* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Origin of magma (pg.270-273)
Ice-sheet dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Diamond anvil cell wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
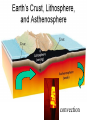
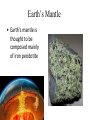
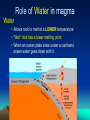
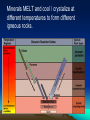
Objectives: the origin of MAGMA 1. Define/describe geothermal gradient and how it applies to rock melting. 2. How does reducing confining pressure change rock’s melting temperature? 3. Decompression melting of rock occurs when rocks (ascend, descend)? Explain. 4. What effect do volatiles (such as water) have on the melting temperature of rock? 5. Do all minerals melt at the same temperature? Explain the partial melting of magma? Bellringer: Review: Name and describe Earth layers. Which layers are solid? Liquid? From which layer does magma originate? A. B. C. D. E. convection Earth’s Mantle • Earth's mantle is thought to be composed mainly of iron peridotite Origin of magma (pg.270-273) Magma forms when SOLID rock and minerals, located in the asthenosphere and upper mantle, melt Factors that form magma: • Heat • Pressure • Volatiles (refers to the volatile or reactive components of magma [mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide]) Role of Heat Earth’s natural temperature increases with depth 20°-30°/ km in the upper crust. (geothermal gradient) In the asthenosphere (60 miles) temps. are 1200°-1400° Yet this is NOT hot enough to melt rock…due to the fact that the pressure at that depth is too great. Role of Pressure Pressure increase with depth. Because of pressure melting must occur at a higher temperature. • Increase in pressure causes an increase in melting temperature • So….DECREASE in pressure can cause decompression melting: • when mantle rock rises, pressure decreases and melting can occur !! • Role of Water in magma Water • Allows rock to melt at a LOWER temperature • “Wet” rock has a lower melting point • When an ocean plate sinks under a continent, ocean water goes down with it. Minerals MELT and cool / crystalize at different temperatures to form different igneous rocks. Origin of magma Partial melting • Rocks are MIXTURES of minerals • Melting occurs over a range of temperatures • Minerals with the lowest melting point melt first producing magmas with a higher silica content than the original rock. (felsic) • Minerals that melt last with higher melting points produce mafic magma (basaltic) – (hot mantle plumes, Hawaiian Islands, basaltic rocks) Different types of magma react differently and give different types of eruptions…