AP gas notes 2010
... Each exerts a specific pressure(called partial pressure) as it would by itself Total Pressure of gas mixture = sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas ...
... Each exerts a specific pressure(called partial pressure) as it would by itself Total Pressure of gas mixture = sum of the partial pressures of each individual gas ...
Ch1-2
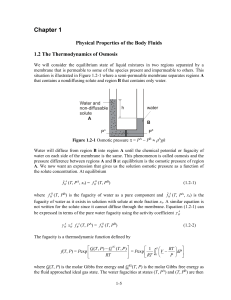
... The ideal dilute solution osmotic pressure, described by equation (1.2-4), is known as van’t Hoff’s law. This equation can also be written in terms of the mass concentration S ...
... The ideal dilute solution osmotic pressure, described by equation (1.2-4), is known as van’t Hoff’s law. This equation can also be written in terms of the mass concentration S ...
Properties of TiAl6V4 alloy parts produced by selective
... minimum at the stage of the powder-layer consolidation. This requires a careful process optimization procedure to obtain a high quality material [1]. For this reason more than 60 test samples were produced by SLM from TiAl6V4 powder varying different scan parameters: laser power, scanning rate, hatc ...
... minimum at the stage of the powder-layer consolidation. This requires a careful process optimization procedure to obtain a high quality material [1]. For this reason more than 60 test samples were produced by SLM from TiAl6V4 powder varying different scan parameters: laser power, scanning rate, hatc ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... of isoperibolic or isothermal calorimeters. The substance is being heated to the desired temperature and dropped into the calorimeter. The hot sample is either directly dropped into the liquid within the calorimeter (water, paraffin,...) or into a beaker that is surrounded by water. In the case of p ...
... of isoperibolic or isothermal calorimeters. The substance is being heated to the desired temperature and dropped into the calorimeter. The hot sample is either directly dropped into the liquid within the calorimeter (water, paraffin,...) or into a beaker that is surrounded by water. In the case of p ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... CHEMISTRY– 2nd SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and r ...
... CHEMISTRY– 2nd SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and r ...
The Effects of Varying Force and Contact on ATR
... A common practice is to adjust the applied force so that the strongest band intensities reach a specified level. The PerkinElmer UATR accessories display both the applied force and the spectrum as the pressure is adjusted. It is advisable to check the force as well as the intensities, especially wit ...
... A common practice is to adjust the applied force so that the strongest band intensities reach a specified level. The PerkinElmer UATR accessories display both the applied force and the spectrum as the pressure is adjusted. It is advisable to check the force as well as the intensities, especially wit ...
ap unit 5 worksheet answers
... 29. Under what conditions of temp. and pressure do gases usually behave nonideally? Low temp and high pressure 30. Would you expect water or carbon dioxide to behave more like an ideal gas at high pressures? Carbon dioxide 31. How do viscosity and surface tension change as intermolecular forces beco ...
... 29. Under what conditions of temp. and pressure do gases usually behave nonideally? Low temp and high pressure 30. Would you expect water or carbon dioxide to behave more like an ideal gas at high pressures? Carbon dioxide 31. How do viscosity and surface tension change as intermolecular forces beco ...
Equilibrium and Pressure
... C. How does this value of Kp compare to the value you found before? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________ D. As the experiment reached equilibrium again, did the reactants or products increase? _____________________________________________________________ ...
... C. How does this value of Kp compare to the value you found before? ______________ ___________________________________________________________________ D. As the experiment reached equilibrium again, did the reactants or products increase? _____________________________________________________________ ...
constant power parallel heating cable
... operations. Among the manifold advantages offered by this heating cable, attention should be paid to the possibility to control the operation status of each e heating circuit, and to the easiness and low price of assembly thanks to the accessories that Calorflex can provide for its application (see ...
... operations. Among the manifold advantages offered by this heating cable, attention should be paid to the possibility to control the operation status of each e heating circuit, and to the easiness and low price of assembly thanks to the accessories that Calorflex can provide for its application (see ...
Ch. 11: Gases
... independent of its chemical identity! • Gas behavior is markedly different than solid or liquid behavior. • We look at a theory that explains why gas behavior is universal and then at the origin of equations that allow us to do gas calculations. ...
... independent of its chemical identity! • Gas behavior is markedly different than solid or liquid behavior. • We look at a theory that explains why gas behavior is universal and then at the origin of equations that allow us to do gas calculations. ...
CST Review Part 2
... A balanced equation reveals mole ratios, which can be converted, as needed, into information in grams, and used to solve stoichiometry problems. Solve the following. Write a balanced equation for each. Then, after carrying out calculations in the space provided, write your answers in the blanks. ...
... A balanced equation reveals mole ratios, which can be converted, as needed, into information in grams, and used to solve stoichiometry problems. Solve the following. Write a balanced equation for each. Then, after carrying out calculations in the space provided, write your answers in the blanks. ...
PRE AP CHEMISTRY REVIEW PROBLEMS NON COLLEGE
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
Chemistry I Review - BarbaraElam-Rice
... 30) An atom has 2 electrons in its valence shell. To what group does the atom belong? Will the atom for an anion or a cation? What will be the oxidation number of the ion? 31) An intermolecular force that holds ionic compounds together is called electrostatic attraction. 32) Describe the 3 intermole ...
... 30) An atom has 2 electrons in its valence shell. To what group does the atom belong? Will the atom for an anion or a cation? What will be the oxidation number of the ion? 31) An intermolecular force that holds ionic compounds together is called electrostatic attraction. 32) Describe the 3 intermole ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... nitrogen. If air is made up of 0.6 atm of carbon monoxide, 12.6 atm of oxygen, what would be the partial pressure of nitrogen? c) If a sample of gas occupies 15.9 L at 34 C, what will its volume be at 27 C if the pressure does not change? d) The volume of a sample of oxygen gas is 300.0 ml when the ...
... nitrogen. If air is made up of 0.6 atm of carbon monoxide, 12.6 atm of oxygen, what would be the partial pressure of nitrogen? c) If a sample of gas occupies 15.9 L at 34 C, what will its volume be at 27 C if the pressure does not change? d) The volume of a sample of oxygen gas is 300.0 ml when the ...
Monitoring Reactions by TLC The fastest and most commonly used
... (2) silica gel plates (6 cm x 2.5 cm) impregnated with a phosphorescent dye (Merck silica gel 60 F-254 or JT-Baker Si250F, 0.25 mm thickness). (3) TLC solvents - A binary mixture of miscible solvents usually works best. TLC solvents are conveniently made up in the TLC chamber just before analysis fr ...
... (2) silica gel plates (6 cm x 2.5 cm) impregnated with a phosphorescent dye (Merck silica gel 60 F-254 or JT-Baker Si250F, 0.25 mm thickness). (3) TLC solvents - A binary mixture of miscible solvents usually works best. TLC solvents are conveniently made up in the TLC chamber just before analysis fr ...
Chapter 5 of Zumdahl
... Kr gas in a 18.5 L cylinder exerts a pressure of 8.61 atm at 24.8ºC What is the mass of Kr? A sample of gas has a volume of 4.18 L at 29ºC and 732 torr. What would its volume be at 24.8ºC and 756 torr? ...
... Kr gas in a 18.5 L cylinder exerts a pressure of 8.61 atm at 24.8ºC What is the mass of Kr? A sample of gas has a volume of 4.18 L at 29ºC and 732 torr. What would its volume be at 24.8ºC and 756 torr? ...
Earth Science Weather Variable Review Sheet Topics: Air
... Instrument used to take temperature. Air Pressure: Know how to use the conversion pressure scale on pg. 13 of the ESRT. Instruments used to measure pressure. Understand the factors for air pressure: temperature, moisture/humidity, and altitude. What are the differences between high and low ...
... Instrument used to take temperature. Air Pressure: Know how to use the conversion pressure scale on pg. 13 of the ESRT. Instruments used to measure pressure. Understand the factors for air pressure: temperature, moisture/humidity, and altitude. What are the differences between high and low ...
LABORATORY FACILITIES IN THE
... via alternating-current susceptibility measurements using a mutual inductance bridge. Easy and rapid temperature control is available at frequencies ranging from a few hertz to several megahertz. A broadband high-sensitivity nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer is used to observe the nuclear magn ...
... via alternating-current susceptibility measurements using a mutual inductance bridge. Easy and rapid temperature control is available at frequencies ranging from a few hertz to several megahertz. A broadband high-sensitivity nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer is used to observe the nuclear magn ...
Homework 3
... with a high content of dissolved gases flows more readily (less viscous) than one with a lesser amount of gases…” But on page 90, it is claimed that “In highly viscous, felsic magma, expansion is ...
... with a high content of dissolved gases flows more readily (less viscous) than one with a lesser amount of gases…” But on page 90, it is claimed that “In highly viscous, felsic magma, expansion is ...
review sheet
... 12.Adding heat to a solid will ____________ increase/decrease the kinetic energy and cause the intermolecular forces to ________________. 13. Of the three phases of matter, ______________ has the strongest attractive forces, and _________________ has the weakest. 14. Where will water boil at a lower ...
... 12.Adding heat to a solid will ____________ increase/decrease the kinetic energy and cause the intermolecular forces to ________________. 13. Of the three phases of matter, ______________ has the strongest attractive forces, and _________________ has the weakest. 14. Where will water boil at a lower ...
Fall Final 2009
... 1. A sample that cannot be separated into two or more substances by physical means is: a. A compound b. An element c. Either a compound or an element d. A homogeneous mixture e. A heterogenous mixture 2. Given the following enthalpies of formation, Hf°: CH4(g), -74.8 kJ/mol; H2O(g), -242 kJ/mol; CO ...
... 1. A sample that cannot be separated into two or more substances by physical means is: a. A compound b. An element c. Either a compound or an element d. A homogeneous mixture e. A heterogenous mixture 2. Given the following enthalpies of formation, Hf°: CH4(g), -74.8 kJ/mol; H2O(g), -242 kJ/mol; CO ...
How Diamonds Are Formed
... earth very quickly – in a matter of hours. The speed is critical to diamond material, because if it traveled too slowly, it would turn to graphite. By moving quickly, the carbon is locked into the diamond atomic formation. The rapid cooling does not leave enough energy to rearrange the diamond struc ...
... earth very quickly – in a matter of hours. The speed is critical to diamond material, because if it traveled too slowly, it would turn to graphite. By moving quickly, the carbon is locked into the diamond atomic formation. The rapid cooling does not leave enough energy to rearrange the diamond struc ...
Earth Interior quest
... 13. Where and what are the convection currents? (p.17) Read this section. 14. How hot is the inner core? 15. What does melting point mean? 16. If the temperature of material is hotter than the melting point what should happen to it? 17. What is the outer core made of? What is the inner core made of? ...
... 13. Where and what are the convection currents? (p.17) Read this section. 14. How hot is the inner core? 15. What does melting point mean? 16. If the temperature of material is hotter than the melting point what should happen to it? 17. What is the outer core made of? What is the inner core made of? ...
unit - i principles of dynamics (9)
... methods for massive parallelization of these newly developed machine-phase techniques for molecularly precise fabrication. This combined effort will result in the full realization of the tremendous potential for 21st century manufacturing 12. (A) Illuminate with neat sketch of Scanning Probe Microsc ...
... methods for massive parallelization of these newly developed machine-phase techniques for molecularly precise fabrication. This combined effort will result in the full realization of the tremendous potential for 21st century manufacturing 12. (A) Illuminate with neat sketch of Scanning Probe Microsc ...
Haley CHM2045 Final Review
... 2. A 1.0 L mixture of He, Ar, and Ne has a total pressure of 654 mmHg at 298 K. If the partial pressure of He is 378 mmHg and the partial pressure of Ne is 112 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of Ar? 3. Lithium reacts with nitrogen gas in the following reaction, 6Li + N2 —> 2Li3N What mass of lith ...
... 2. A 1.0 L mixture of He, Ar, and Ne has a total pressure of 654 mmHg at 298 K. If the partial pressure of He is 378 mmHg and the partial pressure of Ne is 112 mmHg, what is the partial pressure of Ar? 3. Lithium reacts with nitrogen gas in the following reaction, 6Li + N2 —> 2Li3N What mass of lith ...
Diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a device used in scientific experiments. It allows compressing a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, which can exceed 600 gigapascals (6,000,000 bars / 6 million atmospheres).The device has been used to recreate the pressure existing deep inside planets, creating materials and phases not observed under normal conditions. Notable examples include the non-molecular ice X, polymeric nitrogen and metallic xenon (an inert gas at lower pressures).A DAC consists of two opposing diamonds with a sample compressed between the culets (tips). Pressure may be monitored using a reference material whose behavior under pressure is known. Common pressure standards include ruby fluorescence, and various structurally simple metals, such as copper or platinum. The uniaxial pressure supplied by the DAC may be transformed into uniform hydrostatic pressure using a pressure transmitting medium, such as argon, xenon, hydrogen, helium, paraffin oil or a mixture of methanol and ethanol. The pressure-transmitting medium is enclosed by a gasket and the two diamond anvils. The sample can be viewed through the diamonds and illuminated by X-rays and visible light. In this way, X-ray diffraction and fluorescence; optical absorption and photoluminescence; Mössbauer, Raman and Brillouin scattering; positron annihilation and other signals can be measured from materials under high pressure. Magnetic and microwave fields can be applied externally to the cell allowing nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and other magnetic measurements. Attaching electrodes to the sample allows electrical and magnetoelectrical measurements as well as heating up the sample to a few thousand degrees. Much higher temperatures (up to 7000 K) can be achieved with laser-induced heating, and cooling down to millikelvins has been demonstrated.