Chapter 9 Sleep and Biological Rhythms
... The executive mechanism Activation of single neurons in this area are related to the sleep cycle ► Axons of these neurons project to the reticular formation, forebrain, brain stem regions that control eye movements ► Carbachol, an ACh receptor agonist, when infused into the reticular formation, pr ...
... The executive mechanism Activation of single neurons in this area are related to the sleep cycle ► Axons of these neurons project to the reticular formation, forebrain, brain stem regions that control eye movements ► Carbachol, an ACh receptor agonist, when infused into the reticular formation, pr ...
Slide 1
... in beats per quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... in beats per quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. ...
rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induces acetylcholinesterase
... Cazvin Road. Rasht. Cui/an. I.R.Iran. (e-mail: [email protected]). and the *Department of Physiology. Faculty ofMedicine. Shahid Beheshti University ofMedical Sciences. Evin. Tehran. I.R. Iran. ...
... Cazvin Road. Rasht. Cui/an. I.R.Iran. (e-mail: [email protected]). and the *Department of Physiology. Faculty ofMedicine. Shahid Beheshti University ofMedical Sciences. Evin. Tehran. I.R. Iran. ...
of sleep
... the bed, yet you can waken to baby’s cry • REM (rapid eye movement) sleep: recurring sleep ...
... the bed, yet you can waken to baby’s cry • REM (rapid eye movement) sleep: recurring sleep ...
Anatomy Notes on the Brain
... awakened easily and contractions of our muscles can be seen. In stages three and four our brain waves slow and we enter into deep sleep -- it is very difficult to wake someone up in this stage. There is no eye movement or muscle activity at this point. It is during this stage that people can sleep w ...
... awakened easily and contractions of our muscles can be seen. In stages three and four our brain waves slow and we enter into deep sleep -- it is very difficult to wake someone up in this stage. There is no eye movement or muscle activity at this point. It is during this stage that people can sleep w ...
FOR PPT
... The subject’s behavior is affected by the new memory, though he/she may not be aware of it. Ex. Someone may have the ability to speak a complete sentence without being able to describe the grammatical rules used. Or, learning to ride a bicycle. ...
... The subject’s behavior is affected by the new memory, though he/she may not be aware of it. Ex. Someone may have the ability to speak a complete sentence without being able to describe the grammatical rules used. Or, learning to ride a bicycle. ...
Sleep well….Sleep fast!
... Nap prophylactically During the afternoon Brief naps (15-20 minutes) can be helpful Be careful of longer naps (especially nocturnal) as they may result in sleep inertia. ...
... Nap prophylactically During the afternoon Brief naps (15-20 minutes) can be helpful Be careful of longer naps (especially nocturnal) as they may result in sleep inertia. ...
SLEEP
... Hz seen during alert wakefulness and REM sleep Theta activity (3.5-7.5 Hz) in stage 1 sleep (transiting from awake to sleep) Delta waves – high amplitude, low frequency (<3.5 Hz) pattern seen in stage 3 and 4 sleep Sleep spindles – short burst of 12-14 Hz activity during sleep stages 1 – 4 K complex ...
... Hz seen during alert wakefulness and REM sleep Theta activity (3.5-7.5 Hz) in stage 1 sleep (transiting from awake to sleep) Delta waves – high amplitude, low frequency (<3.5 Hz) pattern seen in stage 3 and 4 sleep Sleep spindles – short burst of 12-14 Hz activity during sleep stages 1 – 4 K complex ...
Testing
... synapses that support activation of neurons common to several representations (thus causing these representations to become uncorrelated). Unification is achieved by deletion of synapses that support activation of neurons that are unique to each representation (thus allowing only neurons common to a ...
... synapses that support activation of neurons common to several representations (thus causing these representations to become uncorrelated). Unification is achieved by deletion of synapses that support activation of neurons that are unique to each representation (thus allowing only neurons common to a ...
SLEEP AND EEG
... Infants spent more time in REM sleep. In children, NREM and REM become 50% each. New born sleeps about 16-20 hrs/day. During childhood, child sleeps 10 hrs/day. Adult person needs 7-8 hours of sleep In elderly NREM, Stage IV (deep sleep) and REM sleep decreases. ...
... Infants spent more time in REM sleep. In children, NREM and REM become 50% each. New born sleeps about 16-20 hrs/day. During childhood, child sleeps 10 hrs/day. Adult person needs 7-8 hours of sleep In elderly NREM, Stage IV (deep sleep) and REM sleep decreases. ...
Consciousness
... During REM sleep our brain is very active. This high level of activity causes our brain to produce dreams—as it needs to make sense out of the firing of our neurons in our visual & emotional centers. ...
... During REM sleep our brain is very active. This high level of activity causes our brain to produce dreams—as it needs to make sense out of the firing of our neurons in our visual & emotional centers. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 40.1 Periodic activation in sleep cycles
... quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. FIGURE 40.2 Behavioral states in humans. Body position changes duri ...
... quarter minute, and body movement (BM) in numbers per minute over 100 minutes of uninterrupted sleep. The interval from 242 to 273 minutes is considered the REM period, although eye movements are not continuous during that interval. FIGURE 40.2 Behavioral states in humans. Body position changes duri ...
Perceiving forms, patterns and objects
... - the alpha waves of drowsiness give way to theta waves - hypnic jerks occur in this stage stage 2 lasts 10-25 minutes, and is characterized by sleep spindles and mixed EEG activity. Waves gradually get higher and slower and the body moves toward deep sleep. Stages 3 & 4 are slow wave sleep, or ...
... - the alpha waves of drowsiness give way to theta waves - hypnic jerks occur in this stage stage 2 lasts 10-25 minutes, and is characterized by sleep spindles and mixed EEG activity. Waves gradually get higher and slower and the body moves toward deep sleep. Stages 3 & 4 are slow wave sleep, or ...
Chapter-3-Lecture
... awake, his brain activity slows down to a large amplitude and slow, regular alpha waves (9-14 cps). A meditating person exhibits an alpha brain activity. ...
... awake, his brain activity slows down to a large amplitude and slow, regular alpha waves (9-14 cps). A meditating person exhibits an alpha brain activity. ...
Unit 2, the Brain
... During early, light sleep (stages 1-2) the brain enters a high-amplitude, slow, regular wave form called theta waves. A person who is daydreaming shows theta activity. (Hallucinations) ...
... During early, light sleep (stages 1-2) the brain enters a high-amplitude, slow, regular wave form called theta waves. A person who is daydreaming shows theta activity. (Hallucinations) ...
CONSCIOUSNESS-INTRO-Part-I1
... rhythm and corresponding changes in brain activity and behavior. •The average person progresses through the stages of sleep 3 to 6 times per night. ...
... rhythm and corresponding changes in brain activity and behavior. •The average person progresses through the stages of sleep 3 to 6 times per night. ...
questions from - AP Psychology: 6(A)
... reactions, and provide a secondary source of sex hormones affecting the sexual changes that occur during adolescence. 35. The __________ is a structure in the brain stem that connects the top of the brain to the bottom and plays a role in sleep, dreaming, left–right body coordination, and arousal. 3 ...
... reactions, and provide a secondary source of sex hormones affecting the sexual changes that occur during adolescence. 35. The __________ is a structure in the brain stem that connects the top of the brain to the bottom and plays a role in sleep, dreaming, left–right body coordination, and arousal. 3 ...
This is Your Brain. This Is How It Works.
... • is responsible for language development. It develops slower in boys, that is why males usually develop more language problems than ...
... • is responsible for language development. It develops slower in boys, that is why males usually develop more language problems than ...
MEMORY, SLEEP AND OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNEA Although
... memory deficit. This is mainly an effect of hypoxia, the inadequate supply of oxygen to the body. Spatial and working memory also may be compromised by injury to the mammillary bodies, two round groups of nuclei on the undersurface of the brain, and the fornix, a c-shaped group of fibers in the brai ...
... memory deficit. This is mainly an effect of hypoxia, the inadequate supply of oxygen to the body. Spatial and working memory also may be compromised by injury to the mammillary bodies, two round groups of nuclei on the undersurface of the brain, and the fornix, a c-shaped group of fibers in the brai ...
bYTEBoss brain_notes
... activity • Totally out of it – dreams usually not remembered. • Difficult to awake (may try to hit etc.) • Not conscious of surroundings (talk with you, but not aware.) • If disorder or young you may spend too much time in III ...
... activity • Totally out of it – dreams usually not remembered. • Difficult to awake (may try to hit etc.) • Not conscious of surroundings (talk with you, but not aware.) • If disorder or young you may spend too much time in III ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY OF SLEEP By Dr. Mohammad
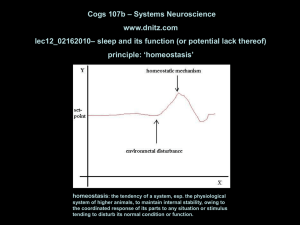
... • principal value of sleep is to restore natural balances among the neuronal centers. • The entrainment of biological processes to the light–dark cycle is regulated by the SCN. • The diurnal change in melatonin secretion from serotonin in the pineal gland functions as a timing signal to coordinate e ...
... • principal value of sleep is to restore natural balances among the neuronal centers. • The entrainment of biological processes to the light–dark cycle is regulated by the SCN. • The diurnal change in melatonin secretion from serotonin in the pineal gland functions as a timing signal to coordinate e ...