Chapter 14 THE LAW OF GRAVITY
... In this chapter we study the law of gravity. Emphasis is placed on describing the motion of the planets, because astronomical data provide an important test of the validity of the law of gravity. We show that the laws of planetary motion developed by Johannes Kepler follow from the law of gravity an ...
... In this chapter we study the law of gravity. Emphasis is placed on describing the motion of the planets, because astronomical data provide an important test of the validity of the law of gravity. We show that the laws of planetary motion developed by Johannes Kepler follow from the law of gravity an ...
Quiz Suppose a particle of mass m is attracted to the origin with a
... end of a string of length L. The string will break if the tension in it exceeds a critical value, Tc. What is the largest constant angular velocity the ball can have without breaking the string? ...
... end of a string of length L. The string will break if the tension in it exceeds a critical value, Tc. What is the largest constant angular velocity the ball can have without breaking the string? ...
Class 11
... You have sphere of uniform charge. (The charge is spread out evenly throughout the sphere.) The charge is Q. The radius is R. •What is the Electric Field strength at point A where the distance from A to the center of the sphere is r A (rA > R). ...
... You have sphere of uniform charge. (The charge is spread out evenly throughout the sphere.) The charge is Q. The radius is R. •What is the Electric Field strength at point A where the distance from A to the center of the sphere is r A (rA > R). ...
THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT
... 5. What is the work done by gravity in bringing a 150-kg mass from very far away to the center of the configuration? 5. _________________ ...
... 5. What is the work done by gravity in bringing a 150-kg mass from very far away to the center of the configuration? 5. _________________ ...
Physics 101 Fall 02
... ie to make one complete revolution: T=2 R/v Physics 101: Lecture 11, Pg 2 ...
... ie to make one complete revolution: T=2 R/v Physics 101: Lecture 11, Pg 2 ...
PDF file
... Apparent weight in a satellite is zero just as in a free falling elevator : Person and scale fall with the same acceleration towards the center of earth => they cannot push against each other. z Artificial gravity: In a rotating space laboratory a push on a persons feet equal to mg can be simulated ...
... Apparent weight in a satellite is zero just as in a free falling elevator : Person and scale fall with the same acceleration towards the center of earth => they cannot push against each other. z Artificial gravity: In a rotating space laboratory a push on a persons feet equal to mg can be simulated ...
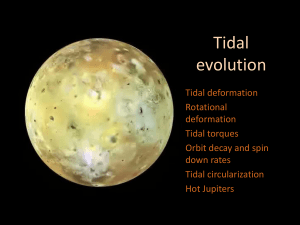
The Rings and Moons of the Outer Planets
... • A satellite gets stretched by the tidal force as it nears the planet • In principle, a large enough tidal force could break satellite apart, although that would be an extreme case • A collision inside Roche limit would result in many small pieces that cannot coalesce because of the tidal force. ...
... • A satellite gets stretched by the tidal force as it nears the planet • In principle, a large enough tidal force could break satellite apart, although that would be an extreme case • A collision inside Roche limit would result in many small pieces that cannot coalesce because of the tidal force. ...
Worksheet "Universal Gravitation"
... (17) If the distance between 2 objects is doubled and the mass of one of the objects is tripled, the gravitational force between the 2 objects will _______________________________________ (18) An object whose weight is 20 N at the surface of the earth is moved to an altitude where its weight is ...
... (17) If the distance between 2 objects is doubled and the mass of one of the objects is tripled, the gravitational force between the 2 objects will _______________________________________ (18) An object whose weight is 20 N at the surface of the earth is moved to an altitude where its weight is ...
student handout
... energy of an object to its position from Earth since ‘g’ is NOT constant as you move away from Earth. All previous problems dealt with objects ‘close’ to the earth where changes in ‘g’ were negligible. ...
... energy of an object to its position from Earth since ‘g’ is NOT constant as you move away from Earth. All previous problems dealt with objects ‘close’ to the earth where changes in ‘g’ were negligible. ...
Gravitational and electric fields
... Take G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2 and o = 8.84x10-12 Fm-1 1. State one way in which : (a) electric fields are similar to gravitational fields (b) one way in which they differ 2. Draw diagrams showing the gravitational field of the earth when viewed from: (a) a large distance away (b) close to the earth's ...
... Take G = 6.67x10-11 Nm2kg-2 and o = 8.84x10-12 Fm-1 1. State one way in which : (a) electric fields are similar to gravitational fields (b) one way in which they differ 2. Draw diagrams showing the gravitational field of the earth when viewed from: (a) a large distance away (b) close to the earth's ...
homeworklesson4.26.2012
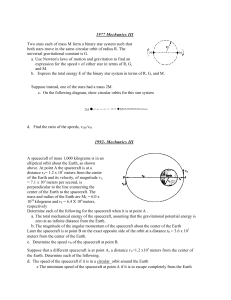
... elliptical orbit about the Earth, as shown above. At point A the spacecraft is at a distance rA= 1.2 x 107 meters from the center of the Earth and its velocity, of magnitude vA = 7.1 x 103 meters per second, is perpendicular to the line connecting the center of the Earth to the spacecraft. The mass ...
... elliptical orbit about the Earth, as shown above. At point A the spacecraft is at a distance rA= 1.2 x 107 meters from the center of the Earth and its velocity, of magnitude vA = 7.1 x 103 meters per second, is perpendicular to the line connecting the center of the Earth to the spacecraft. The mass ...
doc - RPI
... ___ 8. The textbook used in Physics I this semester (Fall 1999) is: A. “PHYSICS”, by Holliday, Resnick, and Krane. A. “PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS”, by Halliday, Redneck, and Walker. A. “INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS”, by Casabella, Cummings, and Wagner. A. “FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS”, by Halliday, Resnick, and W ...
... ___ 8. The textbook used in Physics I this semester (Fall 1999) is: A. “PHYSICS”, by Holliday, Resnick, and Krane. A. “PRINCIPLES OF PHYSICS”, by Halliday, Redneck, and Walker. A. “INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS”, by Casabella, Cummings, and Wagner. A. “FUNDAMENTALS OF PHYSICS”, by Halliday, Resnick, and W ...
Speeding up and slowing down
... 1. If the force of a hockey stick on a hockey ball is 200N what is the force of the ball on the stick? (Give both the size and the direction compared with the stick on the ball) ...
... 1. If the force of a hockey stick on a hockey ball is 200N what is the force of the ball on the stick? (Give both the size and the direction compared with the stick on the ball) ...
Electric and gravitational fields
... 2. Draw diagrams showing the gravitational field of the Earth when viewed from: (a) a large distance away (b) close to the Earth's surface (c) over an area of high density rock 3. The gravitational field of the Earth is 10 Nkg-1. What would the field strength be at a distance above the Earth's surfa ...
... 2. Draw diagrams showing the gravitational field of the Earth when viewed from: (a) a large distance away (b) close to the Earth's surface (c) over an area of high density rock 3. The gravitational field of the Earth is 10 Nkg-1. What would the field strength be at a distance above the Earth's surfa ...
hp1f2013_class05_NewtonsLawsApplications
... Activity: Application The Spinning Terror ride The spinning terror is a large vertical drum which spins so fast that everyone stays pinned to the wall when the floor drops out. For a typical ride the radius of the drum is 2 m. What is the minimum angular velocity if the coefficient of friction betw ...
... Activity: Application The Spinning Terror ride The spinning terror is a large vertical drum which spins so fast that everyone stays pinned to the wall when the floor drops out. For a typical ride the radius of the drum is 2 m. What is the minimum angular velocity if the coefficient of friction betw ...
Homework #5 Solutions Astronomy 10, Section 2 due: Wednesday
... gravitational attraction between the Earth and the shuttle keeps the shuttle in orbit. We generally use the word “weight” to refer to the gravitational force. Here, the astronaut is effectively in free fall. Therefore, there is no floor to push back on his feet and he feels weight-less even though t ...
... gravitational attraction between the Earth and the shuttle keeps the shuttle in orbit. We generally use the word “weight” to refer to the gravitational force. Here, the astronaut is effectively in free fall. Therefore, there is no floor to push back on his feet and he feels weight-less even though t ...
Solutions for Homework #3, ASTR 314, Spring 2013
... The angular rotation rate of the Earth is |Ω| and we are given that |~v | = 25 m/s. The cross product above gives a = 2vΩ sin θ, where theta = 90◦ − ℓ where ℓ is the latitude (i.e., at the equator, ℓ = 0◦ , the coriolis force of an object moving directly N would be zero). The acceleration is therefo ...
... The angular rotation rate of the Earth is |Ω| and we are given that |~v | = 25 m/s. The cross product above gives a = 2vΩ sin θ, where theta = 90◦ − ℓ where ℓ is the latitude (i.e., at the equator, ℓ = 0◦ , the coriolis force of an object moving directly N would be zero). The acceleration is therefo ...
gravitation-1 - Physics Point in Gurgaon
... The radius of the earth is reduced by 4%. The mass of the earth remains unchanged. What will be the change in escape velocity? Satellite A is in a certain circular orbit about a planet, while satellite B is in a larger circular orbit. Which satellite has (i) the longer period and (ii) the greater sp ...
... The radius of the earth is reduced by 4%. The mass of the earth remains unchanged. What will be the change in escape velocity? Satellite A is in a certain circular orbit about a planet, while satellite B is in a larger circular orbit. Which satellite has (i) the longer period and (ii) the greater sp ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.