Fig. 6. Typical circuits with high magnetic permeability
... presenting a result of Stewart's, Frenkel's and Eiring's (1, 2) views. This version is true indeed for the transition metals, becaus any of the purestmelt of such an element owing to its ambivalent nature could be consied as a particular version of the model. It's main concept is as follows: a) The ...
... presenting a result of Stewart's, Frenkel's and Eiring's (1, 2) views. This version is true indeed for the transition metals, becaus any of the purestmelt of such an element owing to its ambivalent nature could be consied as a particular version of the model. It's main concept is as follows: a) The ...
Magnetoelectric coupling on multiferroic cobalt ferrite–barium
... Magnetoelectric (ME) materials can be electrically polarized by a magnetic field or magnetized by an electric field. They can be used in different technological applications such as magnetic sensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), and energy harvesters [1-3]. Composite multiferroic materials ...
... Magnetoelectric (ME) materials can be electrically polarized by a magnetic field or magnetized by an electric field. They can be used in different technological applications such as magnetic sensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), and energy harvesters [1-3]. Composite multiferroic materials ...
Use of partially oxidized SiC particle bed for microwave sintering of
... Kitchen microwave ovens provide inexpensive multimode cavities for experimental materials processing. The modes generated within such a cavity result in a complex electric field distribution, so that the specimen position within the cavity is an important variable in the heating process. More unifor ...
... Kitchen microwave ovens provide inexpensive multimode cavities for experimental materials processing. The modes generated within such a cavity result in a complex electric field distribution, so that the specimen position within the cavity is an important variable in the heating process. More unifor ...
G2S15Lesson1 Introd
... The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are darker colored rocks and include abundant d ...
... The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are darker colored rocks and include abundant d ...
FOREWORD.PDF
... in SCSS was focussed around the response of solids under dynamic high pressures and high temperatures where the effect of shear was considered secondary. In recent years, however, there has been an increasing realization, both from theoretical studies and experimental measurements, that the paradigm ...
... in SCSS was focussed around the response of solids under dynamic high pressures and high temperatures where the effect of shear was considered secondary. In recent years, however, there has been an increasing realization, both from theoretical studies and experimental measurements, that the paradigm ...
Chapter 2 - Portal UniMAP
... 79 % N2, 21 % O2 and (b) from its approximate mass composition of 76.7 % N2, 23.3 % O2 ...
... 79 % N2, 21 % O2 and (b) from its approximate mass composition of 76.7 % N2, 23.3 % O2 ...
Thermoanalytical characterization of carbon/carbon hybrid material
... mass loss, since evolution of CO2 and low molecular fragments (m/z = 55 and 78) was observed by mass spectroscopy [3]. At even higher temperatures, cross-linking may take place at the same time. In the earlier study [3] using MS for evolved gas analysis, the heating rate was high as 20◦ min−1 , and ...
... mass loss, since evolution of CO2 and low molecular fragments (m/z = 55 and 78) was observed by mass spectroscopy [3]. At even higher temperatures, cross-linking may take place at the same time. In the earlier study [3] using MS for evolved gas analysis, the heating rate was high as 20◦ min−1 , and ...
2nd Semester final review
... 1. What is a family or group on the periodic table and what is so important about it. Elements in a family or group (an up-down column) share similar chemical properties 2. Complete the chart below: Symbol Protons C-14 ...
... 1. What is a family or group on the periodic table and what is so important about it. Elements in a family or group (an up-down column) share similar chemical properties 2. Complete the chart below: Symbol Protons C-14 ...
Scientific Dating in Archaeology
... the age of archaeological remains. One of them is concerned with the sample used for ...
... the age of archaeological remains. One of them is concerned with the sample used for ...
File
... Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to 12. No odor can be detected when a sample of the the numbered statements immediately following it. solution is added drop by drop to a warm solution Select the one lettered choice that best fits each of sodium hydroxide. statement and then bla ...
... Directions: Each set of lettered choices below refers to 12. No odor can be detected when a sample of the the numbered statements immediately following it. solution is added drop by drop to a warm solution Select the one lettered choice that best fits each of sodium hydroxide. statement and then bla ...
G2S15Lesson1 Introd
... The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are darker colored rocks and include abundant d ...
... The composition (mineral makeup) of igneous rocks can be divided into two main groups: 1. Felsic (silicic) rocks: These are lighter colored rocks and include abundant quartz, potassium feldspar – this includes Granite and Rhyolite 2. Mafic Rocks: These are darker colored rocks and include abundant d ...
Document
... a) A ball rolls down a hill but never spontaneously rolls back up the hill. b) If exposed to air and moisture, steel rusts spontaneously but the reverse process does not naturally ...
... a) A ball rolls down a hill but never spontaneously rolls back up the hill. b) If exposed to air and moisture, steel rusts spontaneously but the reverse process does not naturally ...
AP 3rd 9 weeks notes
... a) A ball rolls down a hill but never spontaneously rolls back up the hill. b) If exposed to air and moisture, steel rusts spontaneously but the reverse process does not naturally ...
... a) A ball rolls down a hill but never spontaneously rolls back up the hill. b) If exposed to air and moisture, steel rusts spontaneously but the reverse process does not naturally ...
Gaseous state - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... Dimer N2O4 at 262 K is solid. A 250 mL flask and a 100 mL flask are separated by a stop cock. At 300 K, the nitric oxide in the larger flask exerts a pressure of 1.053 atm and smaller one contains O2 at 0.789 atm.The gases are mixed by opening the stop cock and after the end of the reaction, the fla ...
... Dimer N2O4 at 262 K is solid. A 250 mL flask and a 100 mL flask are separated by a stop cock. At 300 K, the nitric oxide in the larger flask exerts a pressure of 1.053 atm and smaller one contains O2 at 0.789 atm.The gases are mixed by opening the stop cock and after the end of the reaction, the fla ...
0922085
... B The explosivity range of UN No. 1547 ANILINE is 1.2% to 11% (by volume). What would the properties of a mixture of 0.1% (by volume) of aniline and 99.9% (by volume) of air be? A ...
... B The explosivity range of UN No. 1547 ANILINE is 1.2% to 11% (by volume). What would the properties of a mixture of 0.1% (by volume) of aniline and 99.9% (by volume) of air be? A ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry
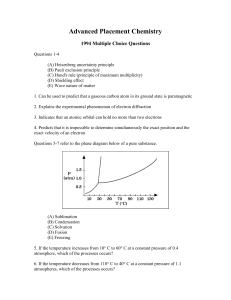
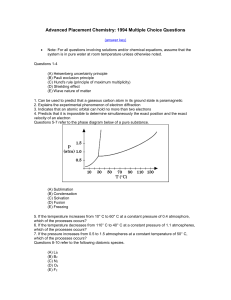
... (D) Shielding effect (E) Wave nature of matter 1. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic 2. Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 3. Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no more than two electrons 4. Predicts that it is impos ...
... (D) Shielding effect (E) Wave nature of matter 1. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in its ground state is paramagnetic 2. Explains the experimental phenomenon of electron diffraction 3. Indicates that an atomic orbital can hold no more than two electrons 4. Predicts that it is impos ...
Cryoetching processes applied to ULK material
... These values were again obtained after the annealing ...
... These values were again obtained after the annealing ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... 61. When a solution of potassium dichromate is (A) 0.23 (C) 0.50 (E) 0.83 added to an acidified solution of iron(II) sulfate, (B) 0.29 (D) 0.77 the products of the reaction are (A) FeCr2O7(s) and H2O 56. A cube of ice is added to some hot water in a (B) FeCrO4(s) and H2O rigid, insulated container, ...
... 61. When a solution of potassium dichromate is (A) 0.23 (C) 0.50 (E) 0.83 added to an acidified solution of iron(II) sulfate, (B) 0.29 (D) 0.77 the products of the reaction are (A) FeCr2O7(s) and H2O 56. A cube of ice is added to some hot water in a (B) FeCrO4(s) and H2O rigid, insulated container, ...
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and
... This study is conducted to provide a new solution for the problem of electricity in the world represented mainly in the full dependence on fossil fuel resources which causes a huge damage to the environment besides its increasing high cost and non-renew ability. The development of a new method for h ...
... This study is conducted to provide a new solution for the problem of electricity in the world represented mainly in the full dependence on fossil fuel resources which causes a huge damage to the environment besides its increasing high cost and non-renew ability. The development of a new method for h ...
Chemistry Exam 2 Specifications and Sample Exam
... 0.30 mol of COCl2(g) and 0.20 mol of CO(g) are introduced in a 5.0 L container at 40°C. When equilibrium is reached, 0.10 mol of Cl2(g) has formed. The temperature is maintained at 40°C throughout the experiment. a. i. Calculate the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, K, for the forward rea ...
... 0.30 mol of COCl2(g) and 0.20 mol of CO(g) are introduced in a 5.0 L container at 40°C. When equilibrium is reached, 0.10 mol of Cl2(g) has formed. The temperature is maintained at 40°C throughout the experiment. a. i. Calculate the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, K, for the forward rea ...
Laboratory Practices from Physical Chemistry
... Using analytical scales, we determine the weight, m1, of empty Dumas flask with stopper. We add ca 1–2 ml of sample to Dumas flask and we place it in the thermostatic bath with temperature Tk. Only the end of the flask neck (1–2 cm) has to project from the bath. During sample evaporation, all air fr ...
... Using analytical scales, we determine the weight, m1, of empty Dumas flask with stopper. We add ca 1–2 ml of sample to Dumas flask and we place it in the thermostatic bath with temperature Tk. Only the end of the flask neck (1–2 cm) has to project from the bath. During sample evaporation, all air fr ...
Chapter 13: Properties of Solutions
... o In digestion, bile is released, and one specific component in it emulsifies the fats, which helps the absorption of them through the intestine wall. o The component in bile is an emulsifying agent. ...
... o In digestion, bile is released, and one specific component in it emulsifies the fats, which helps the absorption of them through the intestine wall. o The component in bile is an emulsifying agent. ...
MC94 - Southchemistry.com
... Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1994 Multiple Choice Questions (answer key) ...
... Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1994 Multiple Choice Questions (answer key) ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Illinois State University
... 4. Temperature is an agent 5. Pressure is an agent 6. Generates foliated rocks 7. Forms as a result of being near an intrusion of magma 8. Found in mountain belts 9. May have been originally been a metamorphic rock 10.Form at temperatures above 200 oC 11.May underlie several adjacent states ...
... 4. Temperature is an agent 5. Pressure is an agent 6. Generates foliated rocks 7. Forms as a result of being near an intrusion of magma 8. Found in mountain belts 9. May have been originally been a metamorphic rock 10.Form at temperatures above 200 oC 11.May underlie several adjacent states ...
Diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a device used in scientific experiments. It allows compressing a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, which can exceed 600 gigapascals (6,000,000 bars / 6 million atmospheres).The device has been used to recreate the pressure existing deep inside planets, creating materials and phases not observed under normal conditions. Notable examples include the non-molecular ice X, polymeric nitrogen and metallic xenon (an inert gas at lower pressures).A DAC consists of two opposing diamonds with a sample compressed between the culets (tips). Pressure may be monitored using a reference material whose behavior under pressure is known. Common pressure standards include ruby fluorescence, and various structurally simple metals, such as copper or platinum. The uniaxial pressure supplied by the DAC may be transformed into uniform hydrostatic pressure using a pressure transmitting medium, such as argon, xenon, hydrogen, helium, paraffin oil or a mixture of methanol and ethanol. The pressure-transmitting medium is enclosed by a gasket and the two diamond anvils. The sample can be viewed through the diamonds and illuminated by X-rays and visible light. In this way, X-ray diffraction and fluorescence; optical absorption and photoluminescence; Mössbauer, Raman and Brillouin scattering; positron annihilation and other signals can be measured from materials under high pressure. Magnetic and microwave fields can be applied externally to the cell allowing nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and other magnetic measurements. Attaching electrodes to the sample allows electrical and magnetoelectrical measurements as well as heating up the sample to a few thousand degrees. Much higher temperatures (up to 7000 K) can be achieved with laser-induced heating, and cooling down to millikelvins has been demonstrated.