PHY2049 Exam #1 Solutions – Fall 2012
... radius 3 cm and outer radius 4cm. If the electric field at r=2 cm is going outwards with magnitude 300 V/cm and at r=5 cm is also going outwards with magnitude 300 V/cm. What is the net charge on conducting spherical shell? Solution: Make a Gauss surface consists of sphere of radius r1 =2 cm and sph ...
... radius 3 cm and outer radius 4cm. If the electric field at r=2 cm is going outwards with magnitude 300 V/cm and at r=5 cm is also going outwards with magnitude 300 V/cm. What is the net charge on conducting spherical shell? Solution: Make a Gauss surface consists of sphere of radius r1 =2 cm and sph ...
10_HSPE Review Physical B
... 3. A hammer strikes a nail and drives the nail into a block of wood. If the action force is the hammer striking the nail, the reaction force is A. the nail striking the wood with an equal and opposite force. B. the nail striking the hammer with an equal and opposite force. ...
... 3. A hammer strikes a nail and drives the nail into a block of wood. If the action force is the hammer striking the nail, the reaction force is A. the nail striking the wood with an equal and opposite force. B. the nail striking the hammer with an equal and opposite force. ...
Session Objectives
... A plank with a body of mass m placed on it starts moving straight up according to the law X = a(1 – coswt), where X is the displacement from the initial position, w = 11 s–1. Find the time dependence of the force that the body exerts on the plank. If a = 4.0 cm plot ...
... A plank with a body of mass m placed on it starts moving straight up according to the law X = a(1 – coswt), where X is the displacement from the initial position, w = 11 s–1. Find the time dependence of the force that the body exerts on the plank. If a = 4.0 cm plot ...
Forces and Gravity (Part 1)
... down. Your gravitational force also pulls the Earth towards you, but you don’t notice it because the Earth is too heavy to be visibly affected by your gravity. 24 of 54 ...
... down. Your gravitational force also pulls the Earth towards you, but you don’t notice it because the Earth is too heavy to be visibly affected by your gravity. 24 of 54 ...
Lecture #1, June 9
... the wheels are not only rotating but also performing translational motion along the surface of the road. Let us consider this type of motion in details. We shall consider a wheel rolling smoothly (without slipping) along the road. It participates in both translational and rotational motions. Let the ...
... the wheels are not only rotating but also performing translational motion along the surface of the road. Let us consider this type of motion in details. We shall consider a wheel rolling smoothly (without slipping) along the road. It participates in both translational and rotational motions. Let the ...
Circular
... Universal Law of Gravitation o Any two objects will attract each other with a gravitational force. This force is directly proportional to the objects masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. Gm1m2 Fg d2 Directly proportional means that if one varia ...
... Universal Law of Gravitation o Any two objects will attract each other with a gravitational force. This force is directly proportional to the objects masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. Gm1m2 Fg d2 Directly proportional means that if one varia ...
CARMEL ALISON LAM FOUNDATION SECONDARY SCHOOL
... A student whirls a small bucket of water in a vertical circle of radius 0.6 m. For no spilling, what is the minimum speed of the bucket at the highest point of its path ? A. 2.45 ms-1 B. 3.46 ms-1 C. 4.08 ms-1 D. 4.90 ms-1 E. 5.77 ms-1 1995I5(AL)/4(AS) A small object of mass 0.05 kg is released fr ...
... A student whirls a small bucket of water in a vertical circle of radius 0.6 m. For no spilling, what is the minimum speed of the bucket at the highest point of its path ? A. 2.45 ms-1 B. 3.46 ms-1 C. 4.08 ms-1 D. 4.90 ms-1 E. 5.77 ms-1 1995I5(AL)/4(AS) A small object of mass 0.05 kg is released fr ...
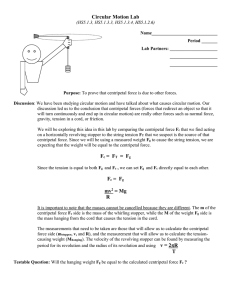
Circular Motion Lab
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
... Discussion: We have been studying circular motion and have talked about what causes circular motion. Our discussion led us to the conclusion that centripetal forces (forces that redirect an object so that it will turn continuously and end up in circular motion) are really other forces such as normal ...
Torque and Motion Relationships
... The acceleration of the COM is proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. – It is the only point that follows a parabolic flight pattern when free of contact with earth – External forces through the COM cause produce only linear ...
... The acceleration of the COM is proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass. – It is the only point that follows a parabolic flight pattern when free of contact with earth – External forces through the COM cause produce only linear ...
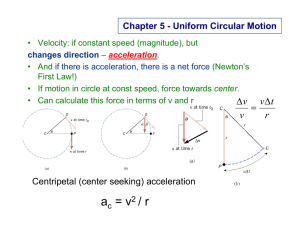
Uniform Circular Motion.
... • Gravity not 'off' (r not ∞) • If falling same as surrounding, no Normal Force (“zero” gravity in a falling elevator?) ...
... • Gravity not 'off' (r not ∞) • If falling same as surrounding, no Normal Force (“zero” gravity in a falling elevator?) ...
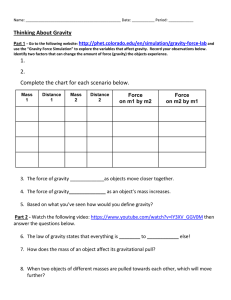
Thinking About Gravity
... Gravity: Everything has its own gravity. Everything exerts a pulling force on everything else. However, only large things have enough gravity to successfully pull other objects towards them. The force of gravity depends on how much mass you have. The larger the object is, the more gravity it has (Th ...
... Gravity: Everything has its own gravity. Everything exerts a pulling force on everything else. However, only large things have enough gravity to successfully pull other objects towards them. The force of gravity depends on how much mass you have. The larger the object is, the more gravity it has (Th ...
BITSAT – Grand Test - 2
... 25. A dog weighing 5 kg is standing on a flat boat so that it is 10 meters from the shore. It walks 4 m on the boat toward the shore and then halts. The boat weighs 20 kg and one can assume that there is no friction between it and water. How far is the dog from the shore at the end of this time? ...
... 25. A dog weighing 5 kg is standing on a flat boat so that it is 10 meters from the shore. It walks 4 m on the boat toward the shore and then halts. The boat weighs 20 kg and one can assume that there is no friction between it and water. How far is the dog from the shore at the end of this time? ...
Calculating Moment of Inertia Example: Hoop vs. Disk Rolling
... depends on – Total mass of the object – Distribution of the mass relative to axis ...
... depends on – Total mass of the object – Distribution of the mass relative to axis ...
1 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 26. Sheila (m=62 kg) is riding the Demon roller coaster ride. The turning radius of the top of the loop is 12 m. Sheila is upside down at the top of the loop and experiencing a normal force that is one-half of her weight. Draw a free body diagram and determine Sheila's speed. (13.3m/s) 27. In 2002, ...
... 26. Sheila (m=62 kg) is riding the Demon roller coaster ride. The turning radius of the top of the loop is 12 m. Sheila is upside down at the top of the loop and experiencing a normal force that is one-half of her weight. Draw a free body diagram and determine Sheila's speed. (13.3m/s) 27. In 2002, ...
Also except answer if student derive for particular two bodies.
... Gravitational Force:The gravitational force is the force of mutual attraction between any two objects by virtue of their masses. It is a universal force. Every object experiences this force due to every other object in the universe. All objects on the earth, for example, experience the force of grav ...
... Gravitational Force:The gravitational force is the force of mutual attraction between any two objects by virtue of their masses. It is a universal force. Every object experiences this force due to every other object in the universe. All objects on the earth, for example, experience the force of grav ...
Torque
... 17. Run experiment: rotate the platen to windup the string on the largest spool. Windup the string until the mass holder is just below the pulley. 18. Press start and release the platen. Allow the apparatus to run through a few (three) oscillations and click stop. 19. Using the mouse to place the cu ...
... 17. Run experiment: rotate the platen to windup the string on the largest spool. Windup the string until the mass holder is just below the pulley. 18. Press start and release the platen. Allow the apparatus to run through a few (three) oscillations and click stop. 19. Using the mouse to place the cu ...
Mechanics Centrifugal force 1.3.16-01
... the force measurement involves movement. This should be compensated by moving the spring balance up and downwards. Determination of the centrifugal force as the function of mass. The experimental car is gradually loaded with the additional weights. The centrifugal force apparatus with a constant ang ...
... the force measurement involves movement. This should be compensated by moving the spring balance up and downwards. Determination of the centrifugal force as the function of mass. The experimental car is gradually loaded with the additional weights. The centrifugal force apparatus with a constant ang ...
B - AQA
... These geosynchronous and polar satellites have different applications because of their different orbits in relation to the rotation of the Earth. Compare the principal features of the geosynchronous and polar orbits and explain the consequences for possible uses of satellites in these orbits. In you ...
... These geosynchronous and polar satellites have different applications because of their different orbits in relation to the rotation of the Earth. Compare the principal features of the geosynchronous and polar orbits and explain the consequences for possible uses of satellites in these orbits. In you ...
If two identical balls each of mass m and having charge q
... There is an electric field E in x ‐ direction. If the work done on a moving charge 0 2 C through a moving charge 0.2 C through a distance of 2 meters along a line making an angle 600 with the x‐ axis is 4 0 J What is the value of E? is 4.0 J What is the value of E? ...
... There is an electric field E in x ‐ direction. If the work done on a moving charge 0 2 C through a moving charge 0.2 C through a distance of 2 meters along a line making an angle 600 with the x‐ axis is 4 0 J What is the value of E? is 4.0 J What is the value of E? ...
Projectile Motion Projectile Motion
... Bell Work 4/11/12 1. What is a satellite? 2. What are the forces acting on a satellite? 3. How long does it take a satellite to orbit Earth? 4. Can we see satellites with the naked eye? 5. How fast do you have to throw a ball to throw it off of the planet? ...
... Bell Work 4/11/12 1. What is a satellite? 2. What are the forces acting on a satellite? 3. How long does it take a satellite to orbit Earth? 4. Can we see satellites with the naked eye? 5. How fast do you have to throw a ball to throw it off of the planet? ...
Document
... 1. On an isolated conducting sphere the charge is uniformly distributed on the outside surface. 2. In regions outside the sphere, the electric field and potential are the same as though all the charge was a point charge at the center of the sphere. 3. Inside a conducting sphere the electric field i ...
... 1. On an isolated conducting sphere the charge is uniformly distributed on the outside surface. 2. In regions outside the sphere, the electric field and potential are the same as though all the charge was a point charge at the center of the sphere. 3. Inside a conducting sphere the electric field i ...
A 10 kg block is pulled in the vertical plane along a frictionless
... Q14. A disk, subjected to a constant net torque, rotates around a fixed axis starting from rest. The ratio of work done by the torque during the (0 – 5.0 s) interval to the work done during the (5.0 s-10 s) interval is: A) B) C) D) E) ...
... Q14. A disk, subjected to a constant net torque, rotates around a fixed axis starting from rest. The ratio of work done by the torque during the (0 – 5.0 s) interval to the work done during the (5.0 s-10 s) interval is: A) B) C) D) E) ...
Physics 7701: Problem Set #10
... November 21. Check the 7701 webpage for suggestions and hints. Please give feedback early and often (and email or stop by M2048 to ask about anything). There are two groups of problems. The first group is required of everyone. The second group is optional but is recommended to go into greater depth ...
... November 21. Check the 7701 webpage for suggestions and hints. Please give feedback early and often (and email or stop by M2048 to ask about anything). There are two groups of problems. The first group is required of everyone. The second group is optional but is recommended to go into greater depth ...
Balancing Rotating Masses The balancing of rotating bodies is
... System of Co-Planar Concurrent Masses Rotating at 10 rev/min 3. Four masses A, B, C, and D, rotate together in a plane about a common axis O. The masses and radii of rotation are as follows: A, 2 kg, 0.6 m: B, 3 kg, 0.9 m; C, 4 kg, 1.2 m; D, 5kg, 1.5 m. The angles between the masses are : Angle AOB ...
... System of Co-Planar Concurrent Masses Rotating at 10 rev/min 3. Four masses A, B, C, and D, rotate together in a plane about a common axis O. The masses and radii of rotation are as follows: A, 2 kg, 0.6 m: B, 3 kg, 0.9 m; C, 4 kg, 1.2 m; D, 5kg, 1.5 m. The angles between the masses are : Angle AOB ...
Ch12
... body with respect to any specified point must be zero. • Note that the above conditions apply to a rigid body in uniform translational motion or to constant rotation (if L is constant) as well. But in the following we will mostly consider situations in which a rigid body is at rest, i.e., in a stati ...
... body with respect to any specified point must be zero. • Note that the above conditions apply to a rigid body in uniform translational motion or to constant rotation (if L is constant) as well. But in the following we will mostly consider situations in which a rigid body is at rest, i.e., in a stati ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.