Section 2. Mechanics Course Notes
... (g) solve problems using equations that represent uniformly accelerated motion in a straight line, including the motion of bodies falling in a uniform gravitational field without air resistance If a body falls in a vacuum near the Earths surface it has an acceleration g of freefall ...
... (g) solve problems using equations that represent uniformly accelerated motion in a straight line, including the motion of bodies falling in a uniform gravitational field without air resistance If a body falls in a vacuum near the Earths surface it has an acceleration g of freefall ...
Momentum and Impulse
... Newton’s Second Law can be used to relate the momentum of an object to the resultant force acting on it ...
... Newton’s Second Law can be used to relate the momentum of an object to the resultant force acting on it ...
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
... II. The same work was done to accelerate each from rest. III. Both deliver the same impulse when stopped. Which of the above statements is/are correct? a) I only d) I and III only b) II only e) II and III only c) III only ...
... II. The same work was done to accelerate each from rest. III. Both deliver the same impulse when stopped. Which of the above statements is/are correct? a) I only d) I and III only b) II only e) II and III only c) III only ...
AP® Physics C: Mechanics 2015 Free-Response
... 3 Questions Directions: Answer all three questions. The suggested time is about 15 minutes for answering each of the questions, which are worth 15 points each. The parts within a question may not have equal weight. Show all your work in this booklet in the spaces provided after each part. ...
... 3 Questions Directions: Answer all three questions. The suggested time is about 15 minutes for answering each of the questions, which are worth 15 points each. The parts within a question may not have equal weight. Show all your work in this booklet in the spaces provided after each part. ...
Chapter 30
... There are circuit elements that behave in this manner and they are called inductors and they are used to oppose any change in the current in the circuit ...
... There are circuit elements that behave in this manner and they are called inductors and they are used to oppose any change in the current in the circuit ...
Inductance - UTK Department of Physics and Astronomy
... There are circuit elements that behave in this manner and they are called inductors and they are used to oppose any change in the current in the circuit As to how they actually affect a circuit’s behavior will be discussed shortly ...
... There are circuit elements that behave in this manner and they are called inductors and they are used to oppose any change in the current in the circuit As to how they actually affect a circuit’s behavior will be discussed shortly ...
Chapter 11 Hand Tool Design Guidelines
... • The strategy of lowering the CG prior to takeoff enables the athlete to lengthen the vertical path over which the body is accelerated during takeoff, thus facilitating a high vertical velocity at takeoff. ...
... • The strategy of lowering the CG prior to takeoff enables the athlete to lengthen the vertical path over which the body is accelerated during takeoff, thus facilitating a high vertical velocity at takeoff. ...
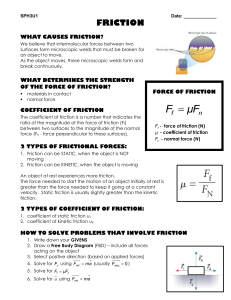
Pull my Strings: Normal Forces, Force Vectors
... •Is the result of contact between two bodies. •Always acts to oppose (slow down) the motion. •Is proportional to the Normal force. •Does not depend on area of contact. Why not? ...
... •Is the result of contact between two bodies. •Always acts to oppose (slow down) the motion. •Is proportional to the Normal force. •Does not depend on area of contact. Why not? ...
Engineering Science - Mechanics Statics – Course Content
... maximum frictional force which can develop between the block and the surface and is termed the static friction. Once the body has started to move then a lesser force P is required to keep the body moving (without accelerating) the friction force which is being overcome is referred to as the dynamic ...
... maximum frictional force which can develop between the block and the surface and is termed the static friction. Once the body has started to move then a lesser force P is required to keep the body moving (without accelerating) the friction force which is being overcome is referred to as the dynamic ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.