Lecture 6: Maxwell´s Equations
... Example 6.1: In a conductive material we may assume that the conductive current density is much greater than the displacement current density. Show that the Maxwell’s equations can be put in a form of a Diffusion equation in this material. B ...
... Example 6.1: In a conductive material we may assume that the conductive current density is much greater than the displacement current density. Show that the Maxwell’s equations can be put in a form of a Diffusion equation in this material. B ...
File
... Newton’s third law is action and reaction- the action of the gas leaving the bottom of the rocket pushing down towards earth then has the reaction of the gas against the rocket pushing the rocket towards the sky. ...
... Newton’s third law is action and reaction- the action of the gas leaving the bottom of the rocket pushing down towards earth then has the reaction of the gas against the rocket pushing the rocket towards the sky. ...
IGCSE-12-Forces&Shape
... Drag is a more general term used for the opposition force in any gas or liquid. Objects are often streamlined to reduce this force. ...
... Drag is a more general term used for the opposition force in any gas or liquid. Objects are often streamlined to reduce this force. ...
Section 2 What Is a Force?
... Forces acting on an object can be combined and may cause changes in motion. ...
... Forces acting on an object can be combined and may cause changes in motion. ...
Carriers of negative electricity J.
... have air saturated with water vapour and cool it, so that it would be supersaturated if there were no deposition of moisture, we know that if any dust is present, the particles of dust act as nuclei round which the water condenses and we get the familiar phenomena of fog and rain. If the air is quit ...
... have air saturated with water vapour and cool it, so that it would be supersaturated if there were no deposition of moisture, we know that if any dust is present, the particles of dust act as nuclei round which the water condenses and we get the familiar phenomena of fog and rain. If the air is quit ...
CT15a
... Answer: The Hoop has the larger I about the pivot than the Disk, so the hoop has the longer period T. Ihoop, edge pivot = Icm + MR2 = MR2+MR2=2MR2, Idisk, edge pivot = (1/2) MR2+MR2=(3/2)MR2. On the moon, is the period different than on the Earth? A: longer on Moon B: shorter C: The periods are the ...
... Answer: The Hoop has the larger I about the pivot than the Disk, so the hoop has the longer period T. Ihoop, edge pivot = Icm + MR2 = MR2+MR2=2MR2, Idisk, edge pivot = (1/2) MR2+MR2=(3/2)MR2. On the moon, is the period different than on the Earth? A: longer on Moon B: shorter C: The periods are the ...
3_Newton_s_Laws_1_2
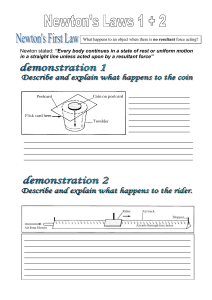
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
... _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.