Pressure Gradient Force
... fixed in space will remain in uniform motion in the absence of any forces. Non-Newtonian Motion An object at rest w. r. t. the rotating earth is not at rest or in uniform motion relative to the coordinate system fixed in space. Apparent forces are the inertial reaction terms which arise because of t ...
... fixed in space will remain in uniform motion in the absence of any forces. Non-Newtonian Motion An object at rest w. r. t. the rotating earth is not at rest or in uniform motion relative to the coordinate system fixed in space. Apparent forces are the inertial reaction terms which arise because of t ...
ENERGY- Is the ability to do work
... FRICTION_ -A force between objects that slows an object down. ACCELERATION_ -A change in speed or direction. INERTIA_ -A tendency to stay at rest or in motion until an outside force acts upon an object. FORCE__ -Any push or pull that causes and object to move. GRAVITY_ Pull between two objects. WEIG ...
... FRICTION_ -A force between objects that slows an object down. ACCELERATION_ -A change in speed or direction. INERTIA_ -A tendency to stay at rest or in motion until an outside force acts upon an object. FORCE__ -Any push or pull that causes and object to move. GRAVITY_ Pull between two objects. WEIG ...
mg - UF Physics
... Classic application of non-inertial reference frames is an elevator accelerating or decelerating. Objects inside the elevator appear to be gaining or losing weight depending on the direction of the acceleration. Newton’s 2nd law for the object: a ...
... Classic application of non-inertial reference frames is an elevator accelerating or decelerating. Objects inside the elevator appear to be gaining or losing weight depending on the direction of the acceleration. Newton’s 2nd law for the object: a ...
L10_rotation
... kinetic energy. a. Identify and describe at least one characteristic they share. b. Identify and describe at least two differences between them. ...
... kinetic energy. a. Identify and describe at least one characteristic they share. b. Identify and describe at least two differences between them. ...
Inertial Reference Frame B: Not an inertial reference frame A
... upwards at a constant velocity as you lift it into the truck? 2. What force is required to push the piano up a frictionless ramp at a constant velocity into the truck? Assume the ramp is 3 m long and the floor of the truck is 1 m high? ...
... upwards at a constant velocity as you lift it into the truck? 2. What force is required to push the piano up a frictionless ramp at a constant velocity into the truck? Assume the ramp is 3 m long and the floor of the truck is 1 m high? ...
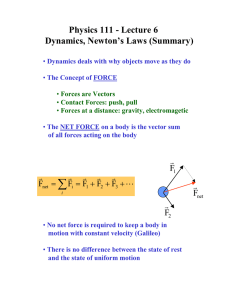
Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary)
... Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary) • Dynamics deals with why objects move as they do • The Concept of FORCE • Forces are Vectors • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the ...
... Physics 111 - Lecture 6 Dynamics, Newton’s Laws (Summary) • Dynamics deals with why objects move as they do • The Concept of FORCE • Forces are Vectors • Contact Forces: push, pull • Forces at a distance: gravity, electromagetic • The NET FORCE on a body is the vector sum of all forces acting on the ...
Introduction to Applied Physics
... Units will be in meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph), or other combinations of distance and time ...
... Units will be in meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph), or other combinations of distance and time ...
The Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when
... reference, the Coriolis and centrifugal forces appear. Both forces are proportional to the mass of the object. The Coriolis force is proportional to the rotation rate, and the centrifugal force is proportional to its square. The Coriolis force acts in a direction perpendicular to the rotation axis a ...
... reference, the Coriolis and centrifugal forces appear. Both forces are proportional to the mass of the object. The Coriolis force is proportional to the rotation rate, and the centrifugal force is proportional to its square. The Coriolis force acts in a direction perpendicular to the rotation axis a ...
Slide 1 - USD 306
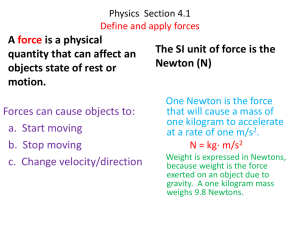
... A force is a physical quantity that can affect an objects state of rest or motion. Forces can cause objects to: a. Start moving b. Stop moving c. Change velocity/direction ...
... A force is a physical quantity that can affect an objects state of rest or motion. Forces can cause objects to: a. Start moving b. Stop moving c. Change velocity/direction ...
Magic Square Vocabulary Game Combinations
... G. Friction H. 3rd Law of Motion I. Gravitational Force ...
... G. Friction H. 3rd Law of Motion I. Gravitational Force ...
MollyHungEmilyROTMOT
... used for two different concepts. Centrifugal force is one of the fictitious forces that appears to act on an object when its motion is viewed from a rotating frame of reference. Magnitude of centripetal force is F=mv2/r. ...
... used for two different concepts. Centrifugal force is one of the fictitious forces that appears to act on an object when its motion is viewed from a rotating frame of reference. Magnitude of centripetal force is F=mv2/r. ...