Name_________________________________________
... 3. If the actual yield is 4.95 g Pb, what is the percent yield? [ANS = 0.415 g, 5.69 g, 87%] Benzocaine is a compound containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. When a sample of benzocaine weighing 3.54 g is burned in excess oxygen, 8.49 g of CO2 and 2.14 g of H2O are formed. In a separate ex ...
... 3. If the actual yield is 4.95 g Pb, what is the percent yield? [ANS = 0.415 g, 5.69 g, 87%] Benzocaine is a compound containing carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen. When a sample of benzocaine weighing 3.54 g is burned in excess oxygen, 8.49 g of CO2 and 2.14 g of H2O are formed. In a separate ex ...
Name AP Chemistry Take Home Quiz – Due Thursday, 1/9/2014
... 26. CH3CH2OH boils at 78 °C and CH3OCH3 boils at - 24 °C, although both compounds have the same composition. This difference in boiling points may be attributed to a difference in a. molecular mass b. density c. specific heat d. hydrogen bonding e. heat of combustion 27. HCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) AgCl(s ...
... 26. CH3CH2OH boils at 78 °C and CH3OCH3 boils at - 24 °C, although both compounds have the same composition. This difference in boiling points may be attributed to a difference in a. molecular mass b. density c. specific heat d. hydrogen bonding e. heat of combustion 27. HCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) AgCl(s ...
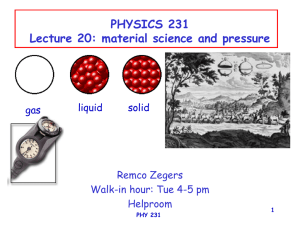
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 20: material science and pressure
... Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformation (a different modulus is defined for different types of deformations) PHY 231 ...
... Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformation (a different modulus is defined for different types of deformations) PHY 231 ...
Equilibrium - District 196
... The forward reaction shown above is favored, therefore there is a higher concentration of products than of reactants at equilibrium ...
... The forward reaction shown above is favored, therefore there is a higher concentration of products than of reactants at equilibrium ...
الشريحة 1
... warmed, you can see bubbles of air on the inside of the glass. - Warm lakes and streams have less O2 dissolved in them than cool lakes (thermal pollution), fish may suffocate and die under these conditions. ...
... warmed, you can see bubbles of air on the inside of the glass. - Warm lakes and streams have less O2 dissolved in them than cool lakes (thermal pollution), fish may suffocate and die under these conditions. ...
Avogadro`s Law is relation between
... a. 4.2 mol Ar b. 3.5 g CO2 c. 2.1 g N2 7- Calculate the volume of each substance at STP. a. 4.2 mol N2 b. 6.5 g He c. 22.0 g CH4 8- What volume does 3.01 × 1021 molecules of N2 occupy at STP? ...
... a. 4.2 mol Ar b. 3.5 g CO2 c. 2.1 g N2 7- Calculate the volume of each substance at STP. a. 4.2 mol N2 b. 6.5 g He c. 22.0 g CH4 8- What volume does 3.01 × 1021 molecules of N2 occupy at STP? ...
Efficient production of monocrystalline semiconductors
... Concept and design: iserundschmidt GmbH, Bonn – Berlin, Germany · Layout: KERSTIN CONRADI · Mediengestaltung, Berlin, Germany ...
... Concept and design: iserundschmidt GmbH, Bonn – Berlin, Germany · Layout: KERSTIN CONRADI · Mediengestaltung, Berlin, Germany ...
Tutorial 4 (PowerPoint)
... • Tip can be operated in “dynamic mode” • The tip and cantilever (beam with the tip on it) have a mechanical natural resonance • The resonance will change as external forces from the sample are exerted on it • The tip’s vibration amplitude must be much less than the distance between it and the sampl ...
... • Tip can be operated in “dynamic mode” • The tip and cantilever (beam with the tip on it) have a mechanical natural resonance • The resonance will change as external forces from the sample are exerted on it • The tip’s vibration amplitude must be much less than the distance between it and the sampl ...
AP Chemistry
... (C) The density of the gas (D) The volume of the gas (E) The number of molecules in the gas 97. A sample of gas in a closed container is raised to double its initial pressure while remaining at constant temperature. Which of the following occurs? (A) The volume of the gas doubles. (B) The density of ...
... (C) The density of the gas (D) The volume of the gas (E) The number of molecules in the gas 97. A sample of gas in a closed container is raised to double its initial pressure while remaining at constant temperature. Which of the following occurs? (A) The volume of the gas doubles. (B) The density of ...
Lab Manual
... small compared to the volume occupied by the gas; and (3) no forces act on the molecules except during elastic collisions of negligible duration. Although no gas has these properties, the behavior of real gases is described quite closely by the ideal gas law at sufficiently high temperatures and low ...
... small compared to the volume occupied by the gas; and (3) no forces act on the molecules except during elastic collisions of negligible duration. Although no gas has these properties, the behavior of real gases is described quite closely by the ideal gas law at sufficiently high temperatures and low ...
Volcanoes Erupt - Lake Science Collaborative Teacher Lesson Plans
... Much of the magma in Earth is produced 100-200 kilometers below the surface. Earth’s heat comes from (1) radioactive decay and (2) residual heat which is gravitational energy left over from Earth’s formation. The hot, moving mantle, consisting of melted rocks and minerals, is responsible for many ge ...
... Much of the magma in Earth is produced 100-200 kilometers below the surface. Earth’s heat comes from (1) radioactive decay and (2) residual heat which is gravitational energy left over from Earth’s formation. The hot, moving mantle, consisting of melted rocks and minerals, is responsible for many ge ...
Materials Needed for the Lesson - Lake Science Collaborative
... Much of the magma in Earth is produced 100-200 kilometers below the surface. Earth’s heat comes from (1) radioactive decay and (2) residual heat which is gravitational energy left over from Earth’s formation. The hot, moving mantle, consisting of melted rocks and minerals, is responsible for many ge ...
... Much of the magma in Earth is produced 100-200 kilometers below the surface. Earth’s heat comes from (1) radioactive decay and (2) residual heat which is gravitational energy left over from Earth’s formation. The hot, moving mantle, consisting of melted rocks and minerals, is responsible for many ge ...
CHM 151LL: States of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes
... of matter are 1) the atoms’ or molecules’ freedom of movement and 2) the amount of space between the atoms or molecules. The physical state of a substance at a specific temperature depends on the attraction between atoms or molecules. Although more than one hundred elements exist; only two naturally ...
... of matter are 1) the atoms’ or molecules’ freedom of movement and 2) the amount of space between the atoms or molecules. The physical state of a substance at a specific temperature depends on the attraction between atoms or molecules. Although more than one hundred elements exist; only two naturally ...
Chemistry 2008–2012 Written examination – November Examination Specifications
... 0.30 mol of COCl2(g) and 0.20 mol of CO(g) are introduced in a 5.0 L container at 40°C. When equilibrium is reached, 0.10 mol of Cl2(g) has formed. The temperature is maintained at 40°C throughout the experiment. a. i. Calculate the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, K, for the forward rea ...
... 0.30 mol of COCl2(g) and 0.20 mol of CO(g) are introduced in a 5.0 L container at 40°C. When equilibrium is reached, 0.10 mol of Cl2(g) has formed. The temperature is maintained at 40°C throughout the experiment. a. i. Calculate the numerical value of the equilibrium constant, K, for the forward rea ...
Wizard Test Maker
... Balance the equation using smallest whole number coefficients. 20. In a laboratory experiment, a student determined the mass of the product, NaNO3(s), to be 0.105 grams. a. Calculate the gram formula mass of NaNO3(s). Round atomic masses from the Periodic Table to the nearest tenth. [ Show all work. ...
... Balance the equation using smallest whole number coefficients. 20. In a laboratory experiment, a student determined the mass of the product, NaNO3(s), to be 0.105 grams. a. Calculate the gram formula mass of NaNO3(s). Round atomic masses from the Periodic Table to the nearest tenth. [ Show all work. ...
Cavitation Erosion in Stream Channels
... depresa10na or protuberences, or even a roughened surface may produce the necessary preasure area. Cavitation may develop any place where vortices may form. If cavitation once starts in any depression, no matter how small, it will develop in intensity and severity as It enlarges the target area. Cav ...
... depresa10na or protuberences, or even a roughened surface may produce the necessary preasure area. Cavitation may develop any place where vortices may form. If cavitation once starts in any depression, no matter how small, it will develop in intensity and severity as It enlarges the target area. Cav ...
pdf - arXiv.org
... Recent studies have been focused on various wide-band gap materials with superior chemical and thermal stability needed for optoelectronics and applications [1-5]. Bulk hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is one of these materials and offers excellent thermal conductivity and bright luminescence in the de ...
... Recent studies have been focused on various wide-band gap materials with superior chemical and thermal stability needed for optoelectronics and applications [1-5]. Bulk hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is one of these materials and offers excellent thermal conductivity and bright luminescence in the de ...
Thin film patterning by surface-plasmon-induced
... to itself, capillarity-driven processes lead to surface free energy minimization; thus, the morphology of functional structures may strongly change in a self-organizing manner.1–3 On the contrary, if a system is exposed to external forces it can be driven to a nonequilibrium state. Thermal gradients ...
... to itself, capillarity-driven processes lead to surface free energy minimization; thus, the morphology of functional structures may strongly change in a self-organizing manner.1–3 On the contrary, if a system is exposed to external forces it can be driven to a nonequilibrium state. Thermal gradients ...
Document
... measure of the amplitude of a wave scattered from an isolated atom (scattering amplitude). • x-rays are scattered by the electron cloud of the atom and hence the scattering power of x-rays increases with the atomic number of the atoms in a sample. • The x-ray form factor is defined as the Fourier tr ...
... measure of the amplitude of a wave scattered from an isolated atom (scattering amplitude). • x-rays are scattered by the electron cloud of the atom and hence the scattering power of x-rays increases with the atomic number of the atoms in a sample. • The x-ray form factor is defined as the Fourier tr ...
Magma Supply Vs Magma Plumbing
... • Unique, orderly internal arrangement of atoms (crystalline) ...
... • Unique, orderly internal arrangement of atoms (crystalline) ...
Reactions of Oxygen with the Platinum Metals
... (or on ruthenium-platinum alloys), for example, resists pickling by boiling aqua regia. The films are most simply removed by hearing to above their decomposition temperature, the metal being then quenched in water to prevent the films from reforming during cooling. Alternatively, of course, they can ...
... (or on ruthenium-platinum alloys), for example, resists pickling by boiling aqua regia. The films are most simply removed by hearing to above their decomposition temperature, the metal being then quenched in water to prevent the films from reforming during cooling. Alternatively, of course, they can ...
Scanning Probe MicroScopy History of Scanning Probe Microscopy
... Figure 10: The de ection of the tip is measured by bouncing a laser o the cantilever arm which gives us the contour of the surface at atomic resolution (since inter-atomic forces are related to the distance between the atoms). One possible complication is formation of bonds between the tip and the ...
... Figure 10: The de ection of the tip is measured by bouncing a laser o the cantilever arm which gives us the contour of the surface at atomic resolution (since inter-atomic forces are related to the distance between the atoms). One possible complication is formation of bonds between the tip and the ...
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN(e) : www.iosrjournals.org
... Nanoparticles are of great scientific interest as they are effectively a bridge between bulk materials and atomic or molecular structures. A bulk material should have constant physical properties regardless of its size, but at the nano-scale size-dependent properties are often observed. Thus, the pr ...
... Nanoparticles are of great scientific interest as they are effectively a bridge between bulk materials and atomic or molecular structures. A bulk material should have constant physical properties regardless of its size, but at the nano-scale size-dependent properties are often observed. Thus, the pr ...
C - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... A. Atoms contain electrons. B. Practically all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. C. Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. T ...
... A. Atoms contain electrons. B. Practically all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. C. Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. T ...
STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF THE BRONZE LASER
... titanium. The laser alloying was done using a pulsed Nd:YAG laser with a generated beam energy of 25-35 J. The microstructure formed under rapid solidification conditions was investigated by scanning electron microscope and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Microhardness was determined using a H ...
... titanium. The laser alloying was done using a pulsed Nd:YAG laser with a generated beam energy of 25-35 J. The microstructure formed under rapid solidification conditions was investigated by scanning electron microscope and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Microhardness was determined using a H ...
Diamond anvil cell
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) is a device used in scientific experiments. It allows compressing a small (sub-millimeter-sized) piece of material to extreme pressures, which can exceed 600 gigapascals (6,000,000 bars / 6 million atmospheres).The device has been used to recreate the pressure existing deep inside planets, creating materials and phases not observed under normal conditions. Notable examples include the non-molecular ice X, polymeric nitrogen and metallic xenon (an inert gas at lower pressures).A DAC consists of two opposing diamonds with a sample compressed between the culets (tips). Pressure may be monitored using a reference material whose behavior under pressure is known. Common pressure standards include ruby fluorescence, and various structurally simple metals, such as copper or platinum. The uniaxial pressure supplied by the DAC may be transformed into uniform hydrostatic pressure using a pressure transmitting medium, such as argon, xenon, hydrogen, helium, paraffin oil or a mixture of methanol and ethanol. The pressure-transmitting medium is enclosed by a gasket and the two diamond anvils. The sample can be viewed through the diamonds and illuminated by X-rays and visible light. In this way, X-ray diffraction and fluorescence; optical absorption and photoluminescence; Mössbauer, Raman and Brillouin scattering; positron annihilation and other signals can be measured from materials under high pressure. Magnetic and microwave fields can be applied externally to the cell allowing nuclear magnetic resonance, electron paramagnetic resonance and other magnetic measurements. Attaching electrodes to the sample allows electrical and magnetoelectrical measurements as well as heating up the sample to a few thousand degrees. Much higher temperatures (up to 7000 K) can be achieved with laser-induced heating, and cooling down to millikelvins has been demonstrated.