Electricity
... 2) Ryan flies to Belgium. His aeroplane has a maximum acceleration on the ground of 3.4ms-2. What is the minimum length of runway needed to reach its take off speed of 110ms-1 and how long will this take? 3) Luke likes watching kangaroos. A kangaroo jumps to a vertical height of 2.8m. For how long w ...
... 2) Ryan flies to Belgium. His aeroplane has a maximum acceleration on the ground of 3.4ms-2. What is the minimum length of runway needed to reach its take off speed of 110ms-1 and how long will this take? 3) Luke likes watching kangaroos. A kangaroo jumps to a vertical height of 2.8m. For how long w ...
Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force Problems
... 6. A flea gets its thrills by riding on the outer edge of a golden oldies record album of radius 15 cm as it is being played with a rotational period of 1.8 seconds. What is the flea’s centripetal acceleration? 7. A 0.100 kg mass is attached to a string 75 cm long and swings in a horizontal circle, ...
... 6. A flea gets its thrills by riding on the outer edge of a golden oldies record album of radius 15 cm as it is being played with a rotational period of 1.8 seconds. What is the flea’s centripetal acceleration? 7. A 0.100 kg mass is attached to a string 75 cm long and swings in a horizontal circle, ...
Lesson 12 questions – Centripetal Force - science
... M = 16π 2R3/GT2 M = (16π 2(0.5x1011)3)/((6.6710-11)86400002) ...
... M = 16π 2R3/GT2 M = (16π 2(0.5x1011)3)/((6.6710-11)86400002) ...
Momentum and Impulse
... the objects bounce off of each other or separate. They then return to their original shape. Kinetic energy is conserved. • Many collisions are neither completely elastic or inelastic. They separate after the collision but do not return to their original shape, so heat is created and kinetic energy i ...
... the objects bounce off of each other or separate. They then return to their original shape. Kinetic energy is conserved. • Many collisions are neither completely elastic or inelastic. They separate after the collision but do not return to their original shape, so heat is created and kinetic energy i ...
Sources of the Magnetic Field
... If the charge is in fact moving then the charge also generates a magnetic field The magnetic field generated by the charge however does not behave in the same way the electric field of the charge does ...
... If the charge is in fact moving then the charge also generates a magnetic field The magnetic field generated by the charge however does not behave in the same way the electric field of the charge does ...
Chapter 28
... A final caution: These results for a current loop only apply on the axis of the loop Physics 231 ...
... A final caution: These results for a current loop only apply on the axis of the loop Physics 231 ...
PHYS114_lecture_slides_Part2
... 1. Comment on whether the following label should be cause for concern: CAUTION: the mass of this product pulls on every other mass in the universe! 2. What would be the path of the Moon if somehow all gravitational forces on it vanished to zero? 3. A friend says that astronauts are weightless in orb ...
... 1. Comment on whether the following label should be cause for concern: CAUTION: the mass of this product pulls on every other mass in the universe! 2. What would be the path of the Moon if somehow all gravitational forces on it vanished to zero? 3. A friend says that astronauts are weightless in orb ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... 3. On a frictionless surface, two boxes with the masses shown are pushed together by a force with magnitude F. What is the force that the larger mass block exerts on the smaller mass block? a) F / 3 ...
... 3. On a frictionless surface, two boxes with the masses shown are pushed together by a force with magnitude F. What is the force that the larger mass block exerts on the smaller mass block? a) F / 3 ...
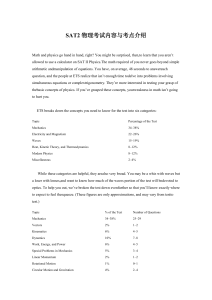
SAT2物理词汇完整版
... Math and physics go hand in hand, right? You might be surprised, then,to learn that you aren’t allowed to use a calculator on SAT II Physics.The math required of you never goes beyond simple arithmetic andmanipulation of equations. You have, on average, 48 seconds to answereach question, and the peo ...
... Math and physics go hand in hand, right? You might be surprised, then,to learn that you aren’t allowed to use a calculator on SAT II Physics.The math required of you never goes beyond simple arithmetic andmanipulation of equations. You have, on average, 48 seconds to answereach question, and the peo ...
Balanced Forces Worksheet 1
... e. After pushing the box with a constant velocity for a while, you reduce your force to half the value needed to maintain a constant velocity. Draw a new qualitative (no numbers) velocity vs. time graph for the box showing all four periods of time on one graph. ...
... e. After pushing the box with a constant velocity for a while, you reduce your force to half the value needed to maintain a constant velocity. Draw a new qualitative (no numbers) velocity vs. time graph for the box showing all four periods of time on one graph. ...
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
... Momentum has a direction as well as a size, what other quantities have we met that have a direction as well as a size _________________________________________________________________________ So you could say that big, fast objects have lots of momentum but small, slow objects have little momentum. ...
... Momentum has a direction as well as a size, what other quantities have we met that have a direction as well as a size _________________________________________________________________________ So you could say that big, fast objects have lots of momentum but small, slow objects have little momentum. ...
Set #8 - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... inclined at 2.10° with the horizontal at 3.90 m/s and down a road inclined at 4.20° at 7.80 m/s. She then holds on to a moving vehicle and coasts on a level road. What power must the vehicle expend to maintain her speed at 3.10 m/s? Assume that the force of air resistance is proportional to her spee ...
... inclined at 2.10° with the horizontal at 3.90 m/s and down a road inclined at 4.20° at 7.80 m/s. She then holds on to a moving vehicle and coasts on a level road. What power must the vehicle expend to maintain her speed at 3.10 m/s? Assume that the force of air resistance is proportional to her spee ...
Document
... can be considered as the friction foresees with the moment proportional to the angle velocity =P/, where is the rotational coefficient of friction that can be connected with Einstein rotational diffusion coefficient (DR = kT /) and P is the moment of molecule rotation. In the case of small macr ...
... can be considered as the friction foresees with the moment proportional to the angle velocity =P/, where is the rotational coefficient of friction that can be connected with Einstein rotational diffusion coefficient (DR = kT /) and P is the moment of molecule rotation. In the case of small macr ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.