File
... 59. The ionization constant, Kb, of the base HONH2 is 1.1 x 108 . The pH of a 1.0 M aqueous soluton of HONH2 is closest to A) 4.0 B) 6.0 C) 8.0 D) 10.0 E) 14.0 60. Which of the following 0.10 M aqueous solutions has a pH less than 7 ? A) KI B) NH4NO3 C) K2CO3 D) NH3 E) Ca(OH)2 61. If 0.15 mol of K2 ...
... 59. The ionization constant, Kb, of the base HONH2 is 1.1 x 108 . The pH of a 1.0 M aqueous soluton of HONH2 is closest to A) 4.0 B) 6.0 C) 8.0 D) 10.0 E) 14.0 60. Which of the following 0.10 M aqueous solutions has a pH less than 7 ? A) KI B) NH4NO3 C) K2CO3 D) NH3 E) Ca(OH)2 61. If 0.15 mol of K2 ...
wind - geophile.net
... it's a giant puddle (or pod) of heated water that sloshes across the Pacific Ocean Similar to an iceberg ...
... it's a giant puddle (or pod) of heated water that sloshes across the Pacific Ocean Similar to an iceberg ...
Powder X-Ray Diffraction
... Fig. 1 Reflection of x-rays from two planes of atoms in a solid. The path difference between two waves: 2x = 2dsin(theta) For constructive interference nλ = 2dsinθ Bragg equation X-ray diffraction has been in use in two main areas, for:1. Fingerprint characterization of crystalline materials and 2. ...
... Fig. 1 Reflection of x-rays from two planes of atoms in a solid. The path difference between two waves: 2x = 2dsin(theta) For constructive interference nλ = 2dsinθ Bragg equation X-ray diffraction has been in use in two main areas, for:1. Fingerprint characterization of crystalline materials and 2. ...
A Study of the Relaxation Dynamics of Local Vibrational Modes... with Hydrogen in Diamond
... A Study of the Relaxation Dynamics of Local Vibrational Modes Associated with Hydrogen in Diamond Hydrogen is abundant in the source gases for the growth of diamond by chemical vapour deposition (CVD). Hydrogen is of considerable experimental and theoretical interest because of its ability to intera ...
... A Study of the Relaxation Dynamics of Local Vibrational Modes Associated with Hydrogen in Diamond Hydrogen is abundant in the source gases for the growth of diamond by chemical vapour deposition (CVD). Hydrogen is of considerable experimental and theoretical interest because of its ability to intera ...
Advanced Physical Chemistry Problems (VIII)
... the century and which will be lost when the web site they were on disappears with my demise. Because these problems are being taken from the web and are being edited, their statements and the hints/answers offered are subject to the typical editorial errors that ensue when such work is undertaken in ...
... the century and which will be lost when the web site they were on disappears with my demise. Because these problems are being taken from the web and are being edited, their statements and the hints/answers offered are subject to the typical editorial errors that ensue when such work is undertaken in ...
Magma ocean influence on early atmosphere composition and mass
... The composition and mass of the atmosphere overlying early terrestrial magma oceans (MOs) likely had a key influence on Earth’s early thermal and dynamical evolution, its geochemical differentiation, its path to an equable climate, and development of prebiotic chemistry. It also set the initial cond ...
... The composition and mass of the atmosphere overlying early terrestrial magma oceans (MOs) likely had a key influence on Earth’s early thermal and dynamical evolution, its geochemical differentiation, its path to an equable climate, and development of prebiotic chemistry. It also set the initial cond ...
Semester 2 Final Exam
... (D) 33.3 g 6. The units for heat are: (A) J (B) J/g (C) J/g·°C (D) J/°C 7. 20.0 gram samples of each of the following metals are originally at 10°C. They are heated evenly for ten minutes. Which metal will have the highest temperature at the end? (A) Aluminum (c = 0.900 J/g·°C) (B) Copper (c = 0.386 ...
... (D) 33.3 g 6. The units for heat are: (A) J (B) J/g (C) J/g·°C (D) J/°C 7. 20.0 gram samples of each of the following metals are originally at 10°C. They are heated evenly for ten minutes. Which metal will have the highest temperature at the end? (A) Aluminum (c = 0.900 J/g·°C) (B) Copper (c = 0.386 ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Words
... Unit 1: Experimental Design – Create vocabulary flash cards for each of the vocabulary words. Be sure to include the word and a picture on the front as well as the definition on the back. Flash card paper will be provided or you can use your own. Standardized units Controlled experiment Independent ...
... Unit 1: Experimental Design – Create vocabulary flash cards for each of the vocabulary words. Be sure to include the word and a picture on the front as well as the definition on the back. Flash card paper will be provided or you can use your own. Standardized units Controlled experiment Independent ...
Earth Science Vocabulary Words
... Unit 1: Experimental Design – Create vocabulary flash cards for each of the vocabulary words. Be sure to include the word and a picture on the front as well as the definition on the back. Flash card paper will be provided or you can use your own. Standardized units Controlled experiment Independent ...
... Unit 1: Experimental Design – Create vocabulary flash cards for each of the vocabulary words. Be sure to include the word and a picture on the front as well as the definition on the back. Flash card paper will be provided or you can use your own. Standardized units Controlled experiment Independent ...
DYNAMIC PLANET I
... • Definition – a motion in a fluid that is caused by heating from below and cooling from above ...
... • Definition – a motion in a fluid that is caused by heating from below and cooling from above ...
Assessment Test Spring 2009- Earth Science
... A. Demonstrate knowledge of and recognize the processes that explain natural earth phenomena. 1. Which process does NOT belong to the water cycle? a. condensation b. soil c. run-off ...
... A. Demonstrate knowledge of and recognize the processes that explain natural earth phenomena. 1. Which process does NOT belong to the water cycle? a. condensation b. soil c. run-off ...
Assessment Test Spring 2009- Earth Science
... A. Demonstrate knowledge of and recognize the processes that explain natural earth phenomena. 1. Which process does NOT belong to the water cycle? a. condensation b. soil c. run-off ...
... A. Demonstrate knowledge of and recognize the processes that explain natural earth phenomena. 1. Which process does NOT belong to the water cycle? a. condensation b. soil c. run-off ...
Practice Unit D Exam - mvhs
... (b) When the balloon described in (a) is cooled further, the volume does not become zero; rather, the gas becomes a liquid or solid. (c) When NH3 gas is introduced at one end of a long tube while HCl gas is introduced simultaneously at the other end, a ring of white ammonium chloride is observed to ...
... (b) When the balloon described in (a) is cooled further, the volume does not become zero; rather, the gas becomes a liquid or solid. (c) When NH3 gas is introduced at one end of a long tube while HCl gas is introduced simultaneously at the other end, a ring of white ammonium chloride is observed to ...
“Honey, I Shrunk the Balloons
... (1) Hold each balloon so that its mouth is above the edge of the jar and the rest of the balloon is inside the jar. (2) Inflate the balloons inside the jar and tie them shut. (3) Mark the balloons just above the rim of each jar. (4) Put one jar inside the freezer for thirty minutes and keep the othe ...
... (1) Hold each balloon so that its mouth is above the edge of the jar and the rest of the balloon is inside the jar. (2) Inflate the balloons inside the jar and tie them shut. (3) Mark the balloons just above the rim of each jar. (4) Put one jar inside the freezer for thirty minutes and keep the othe ...
Watching Plates Move with CORK Observatories
... of the Earth. CORK (Circulation Obviation Retrofit Kit) instrumentation was originally developed to document this flow through observations of temperatures, pressures, and compositions of formation fluids made well after drilling ends. Over the first decade of CORK monitoring experiments installed i ...
... of the Earth. CORK (Circulation Obviation Retrofit Kit) instrumentation was originally developed to document this flow through observations of temperatures, pressures, and compositions of formation fluids made well after drilling ends. Over the first decade of CORK monitoring experiments installed i ...
ME 152 Thermodynamics
... • State - a condition of a system that is fully described by properties • Equilibrium - a state where there are no imbalances due to mechanical, thermal, chemical, or phase effects • State Postulate - gives the number of properties needed to fix the state of a system • Simple Compressible System - a ...
... • State - a condition of a system that is fully described by properties • Equilibrium - a state where there are no imbalances due to mechanical, thermal, chemical, or phase effects • State Postulate - gives the number of properties needed to fix the state of a system • Simple Compressible System - a ...
2nd Semester Final Exam Review
... 3. If a 35.00% solution of NaCl contained 90.0 grams of NaCl, how many grams of water was it dissolved in? 4. How many grams of KBr are needed to make 750.0 ml of a .500 M solution? 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Coll ...
... 3. If a 35.00% solution of NaCl contained 90.0 grams of NaCl, how many grams of water was it dissolved in? 4. How many grams of KBr are needed to make 750.0 ml of a .500 M solution? 5. What is the effect on the number of dissolved particles on: vapor pressure, freezing point, and boiling point? Coll ...
Origin of magma (pg.270-273)
... Magma forms when SOLID rock and minerals, located in the asthenosphere and upper mantle, melt Factors that form magma: • Heat • Pressure • Volatiles (refers to the volatile or reactive components of magma [mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide]) ...
... Magma forms when SOLID rock and minerals, located in the asthenosphere and upper mantle, melt Factors that form magma: • Heat • Pressure • Volatiles (refers to the volatile or reactive components of magma [mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide]) ...
practice test2(Answers)
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... A) The temperature of steam cannot exceed 100°C. B) The temperature of ice remains at 0°C as it melts. C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
1 2016-17 Honors Chemistry Review for the Final Exam Each unit
... What would be the volume of this gas (in liters) if you allowed it to expand to the pressure of the surrounding air (0.974 atm)? Assume temperature remains constant. ...
... What would be the volume of this gas (in liters) if you allowed it to expand to the pressure of the surrounding air (0.974 atm)? Assume temperature remains constant. ...
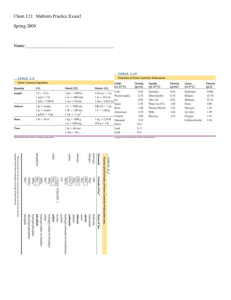
What is inside Jupiter and Saturn? - Physics Illinois
... Invented ~1960 at the National Bureau of Standards ...
... Invented ~1960 at the National Bureau of Standards ...
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... heading south on I-95 one of your tires ruptures. What might have been the possible cause of this? Explain your answer Higher temperature in Florida (and from friction with the road surface) increases the pressure inside the tire. Since the tire has a fixed volume, pressure will increase as temperat ...
... heading south on I-95 one of your tires ruptures. What might have been the possible cause of this? Explain your answer Higher temperature in Florida (and from friction with the road surface) increases the pressure inside the tire. Since the tire has a fixed volume, pressure will increase as temperat ...
Metamorphic rocks
... • Unlike what you may have heard, it’s not just “heat and pressure” applied to existing rocks • Also, not due to partial melting of rocks • What it is: “the solid-state reaction of minerals within the rock to produce new minerals and thus new rocks” ...
... • Unlike what you may have heard, it’s not just “heat and pressure” applied to existing rocks • Also, not due to partial melting of rocks • What it is: “the solid-state reaction of minerals within the rock to produce new minerals and thus new rocks” ...
Chem 1A Practice Final
... 7. A solution is prepared by dissolving 0.115 moles of ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4, in enough water to make 100.0 mL of stock solution. A 11.00 mL sample of this stock solution is added to 50.00 mL of water. Calculate the concentration of ammonium ions in the final solution. a) 1.15 M b) 0.51 M c) ...
... 7. A solution is prepared by dissolving 0.115 moles of ammonium sulfate, (NH4)2SO4, in enough water to make 100.0 mL of stock solution. A 11.00 mL sample of this stock solution is added to 50.00 mL of water. Calculate the concentration of ammonium ions in the final solution. a) 1.15 M b) 0.51 M c) ...
Diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a device used in scientific experiments. It allows compressing a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, which can exceed 600 gigapascals (6,000,000 bars / 6 million atmospheres).The device has been used to recreate the pressure existing deep inside planets, creating materials and phases not observed under normal conditions. Notable examples include the non-molecular ice X, polymeric nitrogen and metallic xenon (an inert gas at lower pressures).A DAC consists of two opposing diamonds with a sample compressed between the culets (tips). Pressure may be monitored using a reference material whose behavior under pressure is known. Common pressure standards include ruby fluorescence, and various structurally simple metals, such as copper or platinum. The uniaxial pressure supplied by the DAC may be transformed into uniform hydrostatic pressure using a pressure transmitting medium, such as argon, xenon, hydrogen, helium, paraffin oil or a mixture of methanol and ethanol. The pressure-transmitting medium is enclosed by a gasket and the two diamond anvils. The sample can be viewed through the diamonds and illuminated by X-rays and visible light. In this way, X-ray diffraction and fluorescence; optical absorption and photoluminescence; Mössbauer, Raman and Brillouin scattering; positron annihilation and other signals can be measured from materials under high pressure. Magnetic and microwave fields can be applied externally to the cell allowing nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and other magnetic measurements. Attaching electrodes to the sample allows electrical and magnetoelectrical measurements as well as heating up the sample to a few thousand degrees. Much higher temperatures (up to 7000 K) can be achieved with laser-induced heating, and cooling down to millikelvins has been demonstrated.