Lecture 5: Planetary system formation theories o Topics to be covered:
... Jeans’ Theory involved interaction between Sun and a very massive star in three stages: 1. Massive star passes within Roche Limit of Sun, pulling out material in the form of a filament. 2. Filament is gravitationally unstable, and breaks into series of blobs of masses greater than the Jeans’ criti ...
... Jeans’ Theory involved interaction between Sun and a very massive star in three stages: 1. Massive star passes within Roche Limit of Sun, pulling out material in the form of a filament. 2. Filament is gravitationally unstable, and breaks into series of blobs of masses greater than the Jeans’ criti ...
Physical Science Review
... Gravitational field is affected by distance and mass. More distance less force. More mass more force. Electric field is affected by distance. The farther away the charge, the less force. In electric field, the opposite charges attract. Like charges repel Magnetic field is affected by distance ...
... Gravitational field is affected by distance and mass. More distance less force. More mass more force. Electric field is affected by distance. The farther away the charge, the less force. In electric field, the opposite charges attract. Like charges repel Magnetic field is affected by distance ...
Gravitational Force Name: Date: 1. What is the
... The net force on a planet is due primarily to the other planets and the Sun. By taking into account all the forces acting on a planet, investigators calculated the orbit of each planet. A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It appeare ...
... The net force on a planet is due primarily to the other planets and the Sun. By taking into account all the forces acting on a planet, investigators calculated the orbit of each planet. A small discrepancy between the calculated orbit and the observed orbit of the planet Uranus was noted. It appeare ...
Gravitation and Rotational Motion
... 3. Kepler’s 3rd LawT is equivalent to the period of a planet revolving around the Sun, and r is the average distance from the sun. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: this says that objects attract other objects with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely propor ...
... 3. Kepler’s 3rd LawT is equivalent to the period of a planet revolving around the Sun, and r is the average distance from the sun. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation: this says that objects attract other objects with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely propor ...
Microsoft Powerpoint
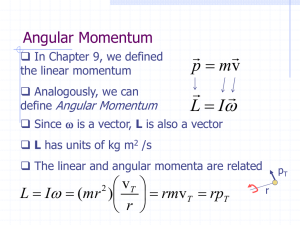
... Method: Apply Conservation of Angular Momentum. The gravitational force due to the Earth keeps the satellite in orbit, but that force as a line of action through the center of the orbit, which is the rotation axis of the satellite. Therefore, the satellite experiences no external torques. ...
... Method: Apply Conservation of Angular Momentum. The gravitational force due to the Earth keeps the satellite in orbit, but that force as a line of action through the center of the orbit, which is the rotation axis of the satellite. Therefore, the satellite experiences no external torques. ...
chapter 6
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation • Always attractive. • Directly proportional to the masses involved. • Inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the masses. • Masses must be large to bring Fg to a size even close to humanly perceptible forces. ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravitation • Always attractive. • Directly proportional to the masses involved. • Inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the masses. • Masses must be large to bring Fg to a size even close to humanly perceptible forces. ...
Circular Motion
... average orbital distance of the Earth. Knowing that the Earth orbits the sun in approximately 365 days, use Kepler’s law of harmonies to predict the time for Mars to orbit the sun. ...
... average orbital distance of the Earth. Knowing that the Earth orbits the sun in approximately 365 days, use Kepler’s law of harmonies to predict the time for Mars to orbit the sun. ...
Universal Gravitation
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that gravity is universal and that all objects attract each other with some force of gravitational attraction ...
... Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation states that gravity is universal and that all objects attract each other with some force of gravitational attraction ...
Newton`s Law of Universal Gravitation
... between two massive objects: Increases as the mass of the objects increases. Decreases as the distance between the objects ...
... between two massive objects: Increases as the mass of the objects increases. Decreases as the distance between the objects ...
PHYSICS 218
... geosynchronous orbit. What is the highest latitude on Earth’s surface that can receive line-of-sight signals from such satellites? The universal constant of gravitation is 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2. The mass of the earth is 6 x 1024 kg. Hint: you don’t need these, only g and the radius of the Earth, 640 ...
... geosynchronous orbit. What is the highest latitude on Earth’s surface that can receive line-of-sight signals from such satellites? The universal constant of gravitation is 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/kg2. The mass of the earth is 6 x 1024 kg. Hint: you don’t need these, only g and the radius of the Earth, 640 ...
Physics 122 – Review Sheets
... You swing a yo-yo, with a mass of 225 g, in a vertical circle. The string has a length of 1.2 m. a. What is the minimum speed at which you can swing the yo-yo? (3.4 m/s) b. What is the tension of the string at the top and bottom of the circle at this speed? (0N, 4.4 N) ...
... You swing a yo-yo, with a mass of 225 g, in a vertical circle. The string has a length of 1.2 m. a. What is the minimum speed at which you can swing the yo-yo? (3.4 m/s) b. What is the tension of the string at the top and bottom of the circle at this speed? (0N, 4.4 N) ...
Forces and Energy Summary Sheet File
... When an object moves through the air the air causes both a resistance and a friction force. When the driving force and the air resistive forces become balanced there is no resultant force and the object moves with a terminal velocity. Objects falling through the air fall due the force of gravity. Th ...
... When an object moves through the air the air causes both a resistance and a friction force. When the driving force and the air resistive forces become balanced there is no resultant force and the object moves with a terminal velocity. Objects falling through the air fall due the force of gravity. Th ...
Newton`s Law of Universal
... The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is accepted at 9.8 m/s2 toward the center of the Earth. This can be derived using Newton’s Law of Gravitation. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law ...
... The acceleration due to gravity on Earth is accepted at 9.8 m/s2 toward the center of the Earth. This can be derived using Newton’s Law of Gravitation. Apply Newton’s 2nd Law ...
Chapter 13: universal gravitation
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Newton’s law of universal gravitation: every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
... Newton’s law of universal gravitation Newton’s law of universal gravitation: every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
Slide 1
... shaft with a number of horizontal arms attached at its upper end. Each arm supports a seat suspended from a 5 m long cable, the upper end of which is fastened to the arm at a point 3m from the central shaft. Find the time of one revolution of the swing if the cable supporting the seat makes an angle ...
... shaft with a number of horizontal arms attached at its upper end. Each arm supports a seat suspended from a 5 m long cable, the upper end of which is fastened to the arm at a point 3m from the central shaft. Find the time of one revolution of the swing if the cable supporting the seat makes an angle ...
SI Physics 221
... height of 2 meters, and is traveling at a velocity of 80m/s how far does it travel before it hits the ground? Review Questions: 5) You wish to launch a satellite into space, and you want the satellite to orbit the earth at a distance of 8x103km from its surface. How fast must you launch the satellit ...
... height of 2 meters, and is traveling at a velocity of 80m/s how far does it travel before it hits the ground? Review Questions: 5) You wish to launch a satellite into space, and you want the satellite to orbit the earth at a distance of 8x103km from its surface. How fast must you launch the satellit ...
ECaliz.com Gravitation
... The planets travel in circular orbits (actually they are elliptical) about the sun. Moons and other satellites travel in circular orbits around planets. In all cases the force causing the centripetal acceleration is the force of gravity. ...
... The planets travel in circular orbits (actually they are elliptical) about the sun. Moons and other satellites travel in circular orbits around planets. In all cases the force causing the centripetal acceleration is the force of gravity. ...
File
... Earth at a rate of 9.8m/s2 regardless of their mass and assuming there is no air resistance. The force of gravity can be found two different ways depending on the location of the object relative to Earth. Near the surface F=mg where rearranging for g, we get g=F/m. Therefore a m/s2 is equivalent ...
... Earth at a rate of 9.8m/s2 regardless of their mass and assuming there is no air resistance. The force of gravity can be found two different ways depending on the location of the object relative to Earth. Near the surface F=mg where rearranging for g, we get g=F/m. Therefore a m/s2 is equivalent ...
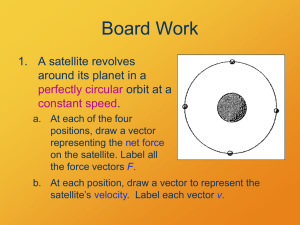
Gravity - barransclass
... a. At each of the four positions, draw a vector representing the net force on the satellite. Label all the force vectors F. b. At each position, draw a vector to represent the satellite’s velocity. Label each vector v. ...
... a. At each of the four positions, draw a vector representing the net force on the satellite. Label all the force vectors F. b. At each position, draw a vector to represent the satellite’s velocity. Label each vector v. ...
gravity ppt - District 196
... As you go further away from the earth’s surface the acceleration due to gravity _decreases____. Two equations for gravitational force F = ma becomes Fg = mg and Fg = G (m1m2) r2 We can set them equal to each other: ...
... As you go further away from the earth’s surface the acceleration due to gravity _decreases____. Two equations for gravitational force F = ma becomes Fg = mg and Fg = G (m1m2) r2 We can set them equal to each other: ...
1.3, 1.4
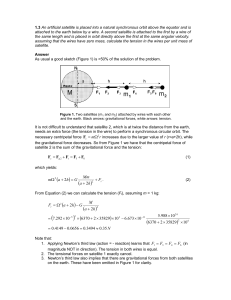
... the same length and is placed in orbit directly above the first at the same angular velocity. assuming that the wires have zero mass, calculate the tension in the wires per unit mass of satellite. Answer As usual a good sketch (Figure 1) is >50% of the solution of the problem. ...
... the same length and is placed in orbit directly above the first at the same angular velocity. assuming that the wires have zero mass, calculate the tension in the wires per unit mass of satellite. Answer As usual a good sketch (Figure 1) is >50% of the solution of the problem. ...
Wizard Test Maker
... following would be the same for objects of equal mass on the surfaces of the two planets? I. The rate at which each would fall freely. II. The amount of force needed to cause a given horizontal acceleration. III. The amount that each of them would stretch a spring that was held vertically. (A) I onl ...
... following would be the same for objects of equal mass on the surfaces of the two planets? I. The rate at which each would fall freely. II. The amount of force needed to cause a given horizontal acceleration. III. The amount that each of them would stretch a spring that was held vertically. (A) I onl ...
Chapter 12
... longer by ~1 second/century and the distance between the Earth and Moon is increasing. There is evidence for this in the fossil record on Earth ...
... longer by ~1 second/century and the distance between the Earth and Moon is increasing. There is evidence for this in the fossil record on Earth ...
F=ma(5) - University of Michigan
... 5. (8 points) In introductory physics one learns the formula F = ma, connecting the force on an object, F , with the mass of the object and the acceleration that the object experiences under the force. One also learns the formula p = mv where p is the momentum of an object, m is the mass, and v is t ...
... 5. (8 points) In introductory physics one learns the formula F = ma, connecting the force on an object, F , with the mass of the object and the acceleration that the object experiences under the force. One also learns the formula p = mv where p is the momentum of an object, m is the mass, and v is t ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.