Concept. Test
... 3) both the same (N = mg) 4) both the same (0 < N < mg) 5) both the same (N = 0) ...
... 3) both the same (N = mg) 4) both the same (0 < N < mg) 5) both the same (N = 0) ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science Safety
... Gravitation is an attractive force that a mass exerts on every other mass. The strength of the gravitational force between two masses is proportional to the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Explain earth-moon interactions (orbital motion) in terms of forc ...
... Gravitation is an attractive force that a mass exerts on every other mass. The strength of the gravitational force between two masses is proportional to the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Explain earth-moon interactions (orbital motion) in terms of forc ...
Static Electricity - Madison County Schools
... object. An electric field is a region around a charged object in which electric force occurs. ...
... object. An electric field is a region around a charged object in which electric force occurs. ...
Solution
... 4. a) A spring with spring constant k is compressed a distance Δx, and a block of mass m rests against the spring. The block is shot up a plane of length d inclined at angle θ. The coefficient of kinetic friction is μk and static is μs. Find the speed of the block with which it leaves the plane. b) ...
... 4. a) A spring with spring constant k is compressed a distance Δx, and a block of mass m rests against the spring. The block is shot up a plane of length d inclined at angle θ. The coefficient of kinetic friction is μk and static is μs. Find the speed of the block with which it leaves the plane. b) ...
Part I
... • Energy: Traditionally defined as the ability to do work. We now know that not all forces are able to do work; however, we are dealing in these chapters with mechanical energy, which does follow this definition. • Kinetic Energy The energy of motion “Kinetic” Greek word for motion An object in ...
... • Energy: Traditionally defined as the ability to do work. We now know that not all forces are able to do work; however, we are dealing in these chapters with mechanical energy, which does follow this definition. • Kinetic Energy The energy of motion “Kinetic” Greek word for motion An object in ...
Physical Science CRCT Study Guide Notes
... **Standard-S8P2 -Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. • According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed. Energy always comes from somewhere and goes ...
... **Standard-S8P2 -Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of energy a. Explain energy transformation in terms of the Law of Conservation of Energy. • According to the Law of Conservation of Energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed. Energy always comes from somewhere and goes ...
Physical Science CRCT Study Guide Notes
... child pushing to the right with 20 N of force. The box will move in the direction of greater force since the force is unbalanced. * Unbalanced forces are not equal and do not cancel each other out, so cannot result in a net force of zero. Every object exerts gravitational force on every other objec ...
... child pushing to the right with 20 N of force. The box will move in the direction of greater force since the force is unbalanced. * Unbalanced forces are not equal and do not cancel each other out, so cannot result in a net force of zero. Every object exerts gravitational force on every other objec ...
F - AdvancedPlacementPhysicsC
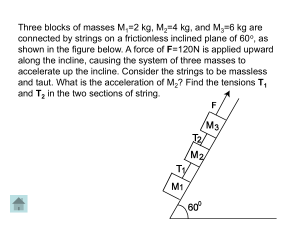
... 1) Three blocks of masses M1=2 kg, M2=4 kg, and M3=6 kg are connected by strings on a frictionless inclined plane of 60 o, as shown in the figure below. A force of F=120N is applied upward along the incline, causing the system of three masses to accelerate up the incline. Consider the strings to be ...
... 1) Three blocks of masses M1=2 kg, M2=4 kg, and M3=6 kg are connected by strings on a frictionless inclined plane of 60 o, as shown in the figure below. A force of F=120N is applied upward along the incline, causing the system of three masses to accelerate up the incline. Consider the strings to be ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.