____________________________________________________ 25. Describe what happens to boys when they are born in Sparta? What if they don’t make the cut? ____________________________________________________ __________________________________________ ...
Greeks_AnswerSheet-MUA - Digital Schoolhouse Resources
... When was Ancient Greece? The Ancient Greek civilization lived between 800BC and 146BC. The earliest Greek civilizations thrived nearly 4,000 years ago. How was ancient Greece governed? The Greeks lived in little city-states, each one like a small town in the United States today, with no more than ab ...
... When was Ancient Greece? The Ancient Greek civilization lived between 800BC and 146BC. The earliest Greek civilizations thrived nearly 4,000 years ago. How was ancient Greece governed? The Greeks lived in little city-states, each one like a small town in the United States today, with no more than ab ...
City-States and Greek Culture: Chapter 8, Lesson 2 acropolis E
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Was Athenian democracy actually “Rule by the people?” ________________________ ...
... ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 2. Was Athenian democracy actually “Rule by the people?” ________________________ ...
SWBAT compare and contrast the lives of individuals in Athens and
... lot, or at random, to serve for a term of one year. Members could be reelected only once. The yearly turnover allowed for a greater number of Athenian citizens to participate in their government at a high level. Laws were passed by a majority vote in the assembly. ...
... lot, or at random, to serve for a term of one year. Members could be reelected only once. The yearly turnover allowed for a greater number of Athenian citizens to participate in their government at a high level. Laws were passed by a majority vote in the assembly. ...
Sparta and Athens - Kenston Local Schools
... reading/writing and trained for the military. From 1820 – trained exclusively for war. 4. At 20 – could marry, but could not live at home until they were 30. Served in the military until 60. 5. Girls – received physical training and studied music (for discipline and coordination). 6. Gave up individ ...
... reading/writing and trained for the military. From 1820 – trained exclusively for war. 4. At 20 – could marry, but could not live at home until they were 30. Served in the military until 60. 5. Girls – received physical training and studied music (for discipline and coordination). 6. Gave up individ ...
Greece: Athens/Sparta Reading
... Council or Senate(apella) of 28 councilmen (men over 60 and elected for life by the citizens) and the 2 kings. They acted as judges and proposed laws to the citizens' assembly. The Assembly of all Spartan males aged 30 or over could support or veto the council's recommendations by shouting out their ...
... Council or Senate(apella) of 28 councilmen (men over 60 and elected for life by the citizens) and the 2 kings. They acted as judges and proposed laws to the citizens' assembly. The Assembly of all Spartan males aged 30 or over could support or veto the council's recommendations by shouting out their ...
Athens
... Even though it was limited, Athenian men had more freedom & political voice then most people during this time period. ...
... Even though it was limited, Athenian men had more freedom & political voice then most people during this time period. ...
File - World History with Ms. Byrne
... • Only free white males that owned property could participate in government • 500 names were drawn from eligible citizens to serve on a council for the city-state. They would serve for one year. • These 500 men were the law makers for the year. All the other citizens would vote on the laws that thes ...
... • Only free white males that owned property could participate in government • 500 names were drawn from eligible citizens to serve on a council for the city-state. They would serve for one year. • These 500 men were the law makers for the year. All the other citizens would vote on the laws that thes ...
Greeks_QuestionSheet-UA - Digital Schoolhouse Resources
... The ancient greek civilization lived ________________________ . How was ancient Greece governed? The Greeks lived in ________________________ ________________________ , each one like a small town in the United States today, with no more than about ________________________ people in each city-state. ...
... The ancient greek civilization lived ________________________ . How was ancient Greece governed? The Greeks lived in ________________________ ________________________ , each one like a small town in the United States today, with no more than about ________________________ people in each city-state. ...
The Story of Ancient Greece Geography of Greece Greece is a small
... II. Greek City-States A. Because Greece is made up of many islands, and has many tall mountains, the Greeks built _________________ instead of one country. B. A city-state is a city with its own _________________________________ C. Greek city-states acted like their own ______________ III. Sparta A. ...
... II. Greek City-States A. Because Greece is made up of many islands, and has many tall mountains, the Greeks built _________________ instead of one country. B. A city-state is a city with its own _________________________________ C. Greek city-states acted like their own ______________ III. Sparta A. ...
The Greeks at War!
... For much of the war, neither side could gain the upper hand over the other. Pericles allowed people from the countryside to move inside the city to protect them from Sparta. In Athens a deadly disease spread throughout the overcrowded city, this killed a third of the people including Pericles. I ...
... For much of the war, neither side could gain the upper hand over the other. Pericles allowed people from the countryside to move inside the city to protect them from Sparta. In Athens a deadly disease spread throughout the overcrowded city, this killed a third of the people including Pericles. I ...
pelponnesian war
... The Delian League was an association of Greek citystates in the 5th century BC. It was led by Athens. Because many of the league's poleis were too poor to contribute ships to the collective navy, they paid taxes to Athens so that there would be enough money to build the expensive triremes. ...
... The Delian League was an association of Greek citystates in the 5th century BC. It was led by Athens. Because many of the league's poleis were too poor to contribute ships to the collective navy, they paid taxes to Athens so that there would be enough money to build the expensive triremes. ...
Topic(s): Cues – themes, terms, people, places, events, ideas
... : girls - must be healthy and fit to bear future soldiers - undergo physical training : Art, Literature, Culture - no long-term contributions - wholly focused on the military ...
... : girls - must be healthy and fit to bear future soldiers - undergo physical training : Art, Literature, Culture - no long-term contributions - wholly focused on the military ...
(Section II): Greek City-States Rise to Power
... To fight against the Persians (in many battles). Sparta and Athens even fought together against the Persians (in the Persian War). At one time Athens and Sparta weren’t doing to well. But they re-grouped and in the battle of Salamis (first naval battle ever recorded) beat the Persians (300 sunk ship ...
... To fight against the Persians (in many battles). Sparta and Athens even fought together against the Persians (in the Persian War). At one time Athens and Sparta weren’t doing to well. But they re-grouped and in the battle of Salamis (first naval battle ever recorded) beat the Persians (300 sunk ship ...
Sparta

Sparta (Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, Spártā; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, Spártē) or Lacedaemon (/ˌlæsəˈdiːmən/; Λακεδαίμων, Lakedaímōn) was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the Eurotas River in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece.Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the overall leader of the combined Greek forces during the Greco-Persian Wars. Between 431 and 404 BC, Sparta was the principal enemy of Athens during the Peloponnesian War, from which it emerged victorious, though at great cost of lives lost. Sparta's defeat by Thebes in the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC ended Sparta's prominent role in Greece. However, it maintained its political independence until the Roman conquest of Greece in 146 BC. It then underwent a long period of decline, especially in the Middle Ages, when many Spartans moved to live in Mystras. Modern Sparta is the capital of the Greek regional unit of Laconia and a center for the processing of goods such as citrus and olives.Sparta was unique in ancient Greece for its social system and constitution, which completely focused on military training and excellence. Its inhabitants were classified as Spartiates (Spartan citizens, who enjoyed full rights), mothakes (non-Spartan free men raised as Spartans), perioikoi (freedmen), and helots (state-owned serfs, enslaved non-Spartan local population). Spartiates underwent the rigorous agoge training and education regimen, and Spartan phalanges were widely considered to be among the best in battle. Spartan women enjoyed considerably more rights and equality to men than elsewhere in the classical world.Sparta was the subject of fascination in its own day, as well as in the West following the revival of classical learning. This love or admiration of Sparta is known as Laconism or Laconophilia. At its peak around 500 BC the size of the city would have been some 20,000 – 35,000 free residents, plus numerous helots and perioikoi (“dwellers around”). At 40,000 – 50,000 it was one of the largest Greek cities; however, according to Thucydides, the population of Athens in 431 BC was 360,000 – 610,000, making it unlikely that Athens was smaller than Sparta in 5th century BC.