Chapter 1 - Conroe High School
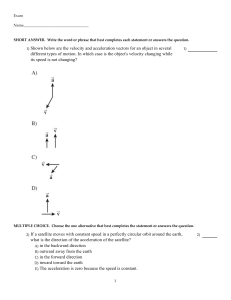
... A properly banked curve tilts _________ the center of the turn to increase _________ . A) towards, the force of kinetic friction. B) towards, the normal force. C) away from, the normal force. D) away from, the force of static friction. ...
... A properly banked curve tilts _________ the center of the turn to increase _________ . A) towards, the force of kinetic friction. B) towards, the normal force. C) away from, the normal force. D) away from, the force of static friction. ...
9. Balancing of Reciprocating Systems
... • If the resultant of all the inertia forces is zero, then there will be no unbalanced force, but even then an unbalanced couple or shaking couple may be present. • Balancing of a mechanism includes counterbalancing both the inertia forces and the inertia couples. In some cases we can eliminate this ...
... • If the resultant of all the inertia forces is zero, then there will be no unbalanced force, but even then an unbalanced couple or shaking couple may be present. • Balancing of a mechanism includes counterbalancing both the inertia forces and the inertia couples. In some cases we can eliminate this ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation and Circular Motion
... You should be able to discuss what happens to the gravitational force when changing the following variables in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation: • Increasing one or both masses • Decreasing one or both masses • Increasing the radial distance • Decreasing the radial distance ...
... You should be able to discuss what happens to the gravitational force when changing the following variables in Newton’s Universal Law of Gravitation: • Increasing one or both masses • Decreasing one or both masses • Increasing the radial distance • Decreasing the radial distance ...
966650d0e579650
... Fluids resist the relative motion of immersed objects through them as well as to the motion of layers with differing velocities within them. Water characterized by a lower viscosity (lower friction force between its different layers), while honey is characterized by a higher viscosity (higher fricti ...
... Fluids resist the relative motion of immersed objects through them as well as to the motion of layers with differing velocities within them. Water characterized by a lower viscosity (lower friction force between its different layers), while honey is characterized by a higher viscosity (higher fricti ...
Circular Motion
... tied at the end of a string and Let us find the minimum velocity the body whirled in a vertical circle of should possess at the lowest point in order to just loop the vertical circle. A/Q to radius r. let v1 and v2 be the principle of conservation of energy, velocities of the body and T and T be t ...
... tied at the end of a string and Let us find the minimum velocity the body whirled in a vertical circle of should possess at the lowest point in order to just loop the vertical circle. A/Q to radius r. let v1 and v2 be the principle of conservation of energy, velocities of the body and T and T be t ...
Proficiency Review
... A. When a magnetic field changes an electric current will be induced. B. Magnets are needed for an electrical current to flow through wires. C. High voltage is needed to transfer electric current long distances. D. A higher voltage is needed to run large appliances than small ones. ...
... A. When a magnetic field changes an electric current will be induced. B. Magnets are needed for an electrical current to flow through wires. C. High voltage is needed to transfer electric current long distances. D. A higher voltage is needed to run large appliances than small ones. ...
Practice final exam.
... Solution: Yes, the condition of equilibrium is the all of the net forces and all of the net torques is equal to zero. If an object is in motion at a constant speed and constant direction, and/or is rotating at a constant rate, then that means there is no linear or angular acceleration which implies ...
... Solution: Yes, the condition of equilibrium is the all of the net forces and all of the net torques is equal to zero. If an object is in motion at a constant speed and constant direction, and/or is rotating at a constant rate, then that means there is no linear or angular acceleration which implies ...
Centripetal Acceleration
... 6. Measure the time for 20 revs 3 times and calculate the average period. 7. Calculate the radial acceleration ar using the average period. 8. Calculate the net force Fnet. Part 2 (Static Equilibrium – Diagram 2) 1. Leave the spring attached to mass Mbob. 2. Attach string with hanger to mass Mbob. 3 ...
... 6. Measure the time for 20 revs 3 times and calculate the average period. 7. Calculate the radial acceleration ar using the average period. 8. Calculate the net force Fnet. Part 2 (Static Equilibrium – Diagram 2) 1. Leave the spring attached to mass Mbob. 2. Attach string with hanger to mass Mbob. 3 ...
MYP FORM 3 term 1 term 2
... Describe the experimental procedure that occurs, in terms of the extension produced when load is added and plot extension/load graphs. Explain and interpret extension/load graphs Explain Hooke’s Law and recall and use the expression F = k x Recognize the significance of the term ‘limit of propo ...
... Describe the experimental procedure that occurs, in terms of the extension produced when load is added and plot extension/load graphs. Explain and interpret extension/load graphs Explain Hooke’s Law and recall and use the expression F = k x Recognize the significance of the term ‘limit of propo ...
Phys 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... How much force is needed to keep the box moving at a constant velocity across the floor? ...
... How much force is needed to keep the box moving at a constant velocity across the floor? ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... Questions of Yesterday 1) You are going through a vertical loop on roller coaster at a constant speed. At what point is the force exerted by the tracks on you (and the cart you are in) the greatest? a) at the highest point b) at the lowest point c) halfway between the highest and lowest point d) th ...
... Questions of Yesterday 1) You are going through a vertical loop on roller coaster at a constant speed. At what point is the force exerted by the tracks on you (and the cart you are in) the greatest? a) at the highest point b) at the lowest point c) halfway between the highest and lowest point d) th ...
Link Segment Model & Inverse Dynamics
... Law of Inertia: A body at rest stays at rest and a body in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a force or torque. Law of Acceleration: The acceleration a body experiences is directly proportional to the force or torque, inversely proportional to the mass or moment of inertia and occurs in th ...
... Law of Inertia: A body at rest stays at rest and a body in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a force or torque. Law of Acceleration: The acceleration a body experiences is directly proportional to the force or torque, inversely proportional to the mass or moment of inertia and occurs in th ...
Statics-introduction
... You and the chair you are sitting on would be a nice example, your ear being attached to your head and not falling off would be another. Field Forces which may be due to gravitation, electro-static,electro-magnetic or nuclear interactions. No contact between the involved bodies is necessary. Actuall ...
... You and the chair you are sitting on would be a nice example, your ear being attached to your head and not falling off would be another. Field Forces which may be due to gravitation, electro-static,electro-magnetic or nuclear interactions. No contact between the involved bodies is necessary. Actuall ...
Homework Week 9 Question 1. Potential of non-uniformly charged sphere
... a. Suppose that on the surface of a sphere of radius R there is a surface charge density σ(θ) = σ0 cos2 θ, where σ0 is a constant. What is V (r, θ) inside and outside the sphere? What is the electric field E(r, θ) inside and outside the sphere? Confirm that the field is discontinuous at the surface ...
... a. Suppose that on the surface of a sphere of radius R there is a surface charge density σ(θ) = σ0 cos2 θ, where σ0 is a constant. What is V (r, θ) inside and outside the sphere? What is the electric field E(r, θ) inside and outside the sphere? Confirm that the field is discontinuous at the surface ...
Circular Motion Centripetal Force MC
... magnitude of the gravitational force they exert on each one is F. The masses are changed to 2m and 2M, and the distance is changed to 4r. What is the magnitude of the new gravitational force? A) 4F B) 16F C) F/2 D) F/4 E) F/16 14) Two small objects, with masses m and M, are originally a distance r a ...
... magnitude of the gravitational force they exert on each one is F. The masses are changed to 2m and 2M, and the distance is changed to 4r. What is the magnitude of the new gravitational force? A) 4F B) 16F C) F/2 D) F/4 E) F/16 14) Two small objects, with masses m and M, are originally a distance r a ...
Dynamics of Rotational Motion
... his goal? (This period gives Superman time to devote to other villains.) ...
... his goal? (This period gives Superman time to devote to other villains.) ...
torque and circular motion - PHYSICS I PRE-AP
... OF A BOOK. EX: EARTH LAYERS DURING A QUAKE. STRETCHING OR COMPRESSING FORCES. EX: BALLOON, STRING BULK FORCES – APPLIES TO FLUIDS. PRESSURE FROM ALL SIDES CAN CAUSE A VOLUME CHANGE. ...
... OF A BOOK. EX: EARTH LAYERS DURING A QUAKE. STRETCHING OR COMPRESSING FORCES. EX: BALLOON, STRING BULK FORCES – APPLIES TO FLUIDS. PRESSURE FROM ALL SIDES CAN CAUSE A VOLUME CHANGE. ...
Experiment 1G Uniform Circular Motion
... By substituting this for v in the equation for centripetal force, we arrive at formula (1): ...
... By substituting this for v in the equation for centripetal force, we arrive at formula (1): ...
Gravitation
... Why does one object exert a gravitational attractive force on another object? (a) Why does m1 attract m2? (b) Why does m2 attract m1? These are different questions and require different answers. Let us consider an analogy first: consider a girl wearing some expensive perfume. This material gives the ...
... Why does one object exert a gravitational attractive force on another object? (a) Why does m1 attract m2? (b) Why does m2 attract m1? These are different questions and require different answers. Let us consider an analogy first: consider a girl wearing some expensive perfume. This material gives the ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.