356 Angular Kinetics
... • The center of mass is the point about which the body's mass is evenly distributed. • The line of gravity is the line that defines the center of mass in the transverse plane. • The sum of the torques about an axis caused by the weights of multiple particles is equal to the distance from the axis to ...
... • The center of mass is the point about which the body's mass is evenly distributed. • The line of gravity is the line that defines the center of mass in the transverse plane. • The sum of the torques about an axis caused by the weights of multiple particles is equal to the distance from the axis to ...
216KB - NZQA
... speed change, therefore, as there is an unbalanced force greater than zero towards the ground, the parachutist’s speed will increase. ...
... speed change, therefore, as there is an unbalanced force greater than zero towards the ground, the parachutist’s speed will increase. ...
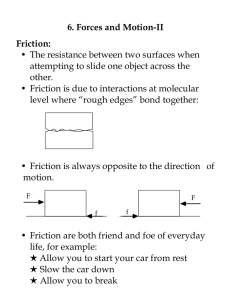
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... but neither objects are moving with respect to each other. • The friction is always equal to the net force parallel to the surface. • If one net force increases or decreases, the friction force will also increase or decrease to compensate. • Experimentally, the maximum magnitude of static friction i ...
... but neither objects are moving with respect to each other. • The friction is always equal to the net force parallel to the surface. • If one net force increases or decreases, the friction force will also increase or decrease to compensate. • Experimentally, the maximum magnitude of static friction i ...
Powerpoint for today
... A. If you park on a hill with a 10 degree slope with the car held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which ...
... A. If you park on a hill with a 10 degree slope with the car held by the parking brake, what is the magnitude of the frictional force that holds your car in place? B. The coefficient of static friction between your car's wheels and the road when wet is 0.30. What is the largest angle slope on which ...
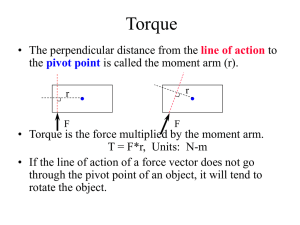
+ • C - Purdue Physics
... Q10 Is it possible that the object pictured in question 9 is moving, given the fact that the two forces acting on it are equal in size but opposite in direction? Explain. Yes, constant velocity ...
... Q10 Is it possible that the object pictured in question 9 is moving, given the fact that the two forces acting on it are equal in size but opposite in direction? Explain. Yes, constant velocity ...
322. Two head lamps of a car are in parallel. They - DST
... Q 56 When a body is projected vertically up from the ground, its PE and KE at a point P are in the ratio 2 : 3. If same body is projected with double the previous velocity, then at the same point P ratio of its P.E. and KE would be: (a) (c) ...
... Q 56 When a body is projected vertically up from the ground, its PE and KE at a point P are in the ratio 2 : 3. If same body is projected with double the previous velocity, then at the same point P ratio of its P.E. and KE would be: (a) (c) ...
Chapter 7
... • Acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path • Although an object is moving at a constant speed, it can still have an acceleration. • Velocity is a vector, which has both magnitude and DIRECTION. • In circular motion, velocity is constantly changing direction. ...
... • Acceleration directed toward the center of a circular path • Although an object is moving at a constant speed, it can still have an acceleration. • Velocity is a vector, which has both magnitude and DIRECTION. • In circular motion, velocity is constantly changing direction. ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.