A particle of mass `m` is attached to a thin uniform rod of length `a` at
... An artificial satellite of mass ‘m’ is revolving around in a circular orbit of radius ‘r’. If the mass of earth is M, then angular momentum of the satellite with respect to the centre of earth is _______ (G = universal gravitational constant) (EAMCET_2012) ...
... An artificial satellite of mass ‘m’ is revolving around in a circular orbit of radius ‘r’. If the mass of earth is M, then angular momentum of the satellite with respect to the centre of earth is _______ (G = universal gravitational constant) (EAMCET_2012) ...
Chapter 9 MOTION IN FIELDS
... Experiment shows that both the horizontal and vertical drag forces depend on the speed of the projectile. he efect of the horizontal drag will be to foreshorten the range of the projectile and the efect of the vertical drag will be to reduce the maximum height reached by the projectile. However, the ...
... Experiment shows that both the horizontal and vertical drag forces depend on the speed of the projectile. he efect of the horizontal drag will be to foreshorten the range of the projectile and the efect of the vertical drag will be to reduce the maximum height reached by the projectile. However, the ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
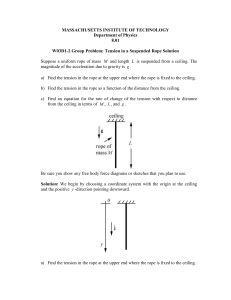
... Suppose a uniform rope of mass M and length L is suspended from a ceiling. The magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is g . a) Find the tension in the rope at the upper end where the rope is fixed to the ceiling. b) Find the tension in the rope as a function of the distance from the ceiling. ...
... Suppose a uniform rope of mass M and length L is suspended from a ceiling. The magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity is g . a) Find the tension in the rope at the upper end where the rope is fixed to the ceiling. b) Find the tension in the rope as a function of the distance from the ceiling. ...
YJC2013 H2 Phy Topic 7 Gravitational field
... In the previous topic 5 on Work, Energy & Power, we have dealt with the calculation of gravitational potential energy (GPE) using the formula, mgh. This formula was applicable in that topic because we were dealing with situations where the height (measured from a certain reference level decided by y ...
... In the previous topic 5 on Work, Energy & Power, we have dealt with the calculation of gravitational potential energy (GPE) using the formula, mgh. This formula was applicable in that topic because we were dealing with situations where the height (measured from a certain reference level decided by y ...
ME 101: Engineering Mechanics
... Kinematics of Particles: Rectilinear motion, curvilinear motion rectangular, normal tangential, polar, cylindrical, spherical (coordinates), relative and constrained motion, space curvilinear motion. Kinetics of Particles: Force, mass and acceleration, work and energy, impulse and momentum, impact. ...
... Kinematics of Particles: Rectilinear motion, curvilinear motion rectangular, normal tangential, polar, cylindrical, spherical (coordinates), relative and constrained motion, space curvilinear motion. Kinetics of Particles: Force, mass and acceleration, work and energy, impulse and momentum, impact. ...
Newton`s Principia-selection of results
... each other by a force inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. Prop. 84: To find the force with which a body is attracted by a segment of a sphere, when it is located along the axis of the segment, beyond the center of the sphere. SECTION 13: ATTRACTIVE FORCES OF N ...
... each other by a force inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. Prop. 84: To find the force with which a body is attracted by a segment of a sphere, when it is located along the axis of the segment, beyond the center of the sphere. SECTION 13: ATTRACTIVE FORCES OF N ...
Conservation of mass and momentum
... flow as steady in time, it is necessary to supply a larger pressure at station 1 than at station 2. Bernoulli’s theorem captures this creation of momentum elegantly, but ultimately the physics comes down to pressure differences accelerating fluid ...
... flow as steady in time, it is necessary to supply a larger pressure at station 1 than at station 2. Bernoulli’s theorem captures this creation of momentum elegantly, but ultimately the physics comes down to pressure differences accelerating fluid ...
Centrifugation - UniMAP Portal
... At the end of the residence time of the particle in the fluid, the particle is at a distance rB m from the axis of rotation. If rB
... At the end of the residence time of the particle in the fluid, the particle is at a distance rB m from the axis of rotation. If rB
Mass Relationships of Atoms
... Compute the moles of product formed 2 ways (assuming P4 is completely consumed and then assuming I2 is completely consumed. See which reactant, if used up completely, gives the least amount of product. It’s limiting. ...
... Compute the moles of product formed 2 ways (assuming P4 is completely consumed and then assuming I2 is completely consumed. See which reactant, if used up completely, gives the least amount of product. It’s limiting. ...
Rooney AP Physics - Ch 7 Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • The gravitational force exerted by a uniform sphere on a particle outside the sphere is the same as the force exerted if the entire mass of the sphere were concentrated on its center – This is called Gauss’ Law ...
... • The gravitational force exerted by a uniform sphere on a particle outside the sphere is the same as the force exerted if the entire mass of the sphere were concentrated on its center – This is called Gauss’ Law ...
Rocket Science and Technology, 4363 Motor Ave
... The total contribution from an image vortex is N I N I , just as in the case of an external vortex. Add all four vortex terms, and multiply by 2 (to account for both fin panels) to the total first stage interference normal force. The remaining issue is the center of pressure of the vortex normal; ...
... The total contribution from an image vortex is N I N I , just as in the case of an external vortex. Add all four vortex terms, and multiply by 2 (to account for both fin panels) to the total first stage interference normal force. The remaining issue is the center of pressure of the vortex normal; ...
statics - SlideBoom
... • The center of mass of a regularly shaped, symmetrical body (such as a sphere, a cylinder, a rectangular solid, etc.) of uniform density, is located at the geometric center of the object. • For bodies consisting of several connected points of mass the center of mass can be found by adding the torqu ...
... • The center of mass of a regularly shaped, symmetrical body (such as a sphere, a cylinder, a rectangular solid, etc.) of uniform density, is located at the geometric center of the object. • For bodies consisting of several connected points of mass the center of mass can be found by adding the torqu ...
Student Class ______ Date ______ MULTIPLE
... we cannot say that the mechanical energy of the system is conserved. (If you like to use a formula, you could say that: W=ET, which means that work that you do, equals the increase in the total mechanical energy of the block). If the speed is constant that means the kinetic energy is constant. If h ...
... we cannot say that the mechanical energy of the system is conserved. (If you like to use a formula, you could say that: W=ET, which means that work that you do, equals the increase in the total mechanical energy of the block). If the speed is constant that means the kinetic energy is constant. If h ...
Unit_3_Part_2_Centripetal_Acceleration_Notes
... In the above example, the N is the entire net Fc as that is the only force that is in the direction of the acceleration. You might be tempted to call the Ff the NET force (Fc) as that is what we did in the last example; but in the last example it truly was the friction that was directed toward the c ...
... In the above example, the N is the entire net Fc as that is the only force that is in the direction of the acceleration. You might be tempted to call the Ff the NET force (Fc) as that is what we did in the last example; but in the last example it truly was the friction that was directed toward the c ...
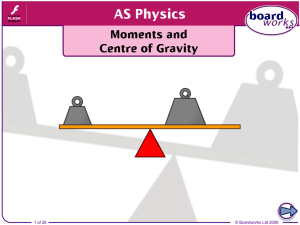
Moments and Centre of Gravity
... moment acts on it. Forces and moments are balanced. Newton’s first law states that a body persists in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force. Bodies in equilibrium are therefore bodies that are at rest or moving at constant velocity (uniform motion). ...
... moment acts on it. Forces and moments are balanced. Newton’s first law states that a body persists in its state of rest or of uniform motion unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force. Bodies in equilibrium are therefore bodies that are at rest or moving at constant velocity (uniform motion). ...
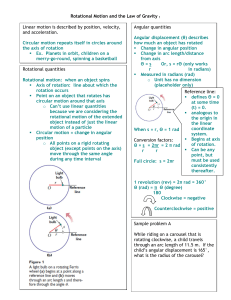
Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular ...
... Units of angular acceleration are rad/s² Positive angular accelerations are in the counterclockwise direction and negative accelerations are in the clockwise direction When a rigid object rotates about a fixed axis, every portion of the object has the same angular speed and the same angular ...
Inverse Square Laws
... 4. Consider these two spheres. They have both Then the teacher rubs a rubber balloon with animal fur and holds been charged. In one case the charge is isolated The stream is observed to deflect from its usual 4. Consider these two spheres. They have both it near theinstream. three distinct locations ...
... 4. Consider these two spheres. They have both Then the teacher rubs a rubber balloon with animal fur and holds been charged. In one case the charge is isolated The stream is observed to deflect from its usual 4. Consider these two spheres. They have both it near theinstream. three distinct locations ...
Conducting Ellipsoid and Circular Disk
... where constant ρ is to be determined from a knowledge of the total charge Q on the conducting ellipsoid. The thickness δd of a thin ellipsoidal shell at some point on its inner surface is the distance between the plane that is tangent to the inner surface at the specified point, and the plane that i ...
... where constant ρ is to be determined from a knowledge of the total charge Q on the conducting ellipsoid. The thickness δd of a thin ellipsoidal shell at some point on its inner surface is the distance between the plane that is tangent to the inner surface at the specified point, and the plane that i ...
Chapter 10 Clickers
... a) When the dog walks, the platform will rotate counterclockwise when viewed from above. b) When the dog walks, the platform will rotate clockwise when viewed from above. ...
... a) When the dog walks, the platform will rotate counterclockwise when viewed from above. b) When the dog walks, the platform will rotate clockwise when viewed from above. ...
Goal: To understand momentum
... • Newton’s First law also applies here. • Something in rotation stays there unless you act upon it. ...
... • Newton’s First law also applies here. • Something in rotation stays there unless you act upon it. ...
Chapter 4 - Newton`s Laws of motion
... Action-at-a-distance forces • The types of forces which result even when the two interacting objects are not in physical contact with each other, yet are able to exert a push or pull despite their physical separation. • Examples of action-at-a-distance forces include – gravitational forces. The sun ...
... Action-at-a-distance forces • The types of forces which result even when the two interacting objects are not in physical contact with each other, yet are able to exert a push or pull despite their physical separation. • Examples of action-at-a-distance forces include – gravitational forces. The sun ...
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity 1 Rotational quantities
... Brahe and used his data for the orbit of Mars. Data only fit if the orbit is an ellipse rather than a circle, with the sun at one focal point of the ellipse. Kepler’s 2nd law shows an imaginary line from the sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times ...
... Brahe and used his data for the orbit of Mars. Data only fit if the orbit is an ellipse rather than a circle, with the sun at one focal point of the ellipse. Kepler’s 2nd law shows an imaginary line from the sun to any planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times ...
Guess Paper – 2012 Class – IX Subject – Science(Physics
... 1. How much work is done by a force of 10N in moving an object through a distance of 1m in the direction of force? 2. Determine the work done is pushing a cart through a distance of 50 m against the force of friction equal to 150N? 3. A body of mass 10 Kg is displaced through a distance of 2m under ...
... 1. How much work is done by a force of 10N in moving an object through a distance of 1m in the direction of force? 2. Determine the work done is pushing a cart through a distance of 50 m against the force of friction equal to 150N? 3. A body of mass 10 Kg is displaced through a distance of 2m under ...
Roche limit
The Roche limit (pronounced /ʁoʃ/ in IPA, similar to the sound of rosh), sometimes referred to as the Roche radius, is the distance within which a celestial body, held together only by its own gravity, will disintegrate due to a second celestial body's tidal forces exceeding the first body's gravitational self-attraction. Inside the Roche limit, orbiting material disperses and forms rings whereas outside the limit material tends to coalesce. The term is named after Édouard Roche, who is the French astronomer who first calculated this theoretical limit in 1848.