for reference Name Period ______ Date ______ Motion Notes from
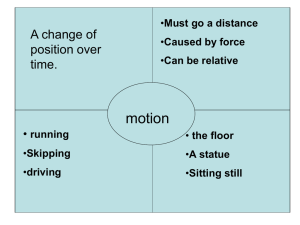
... Earth is the most common frame of reference. Speed: the distance traveled by a moving object per unit of time. To calculate speed, use this equation: Speed = distance / time Speed only specifies distance and time, not direction. Average speed: the speed of moving objects is not always constant ...
... Earth is the most common frame of reference. Speed: the distance traveled by a moving object per unit of time. To calculate speed, use this equation: Speed = distance / time Speed only specifies distance and time, not direction. Average speed: the speed of moving objects is not always constant ...
forces - World of Teaching
... mass to the Earth’s centre. The weight of a body, of mass m, is defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (g ≈ 9.81 m s−2 on Earth). ...
... mass to the Earth’s centre. The weight of a body, of mass m, is defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to gravity (g ≈ 9.81 m s−2 on Earth). ...
Page 407-408 - Cloudfront.net
... • 14. Newton’s second law states that force is equal to mass multiplied by acceleration. • 15. You can throw your empty jet pack away from the space station. As result, the reaction force exerted on you by the jet pack will accelerate you toward the space station. ...
... • 14. Newton’s second law states that force is equal to mass multiplied by acceleration. • 15. You can throw your empty jet pack away from the space station. As result, the reaction force exerted on you by the jet pack will accelerate you toward the space station. ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... 3. Uniform Circular Motion: - I can: distinguish between reference systems (inertial and non-inertial) with respect to real and apparent forces acting within such systems (e.g. apparent force in a rotating frame, apparent gravitational force in a vertically accelerating frame) analyse, in qualit ...
... 3. Uniform Circular Motion: - I can: distinguish between reference systems (inertial and non-inertial) with respect to real and apparent forces acting within such systems (e.g. apparent force in a rotating frame, apparent gravitational force in a vertically accelerating frame) analyse, in qualit ...
Forces Test Review - Ms. Rousseau`s Classroom
... distinguish between reference systems (inertial and non-inertial) with respect to real and apparent forces acting within such systems (e.g. apparent force in a rotating frame, apparent gravitational force in a vertically accelerating frame) analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the rel ...
... distinguish between reference systems (inertial and non-inertial) with respect to real and apparent forces acting within such systems (e.g. apparent force in a rotating frame, apparent gravitational force in a vertically accelerating frame) analyse, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the rel ...
Inertial and Non-inertial Reference Frames
... We can tell if a "force" is fictitious or not by asking whether or not it makes sense when discussed within the context of the 3rd Law. According to the 3rd law, every force is actually a two-way interaction. In the example above, if a force does truly push on the cup, then the cup must also push b ...
... We can tell if a "force" is fictitious or not by asking whether or not it makes sense when discussed within the context of the 3rd Law. According to the 3rd law, every force is actually a two-way interaction. In the example above, if a force does truly push on the cup, then the cup must also push b ...
NewtonsLaws_1151
... Newton-1: Law of Inertia • Newton’s First Law • An object subject to no external forces is at rest or moves with a constant velocity if viewed from an inertial reference frame. – If no net forces act, there is no acceleration. ...
... Newton-1: Law of Inertia • Newton’s First Law • An object subject to no external forces is at rest or moves with a constant velocity if viewed from an inertial reference frame. – If no net forces act, there is no acceleration. ...
How To Calculate Net Force
... How to Calculate Net Forces Continued • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions on an object, the net force is the difference of the two forces ...
... How to Calculate Net Forces Continued • When two unequal forces act in opposite directions on an object, the net force is the difference of the two forces ...
Module 1 - Kinematics Module 2
... Newton’s Laws only hold in an Inertial Reference Frame. That begs the question: What is an Inertial Reference ...
... Newton’s Laws only hold in an Inertial Reference Frame. That begs the question: What is an Inertial Reference ...
Newton*s Second Law
... Find the force of gravity on the ball in terms of the mass of the object m and the acceleration of gravity g. In general, the force of gravity on any ...
... Find the force of gravity on the ball in terms of the mass of the object m and the acceleration of gravity g. In general, the force of gravity on any ...
Newton`s Second and Third Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion Force is proportional to mass and ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion Force is proportional to mass and ...
Newton`s Second Law Questions
... 2. Space shuttle astronauts experience accelerations of 35.0 m/s2 during takeoff. What force does a 75.0 kg astronaut experience during this acceleration? ...
... 2. Space shuttle astronauts experience accelerations of 35.0 m/s2 during takeoff. What force does a 75.0 kg astronaut experience during this acceleration? ...
Forces II
... 5. Show that 2 V 2v sin 2w cos iˆ 2u sin ˆj 2u cos kˆ . 6. An ant is walking on a turntable that is rotating clockwise at 5 revolutions per minute (rpm). A coordinate system (x, y) is rotating with the turntable, the origin of which is the center of the turntable, with t ...
... 5. Show that 2 V 2v sin 2w cos iˆ 2u sin ˆj 2u cos kˆ . 6. An ant is walking on a turntable that is rotating clockwise at 5 revolutions per minute (rpm). A coordinate system (x, y) is rotating with the turntable, the origin of which is the center of the turntable, with t ...
Newton`s Second Law 1 PPT
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
... Objective • SWBAT describe Newton’s second law of motion and use it to explain the movement of objects. ...
Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object
... Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object Motion: Process of moving or being moved Gravity: The force that pulls things toward Earth Height: the measurement from base to top Distance: an amount of space between two things or people Surface: the outside part or uppermost layer o ...
... Force and Motion Vocabulary: Force: A push or pull on an object Motion: Process of moving or being moved Gravity: The force that pulls things toward Earth Height: the measurement from base to top Distance: an amount of space between two things or people Surface: the outside part or uppermost layer o ...