Guess Paper – 2012 Class – IX Subject – Science(Physics
... 1. How much work is done by a force of 10N in moving an object through a distance of 1m in the direction of force? 2. Determine the work done is pushing a cart through a distance of 50 m against the force of friction equal to 150N? 3. A body of mass 10 Kg is displaced through a distance of 2m under ...
... 1. How much work is done by a force of 10N in moving an object through a distance of 1m in the direction of force? 2. Determine the work done is pushing a cart through a distance of 50 m against the force of friction equal to 150N? 3. A body of mass 10 Kg is displaced through a distance of 2m under ...
What is the Centrifugal Force?
... particles in the field, and are thus called centrifugal fertilizers. Their accuracy depends first and foremost on the spacing between the traversals of the spreader. The larger the spacing, the less overlap there is. The amount of overlap largely determines the quality of the fertilizer dispersion t ...
... particles in the field, and are thus called centrifugal fertilizers. Their accuracy depends first and foremost on the spacing between the traversals of the spreader. The larger the spacing, the less overlap there is. The amount of overlap largely determines the quality of the fertilizer dispersion t ...
Notes on Fluid Dynamics These notes are meant for my PHY132
... can show that this result is true for an object of any shape. We will do a number of examples using Archemedes principle in lecture. Fluids in Motion In this introductory class, we will limit our treatment to moving fluids whose density doesn’t change and ones that are at steady state. There are two ...
... can show that this result is true for an object of any shape. We will do a number of examples using Archemedes principle in lecture. Fluids in Motion In this introductory class, we will limit our treatment to moving fluids whose density doesn’t change and ones that are at steady state. There are two ...
File - Meissnerscience.com
... 3. What is the spring constant of an archery bow that is pulled back 0.710 m with a force of 133 N? 4. A physics student, with a mass of 75 kg, is standing on a scale inside an elevator. The scale is calibrated in newtons. What will the scale read if the elevator accelerates upward at 1.7 m/s2? 5. A ...
... 3. What is the spring constant of an archery bow that is pulled back 0.710 m with a force of 133 N? 4. A physics student, with a mass of 75 kg, is standing on a scale inside an elevator. The scale is calibrated in newtons. What will the scale read if the elevator accelerates upward at 1.7 m/s2? 5. A ...
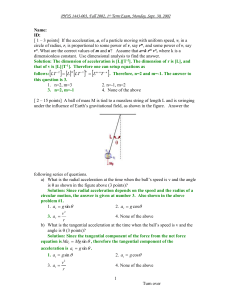
Lesson 12 questions – Centripetal Force - science
... A binary star is a pair of stars that move in circular orbits around their common centre of mass. For stars of equal mass, they move is the same circular orbit, shown by the dotted line in the diagram. In this question, consider the stars to be point masses situated at their centres at opposite ands ...
... A binary star is a pair of stars that move in circular orbits around their common centre of mass. For stars of equal mass, they move is the same circular orbit, shown by the dotted line in the diagram. In this question, consider the stars to be point masses situated at their centres at opposite ands ...
centripetal force - Worth County Schools
... Planets orbit the sun in elliptical orbits. Planets orbiting the sun carve out equal area triangles in equal times. The planet’s year is related to its distance from the sun in a predictable way. ...
... Planets orbit the sun in elliptical orbits. Planets orbiting the sun carve out equal area triangles in equal times. The planet’s year is related to its distance from the sun in a predictable way. ...
PHYSICS 11 – General Physics
... 0.335 kg, calculate the tension in the string when the ball is a) the top of its path , and b) at the bottom of its path. ...
... 0.335 kg, calculate the tension in the string when the ball is a) the top of its path , and b) at the bottom of its path. ...
Torque - University of Toronto Physics
... constant) if the sum of the torques acting on it is zero. An object will be in equilibrium if it is suspended from its center of gravity or its center of gravity is below the suspension point. Elasticity The branch of physics which deals with how objects deform when forces are applied to them. Elast ...
... constant) if the sum of the torques acting on it is zero. An object will be in equilibrium if it is suspended from its center of gravity or its center of gravity is below the suspension point. Elasticity The branch of physics which deals with how objects deform when forces are applied to them. Elast ...
Cutnell/Johnson Physics 7 th edition
... a) The force of the earth on the spaceship and the force of the spaceship on the earth cancel because they are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. b) The spaceship is in free fall and its floor cannot press upwards on the astronauts. c) The centripetal force of the earth on the astronaut i ...
... a) The force of the earth on the spaceship and the force of the spaceship on the earth cancel because they are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. b) The spaceship is in free fall and its floor cannot press upwards on the astronauts. c) The centripetal force of the earth on the astronaut i ...
Short Version : 22. Electric Potential
... Potential difference VAB depends only on positions of A & B. ...
... Potential difference VAB depends only on positions of A & B. ...
Static: PowerPoint Notes
... determined the line of reaction R, a scaled force polygon can be drawn. By measurement, T = 200 N, R = 214 N R = 214 N ...
... determined the line of reaction R, a scaled force polygon can be drawn. By measurement, T = 200 N, R = 214 N R = 214 N ...
9 Torque
... 3. Attach three masses to the meter stick using string. Neglect the masses of the support strings. 4. Attach the force sensor cords to the Interface box as you have done in previous labs. 5. For today's lab you do NOT need to graph the force sensors over time, instead, drag the force icons to the Di ...
... 3. Attach three masses to the meter stick using string. Neglect the masses of the support strings. 4. Attach the force sensor cords to the Interface box as you have done in previous labs. 5. For today's lab you do NOT need to graph the force sensors over time, instead, drag the force icons to the Di ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... A hanging object with mass M will be moved in a circle while attached to a spring. As shown in the diagram, the apparatus is adjusted so the forces on the mass are only vertical or horizontal as it undergoes circular motion. No trigonometry will be needed to break forces into components. We are inte ...
... A hanging object with mass M will be moved in a circle while attached to a spring. As shown in the diagram, the apparatus is adjusted so the forces on the mass are only vertical or horizontal as it undergoes circular motion. No trigonometry will be needed to break forces into components. We are inte ...
Physics 7701: Problem Set #9
... 6. (10 pts) More image charges (Jackson 2.3). A straight-line charge with constant linear charge density λ is located perpendicular to the x–y plane in the first quadrant at (x0 , y0 ). The intersecting planes x = 0, y ≥ 0 and y = 0, x ≥ 0 are conducting boundary surfaces held at zero potential. Con ...
... 6. (10 pts) More image charges (Jackson 2.3). A straight-line charge with constant linear charge density λ is located perpendicular to the x–y plane in the first quadrant at (x0 , y0 ). The intersecting planes x = 0, y ≥ 0 and y = 0, x ≥ 0 are conducting boundary surfaces held at zero potential. Con ...
Phys 7221, Fall 2006: Homework # 4
... (and small) value of the energy which will allow an unstable circular orbit. Positive values of energy smaller than the local maximum allow for either bound orbits, or unbound orbits with a turning point, depending on the initial values of the system. If the angular momentum is small, and the energy ...
... (and small) value of the energy which will allow an unstable circular orbit. Positive values of energy smaller than the local maximum allow for either bound orbits, or unbound orbits with a turning point, depending on the initial values of the system. If the angular momentum is small, and the energy ...
Upgrade Your Physics 1
... and opposite to the force pulling the right brick leftwards. To use more mathematical notation, if the force on block no.1 caused by block no.2 is called f12, then f12=f21. If this were not the case, then if we looked at the bricks together as a whole object, the two internal forces would not cance ...
... and opposite to the force pulling the right brick leftwards. To use more mathematical notation, if the force on block no.1 caused by block no.2 is called f12, then f12=f21. If this were not the case, then if we looked at the bricks together as a whole object, the two internal forces would not cance ...
A2 Fields Part I - Animated Science
... Q11.Gravitational fields and electric fields have many features in common but also have several differences. For both radial and uniform gravitational and electric fields, compare and contrast their common features and their differences. In your answer you should consider: ...
... Q11.Gravitational fields and electric fields have many features in common but also have several differences. For both radial and uniform gravitational and electric fields, compare and contrast their common features and their differences. In your answer you should consider: ...
Force diagrams
... diagram. The main point of this diagram is to make understanding the problem easier. We can draw many types of diagrams in mechanics. Two that will be explained here are: System diagram This is a single diagram of the whole problem. It does not include internal forces, which cancel each other out. F ...
... diagram. The main point of this diagram is to make understanding the problem easier. We can draw many types of diagrams in mechanics. Two that will be explained here are: System diagram This is a single diagram of the whole problem. It does not include internal forces, which cancel each other out. F ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.