33 C? (1)
... pressure then the liquid will (1) freeze; (2) crystallize; (3) melt; (4) boil. ___ 110. In a closed system, as the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules (1) decreases; (2) increases; (3) remains the same. ___ 111. A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 150 milliliter ...
... pressure then the liquid will (1) freeze; (2) crystallize; (3) melt; (4) boil. ___ 110. In a closed system, as the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules (1) decreases; (2) increases; (3) remains the same. ___ 111. A sample of oxygen gas has a volume of 150 milliliter ...
Final Review Sheet Answers (the 6 page packet)
... Represented above are five identical balloons, each filled to the same volume at 25°C and 1.0 atmosphere pressure with the pure gas indicated. (a) Which balloon contains the greatest mass of gas? Explain. If each balloon is filled to the same volume, Avogadro’s principle says that they will all cont ...
... Represented above are five identical balloons, each filled to the same volume at 25°C and 1.0 atmosphere pressure with the pure gas indicated. (a) Which balloon contains the greatest mass of gas? Explain. If each balloon is filled to the same volume, Avogadro’s principle says that they will all cont ...
IGNEOUS and METAMORPHIC PETROLOGY
... 4. Theories on how these rocks formed Tools of the trade include:1. Field relationships 2. Hammer and hand lens 3. Thin sections and petrological microscope 4. Mineralogy and electron microprobe 5. Major element data 6. Trace element data 7. Isotopic data 8. High pressure and temperature experiments ...
... 4. Theories on how these rocks formed Tools of the trade include:1. Field relationships 2. Hammer and hand lens 3. Thin sections and petrological microscope 4. Mineralogy and electron microprobe 5. Major element data 6. Trace element data 7. Isotopic data 8. High pressure and temperature experiments ...
Nitrogen Contamination in Elastic Neutron
... observed in a measurement, is when exchange gas is used in sample environment equipment. Typically helium is employed as the exchange gas because it remains mobile for thermal conduction purposes at all temperatures (if sufficient helium is present) and has a small neutron cross section. Nevertheles ...
... observed in a measurement, is when exchange gas is used in sample environment equipment. Typically helium is employed as the exchange gas because it remains mobile for thermal conduction purposes at all temperatures (if sufficient helium is present) and has a small neutron cross section. Nevertheles ...
AP Chem Test 5 preview Gases
... A different rigid 5.00 L cylinder contains 0.176 mol of NO(g) at 298 K. A 0.176 mol sample of O2(g) is added to the cylinder, when a reaction occurs to produce NO2. d) Write the balanced equation for the reaction. e) Calculate the total pressure, in atm, in the cylinder at 298 K after the reaction i ...
... A different rigid 5.00 L cylinder contains 0.176 mol of NO(g) at 298 K. A 0.176 mol sample of O2(g) is added to the cylinder, when a reaction occurs to produce NO2. d) Write the balanced equation for the reaction. e) Calculate the total pressure, in atm, in the cylinder at 298 K after the reaction i ...
Chapter 6 notes 2015
... Ideal Gas Equation Gas Laws are only exact for ideal gases. ideal gas – an imaginary gas is made up of particles having mass, no volume, and no attractive forces acting between them.(point masses) ...
... Ideal Gas Equation Gas Laws are only exact for ideal gases. ideal gas – an imaginary gas is made up of particles having mass, no volume, and no attractive forces acting between them.(point masses) ...
AP Chemistry Unit 3 Test Review Topics Covered: Gases Liquids
... INVOLVED IN ARRIVING AT YOUR ANSWERS. It is to your advantage to do this, because you may earn partial credit if you do and you will receive little or no credit if you do not. Attention should be paid to significant figures. Be sure to write all your answers to the questions on the lined pages follo ...
... INVOLVED IN ARRIVING AT YOUR ANSWERS. It is to your advantage to do this, because you may earn partial credit if you do and you will receive little or no credit if you do not. Attention should be paid to significant figures. Be sure to write all your answers to the questions on the lined pages follo ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 8. If some of the gas bubbles from the reaction had escaped out the bottom of the tube, how would this have affected your molar volume at STP? Explain. ...
... 8. If some of the gas bubbles from the reaction had escaped out the bottom of the tube, how would this have affected your molar volume at STP? Explain. ...
CHEM 101 Final (Term 151)
... the produced gas, if the total pressure is 1.00 atm. (Vapor pressure of water at 25 °C is 0.0313 atm). A) 3.0 x102 mL B) 2.8 x103 mL C) 9.1 x103 mL D) 5.6 x102 mL E) 1.4 x 102 mL ...
... the produced gas, if the total pressure is 1.00 atm. (Vapor pressure of water at 25 °C is 0.0313 atm). A) 3.0 x102 mL B) 2.8 x103 mL C) 9.1 x103 mL D) 5.6 x102 mL E) 1.4 x 102 mL ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... and gases in regards to density, compressibility, particle size, shape, volume, kinetic energy, attractive forces and movement 3. Explain how a solid melts into a liquid using kinetic energy in your explanation. 4. Define boiling point? 5. What is the difference between normal boiling point and boil ...
... and gases in regards to density, compressibility, particle size, shape, volume, kinetic energy, attractive forces and movement 3. Explain how a solid melts into a liquid using kinetic energy in your explanation. 4. Define boiling point? 5. What is the difference between normal boiling point and boil ...
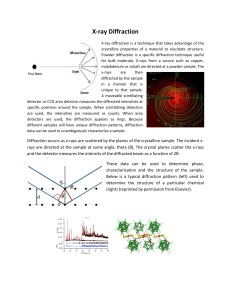
X-ray Diffraction
... Diffraction occurs as x-rays are scattered by the planes of the crystalline sample. The incident xrays are directed at the sample at some angle, theta (θ). The crystal planes scatter the x-rays and the detector measures the intensity of the diffracted beam as a function of 2θ. These data can be used ...
... Diffraction occurs as x-rays are scattered by the planes of the crystalline sample. The incident xrays are directed at the sample at some angle, theta (θ). The crystal planes scatter the x-rays and the detector measures the intensity of the diffracted beam as a function of 2θ. These data can be used ...
Type Of Chemical Reaction
... How many grams of HNO3 are needed to react with 11.45g of Cu? 32. According to the ______________ theory of ______________, the particles in a gas move rapidly, the particles in a gas are relatively far apart, the particles in a gas move independently of each other. ...
... How many grams of HNO3 are needed to react with 11.45g of Cu? 32. According to the ______________ theory of ______________, the particles in a gas move rapidly, the particles in a gas are relatively far apart, the particles in a gas move independently of each other. ...
Chemistry 1- Final Exam Review
... ____ 67. Which of these elements does not exist as a diatomic molecule? a. C c. H b. F d. I ____ 68. At constant temperature and pressure, gas volume is directly proportional to the a. molar mass of the gas. c. density of the gas at STP. b. number of moles of gas. d. pressure of the gas ____ 69. Ca ...
... ____ 67. Which of these elements does not exist as a diatomic molecule? a. C c. H b. F d. I ____ 68. At constant temperature and pressure, gas volume is directly proportional to the a. molar mass of the gas. c. density of the gas at STP. b. number of moles of gas. d. pressure of the gas ____ 69. Ca ...
Tutorial 1
... 14. Diethyl ether has a boiling point of 34.5 C and 1-butanol has a boiling point of 117 C: Diethyl ether ...
... 14. Diethyl ether has a boiling point of 34.5 C and 1-butanol has a boiling point of 117 C: Diethyl ether ...
THERMODYNAMICS III
... Many of the higher mountains in the world have altitudes in excess of 25000 feet above sea level. At these altitudes the atmospheric pressure is around 250 Torr. Calculate the changes in i) the freezing point; and ii) the boiling point of water at this pressure relative to normal conditions, given t ...
... Many of the higher mountains in the world have altitudes in excess of 25000 feet above sea level. At these altitudes the atmospheric pressure is around 250 Torr. Calculate the changes in i) the freezing point; and ii) the boiling point of water at this pressure relative to normal conditions, given t ...
Test Level 8 - IBT | ACER - Australian Council for Educational
... Ahmed places a measuring cylinder on the scales and then resets the scales to zero. He adds 100 mL of water to the measuring cylinder. He then adds 25 g of salt to the water. The reading on the scales is 125 g mL ...
... Ahmed places a measuring cylinder on the scales and then resets the scales to zero. He adds 100 mL of water to the measuring cylinder. He then adds 25 g of salt to the water. The reading on the scales is 125 g mL ...
Practice Questions
... Remarkably, it is used as a preservative in foods and cosmetics, and it is also an isomer of oil of wintergreen which can be prepared from salicylic acid, the same starting material used to prepare aspirin. Name the two functional groups each with one or more oxygen aroms that are present in methylp ...
... Remarkably, it is used as a preservative in foods and cosmetics, and it is also an isomer of oil of wintergreen which can be prepared from salicylic acid, the same starting material used to prepare aspirin. Name the two functional groups each with one or more oxygen aroms that are present in methylp ...
Chapter 4: Properties of Gases
... A 50 mL sample of oxygen at 25oC and 120 torr and a 100 mL sample of nitrogen at 25oC and 160 torr are both placed in a 200 mL flask at 25oC. What is the final pressure in the 200 mL flask? (a)250 torr ...
... A 50 mL sample of oxygen at 25oC and 120 torr and a 100 mL sample of nitrogen at 25oC and 160 torr are both placed in a 200 mL flask at 25oC. What is the final pressure in the 200 mL flask? (a)250 torr ...
Tutorial 1
... 1. Use the second member of each group from Group 1A to Group 7A to show that the number of valance electrons on an atom of the element is the same as its group number. 2. Use Lewis dot symbol to show the formation of aluminum oxide (Al 2O3) 3. Explain what an ionic bond is? And name five metals and ...
... 1. Use the second member of each group from Group 1A to Group 7A to show that the number of valance electrons on an atom of the element is the same as its group number. 2. Use Lewis dot symbol to show the formation of aluminum oxide (Al 2O3) 3. Explain what an ionic bond is? And name five metals and ...
practice quiz5
... E) None of the above Question 9 A mixture of neon, argon, and xenon had a total pressure of 1560 mm Hg at 298 K. The mixture was found to contain 1.50 mol Ne, 2.65 mol Ar, and 1.75 mol Xe. What is the partial pressure of Xe? A) 701 mm Hg B) 658 mm Hg C) 396 mm Hg D) 463 mm Hg E) None of the above Qu ...
... E) None of the above Question 9 A mixture of neon, argon, and xenon had a total pressure of 1560 mm Hg at 298 K. The mixture was found to contain 1.50 mol Ne, 2.65 mol Ar, and 1.75 mol Xe. What is the partial pressure of Xe? A) 701 mm Hg B) 658 mm Hg C) 396 mm Hg D) 463 mm Hg E) None of the above Qu ...
10 TEST 2 (of 3)
... Use the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) to calculate the ideal gas law constant R at standard temperature and pressure (273 K, 1.00 atm) assuming a molar volume of 22.4 L. ...
... Use the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) to calculate the ideal gas law constant R at standard temperature and pressure (273 K, 1.00 atm) assuming a molar volume of 22.4 L. ...
pressure_and_wind_notes
... Convection in the atmosphere is a major cause of weather. Convection is the major mechanism of energy transfers in the oceans, atmosphere, and Earth’s interior. Extreme weather: o Rapidly falling air pressure indicates a storm is approaching. o Tornado – a narrow, violent funnel-shaped column of spi ...
... Convection in the atmosphere is a major cause of weather. Convection is the major mechanism of energy transfers in the oceans, atmosphere, and Earth’s interior. Extreme weather: o Rapidly falling air pressure indicates a storm is approaching. o Tornado – a narrow, violent funnel-shaped column of spi ...
Chemistry 2008 Multiple Choice
... 32. Gaseous cyclobutene undergoes a first-order reaction to form gaseous butadiene. At a particular temperature, the partial pressure of cyclobutene in the reaction vessel drops to one-eighth its original value in 120 seconds. What is the half-life for this reaction at this temperature? (A) 15 s (B) ...
... 32. Gaseous cyclobutene undergoes a first-order reaction to form gaseous butadiene. At a particular temperature, the partial pressure of cyclobutene in the reaction vessel drops to one-eighth its original value in 120 seconds. What is the half-life for this reaction at this temperature? (A) 15 s (B) ...
Gas Laws Practice Test.Ans.Key
... into a 4.00-liter container. The mixture has an equilibrium temperature of 75.0 C. What is the partial pressure (in atm.) of the nitrogen gas in the vessel? No reaction takes place between these two gases. ...
... into a 4.00-liter container. The mixture has an equilibrium temperature of 75.0 C. What is the partial pressure (in atm.) of the nitrogen gas in the vessel? No reaction takes place between these two gases. ...
Diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a device used in scientific experiments. It allows compressing a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, which can exceed 600 gigapascals (6,000,000 bars / 6 million atmospheres).The device has been used to recreate the pressure existing deep inside planets, creating materials and phases not observed under normal conditions. Notable examples include the non-molecular ice X, polymeric nitrogen and metallic xenon (an inert gas at lower pressures).A DAC consists of two opposing diamonds with a sample compressed between the culets (tips). Pressure may be monitored using a reference material whose behavior under pressure is known. Common pressure standards include ruby fluorescence, and various structurally simple metals, such as copper or platinum. The uniaxial pressure supplied by the DAC may be transformed into uniform hydrostatic pressure using a pressure transmitting medium, such as argon, xenon, hydrogen, helium, paraffin oil or a mixture of methanol and ethanol. The pressure-transmitting medium is enclosed by a gasket and the two diamond anvils. The sample can be viewed through the diamonds and illuminated by X-rays and visible light. In this way, X-ray diffraction and fluorescence; optical absorption and photoluminescence; Mössbauer, Raman and Brillouin scattering; positron annihilation and other signals can be measured from materials under high pressure. Magnetic and microwave fields can be applied externally to the cell allowing nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and other magnetic measurements. Attaching electrodes to the sample allows electrical and magnetoelectrical measurements as well as heating up the sample to a few thousand degrees. Much higher temperatures (up to 7000 K) can be achieved with laser-induced heating, and cooling down to millikelvins has been demonstrated.