Standard EPS Shell Presentation
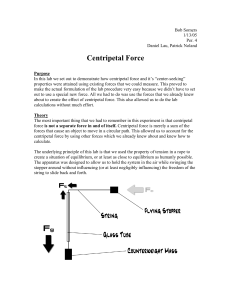
... in the catcher. Case number 3: If the weight is less than the required centripetal force, the ball would move in a larger circle than the track if it could. Instead, the track restrains the ball by exerting a normal force back on the ball, forcing it to follow the circle of the track tightly and the ...
... in the catcher. Case number 3: If the weight is less than the required centripetal force, the ball would move in a larger circle than the track if it could. Instead, the track restrains the ball by exerting a normal force back on the ball, forcing it to follow the circle of the track tightly and the ...
Force of Friction When an object moves or attempts to move along
... When an object moves or attempts to move along another surface, there is a force that opposes this movement called friction. A surface may seem smooth to us when we touch or look at them but as we look with microscopes even the most smooth surface is not truly smooth. As an object slides over anothe ...
... When an object moves or attempts to move along another surface, there is a force that opposes this movement called friction. A surface may seem smooth to us when we touch or look at them but as we look with microscopes even the most smooth surface is not truly smooth. As an object slides over anothe ...
Living Things - Fairfield-Suisun Unified School District
... Elastic Forces What factors determine the strength of the friction force between two surfaces? What factors affect the gravitational force between two objects? Why do objects accelerate during free fall? When is matter considered to be elastic? ...
... Elastic Forces What factors determine the strength of the friction force between two surfaces? What factors affect the gravitational force between two objects? Why do objects accelerate during free fall? When is matter considered to be elastic? ...
Rotational Equilibrium and Dynamics
... • Note that weight doesn’t act at a single point – it is distributed over the entire body • However, we can always calculate the torque due to a body’s weight by assuming that the entire force of gravity (weight) is concentrated at a single point called the center of gravity • If the acceleration of ...
... • Note that weight doesn’t act at a single point – it is distributed over the entire body • However, we can always calculate the torque due to a body’s weight by assuming that the entire force of gravity (weight) is concentrated at a single point called the center of gravity • If the acceleration of ...
click - Uplift Education
... Short wavelength radiation is received from the sun and causes the surface of the Earth to warm up. The Earth will emit infra-red radiation (longer wavelengths than the radiation coming from the sun because the Earth is cooler than the sun). Some of this infra-red radiation is absorbed by gases in t ...
... Short wavelength radiation is received from the sun and causes the surface of the Earth to warm up. The Earth will emit infra-red radiation (longer wavelengths than the radiation coming from the sun because the Earth is cooler than the sun). Some of this infra-red radiation is absorbed by gases in t ...
Momentum and Impulse (PowerPoint)
... pieces impart equal and opposite forces on each other (Newton’s third law) these internal forces cannot provide a net change in momentum so momentum must be conserved in explosions ...
... pieces impart equal and opposite forces on each other (Newton’s third law) these internal forces cannot provide a net change in momentum so momentum must be conserved in explosions ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.