Lecture 5: Time-varying EM Fields
... when any change in magnetic environment around the loop occurs (Faraday’s law). When an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it. The induced ...
... when any change in magnetic environment around the loop occurs (Faraday’s law). When an emf is generated by a change in magnetic flux according to Faraday's Law, the polarity of the induced emf is such that it produces a current whose magnetic field opposes the change which produces it. The induced ...
Unit 7 Review- Static Electricity
... What happens to the force if we decrease the distance of separation by half? ...
... What happens to the force if we decrease the distance of separation by half? ...
2. Electrostriction field and forces caused by it
... from a ferromagnetic material later; the forces have increased then so, that they became difficult for keeping hands, and all doubts about validity (2) have completely disappeared. It is necessary to solve only the nature of the force always working in pair with magnetic force ...
... from a ferromagnetic material later; the forces have increased then so, that they became difficult for keeping hands, and all doubts about validity (2) have completely disappeared. It is necessary to solve only the nature of the force always working in pair with magnetic force ...
FanCartPhysicsSEshorted
... cart. Place fan A on the cart and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ 2. Press Play ( ) and observe the cart. In which direction does the cart move? __________________ By blowing to ...
... cart. Place fan A on the cart and turn it on by clicking the ON/OFF button below. 1. Look at the blue lines coming from the fan. In which direction is the air pushed? ____________________ 2. Press Play ( ) and observe the cart. In which direction does the cart move? __________________ By blowing to ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... 1) A solid sphere and a hoop of equal radius and mass are both rolled up an incline with the same initial velocity. Which object will travel farthest up the inclined plane? a) the sphere b) the hoop c) they’ll both travel the same distance up the plane d) it depends on the angle of the incline 2) If ...
... 1) A solid sphere and a hoop of equal radius and mass are both rolled up an incline with the same initial velocity. Which object will travel farthest up the inclined plane? a) the sphere b) the hoop c) they’ll both travel the same distance up the plane d) it depends on the angle of the incline 2) If ...
Phy I (AP Phy I) Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
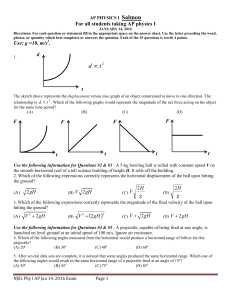
... 6. What happens to the horizontal displacement, if you double the initial velocity of a projectile while keeping all other parameters constant? Assume non-zero parameters. (A) It remains the same (B) It also doubles (C) It quadruples (D) Cannot be determined without more information. ...
... 6. What happens to the horizontal displacement, if you double the initial velocity of a projectile while keeping all other parameters constant? Assume non-zero parameters. (A) It remains the same (B) It also doubles (C) It quadruples (D) Cannot be determined without more information. ...
Lecture 11
... Doped with Boron, Aluminum or Gallium atoms, each with one fewer proton than a silicon atom, each becomes a fixed positive ion, and neutrality means a few extra electrons will be available ...
... Doped with Boron, Aluminum or Gallium atoms, each with one fewer proton than a silicon atom, each becomes a fixed positive ion, and neutrality means a few extra electrons will be available ...
Thursday, Aug. 25, 2011
... You will earn your grade in this class. – You will need to put in sufficient time and sincere efforts – Exams and quizzes will be tough!! • Sometimes problems might not look exactly like what you learned in the class • Just putting the right answer in free response problems does not work! ...
... You will earn your grade in this class. – You will need to put in sufficient time and sincere efforts – Exams and quizzes will be tough!! • Sometimes problems might not look exactly like what you learned in the class • Just putting the right answer in free response problems does not work! ...
Monday, 5 September, Lecture 1, Introduction to Physics - RIT
... o Nuclear (strong) and nuclear (weak) forces ...
... o Nuclear (strong) and nuclear (weak) forces ...
Chapter 1 THE NATURE OF PHYSICS
... is the science, which seeks to understand the properties of inanimate matter, the laws of motion, and the processes of converting energy. - is once called nature philosophy, is the discipline of science most directly concerned with the fundamental laws of nature. According to one of definitions, phy ...
... is the science, which seeks to understand the properties of inanimate matter, the laws of motion, and the processes of converting energy. - is once called nature philosophy, is the discipline of science most directly concerned with the fundamental laws of nature. According to one of definitions, phy ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.