* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet "Universal Gravitation"
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
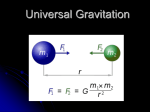
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
2016-17 Universal Gravitation (1) Two objects of fixed mass are moved apart so that they are separated by three times their original distance. Compared to the original gravitational force between them, the new gravitational force is (a) 1/3 as great (b) 1/9 as great (c) 3 times greater (d) 9 times greater (2) A 50-kg student, standing on the surface of the Earth, attracts the Eart with a force closest to (a) 0 Newtons (b) 5 Newtons (c) 50 Newtons (d) 500 Newtons (3) A distance of 1 meter separates 2 equally sized point masses. If one mass is doubled, the gravitational force between the 2 masses would be (a) ½ as great (b) 2 times greater (c) ¼ as great (d) 4 times greater (4) A space probe has a mass of 5.0 kg on the surface of the Earth. What is its mass when placed at a location where the gravitational acceleration is 2.0 m/s2? _______ (5) An astronaut has a mass of 60 kg. and a weight of 12 N in a particular location in space. What is the acceleration due to gravity at that location? _______ (6) Planet X has twice the mass of Earth and twice the radius of Earth. If your weight on Earth is 500 N, what would be your weight on planet X? (a) 50 N (b) 250 N (c) 500 N (d) 1 x 103 N (7) An imaginary star Z has 1/5 the radius of Earth, but 1000 times the Earth’s mass. How much would a mass weighing 1.0 N on Earth weigh on Start Z? (a) 1/5000 N (b) 200 N (c) 5000 N (d) 25,000 N (8) If a satellite moves in a circular orbit around a planet, the satellite would have a constant (a) Displacement (b) velocity (c) speed (d) acceleration (9) The gravitational force of attraction between two objects would be increases by (a) Doubling the mass of both objects, only (b) Doubling the distance between the objects, only (c) Doubling that mass of the objects and doubling the distance between the objects (d) Doubling the mass of one object and doubling the distance between the objects 2016-17 (10) For each of the following changes, indicate by what factor the gravitational force increases or decreases (example: increases by factor of 3 or decreases by factor of 4) (a) the distance between centers is quadrupled _____________________ (b) one mass is made 5 times larger _____________________ (c) one mass is decreased to 1/3 its original size _____________________ (d) one mass is doubled and the other is tripled _____________________ (e) both masses and the distance are all doubled _____________________ (11) The gravitational force between two objects is 60 N. Determine the gravitational force if: (a) one of the masses is tripled __________ (b) one of the masses is halved __________ (c) the distance between their centers is tripled __________ (d) the distance between their centers is halved __________ (e) the distance between their centers is doubled __________ (f) one mass if made 1/3 as large while the other mass is made 4 times as large __________ (g) both masses are doubled __________ (h) both masses are tripled and the distance between their centers is tripled __________ (12) If the distance between a spaceship and the center of the earth is increased from one Earth radius to four Earth radii, the gravitational force acting on the spaceship becomes approximately (a) 1/16 as great (b) 16 times greater (c) ¼ as great (d) 4 times greater (13) Which graph best represents the relationship between the gravitational force and the distance between two masses? (a) (b) (c) (d) 2016-17 (14) Two mass, m1 = 2.5 kg and m2 = 5.5 kg, are located so that their centers are 4.8 meters apart. Calculate the gravitational attraction between them. (15) Calculate the gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon (16) Calculate the gravitational force between the Earth and the Sun (17) If the distance between 2 objects is doubled and the mass of one of the objects is tripled, the gravitational force between the 2 objects will _______________________________________ (18) An object whose weight is 20 N at the surface of the earth is moved to an altitude where its weight is now 10 N. The acceleration due to gravity at this position would be ___________ (19) A rocket weighs 10,000 N on the surface of the earth. If the rocket rises to an altitude equal to the radius of the earth, its weight will be (a) 2,500 N (b) 5,000 N (c) 10,000 N (d) 20,000 N 2016-17 (20) Calculate the force of gravity between an object with a mass of 1000 kg and another object with a mass of 3000 kg when the distance between them is 25 meters. (21) Rearrange the general gravitational equation to solve for m1: (22) A 1200 kg satellite is to be placed into an orbit 15000 km above the surface of the earth: (a) When this satellite travels in a circular path, what kind of force supplies its centripetal force? (b) Calculate the necessary velocity for this satellite to move in this path. (23) A satellite is to be placed into an orbit that allows it to remain stationary relative to a point on the moon (an example of a “geostationary” orbit). In order to do so, it must be placed at a particular altitude (with a particular velocity) so that it moves in a circular orbit with the same period as the rotation of the moon. Calculate this altitude and the corresponding velocity. (the period of rotation of the moon is 27.3 days)