Heading 1 (Arial 14): Title, grouped style
... ignore effectively task-irrelevant events—is a core feature of all efficient information processing. In order to be maximally efficient, attention must be flexible so that it can be responsive to unexpected and potentially significant events outside the focus of attention. Flexibility is achieved by ...
... ignore effectively task-irrelevant events—is a core feature of all efficient information processing. In order to be maximally efficient, attention must be flexible so that it can be responsive to unexpected and potentially significant events outside the focus of attention. Flexibility is achieved by ...
Long term memory & Memory errors
... Rhyming recognition test in retrieval – Both groups presented with the 32 same target word and 32 new words – Indicate whether each word rhymed with one of the words they had heard during acquisition ? – Results : rhyming-task encoding group better » Meaning task would result in deeper processing th ...
... Rhyming recognition test in retrieval – Both groups presented with the 32 same target word and 32 new words – Indicate whether each word rhymed with one of the words they had heard during acquisition ? – Results : rhyming-task encoding group better » Meaning task would result in deeper processing th ...
File4
... • II. pointing trajectories reveal influence of unseen words – Finkbeiner, Song, Nakayama, and Caramazza, Visual Cognition (in press) ...
... • II. pointing trajectories reveal influence of unseen words – Finkbeiner, Song, Nakayama, and Caramazza, Visual Cognition (in press) ...
Color Vision Theories
... • The Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Hering Opponent-colors theory are one-stage models - all of color information processing is accomplished by the initial photopic sensory mechanisms. • The data from hue-cancellation experiments demonstrated that a two-stage model is necessary - a fir ...
... • The Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Hering Opponent-colors theory are one-stage models - all of color information processing is accomplished by the initial photopic sensory mechanisms. • The data from hue-cancellation experiments demonstrated that a two-stage model is necessary - a fir ...
Pattern recognition and visual word forms
... Literate adults group letters together into a single perceptual unit (visual word form). Speed of word recognition is unaffected by the number of letters for 3-6 letter words. Suggests processed in parallel ...
... Literate adults group letters together into a single perceptual unit (visual word form). Speed of word recognition is unaffected by the number of letters for 3-6 letter words. Suggests processed in parallel ...
Making Sense of Internal Logic: Theory and a Case Study
... This implies the presence of a xed point of the description, irrespective of the external world. This is the second extreme case discussed in the Introduction (see also Fig. 1). The functional equation (2) for the internal description of the brain contains a great variety of solutions. When F (Xn ) ...
... This implies the presence of a xed point of the description, irrespective of the external world. This is the second extreme case discussed in the Introduction (see also Fig. 1). The functional equation (2) for the internal description of the brain contains a great variety of solutions. When F (Xn ) ...
Color Vision Theories
... • The Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Hering Opponent-colors theory are one-stage models - all of color information processing is accomplished by the initial photopic sensory mechanisms. • The data from hue-cancellation experiments demonstrated that a two-stage model is necessary - a fir ...
... • The Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic theory and the Hering Opponent-colors theory are one-stage models - all of color information processing is accomplished by the initial photopic sensory mechanisms. • The data from hue-cancellation experiments demonstrated that a two-stage model is necessary - a fir ...
Word Relationship 1 Running head: EFFECTS OF WORD
... will recognize it as a word of his language. This is because there has been a spot in the mental lexicon for that word ever since the person first encountered it. Limitations and Future Research There were several limitations to our study. The sample consisted of mainly 18-22 year old college studen ...
... will recognize it as a word of his language. This is because there has been a spot in the mental lexicon for that word ever since the person first encountered it. Limitations and Future Research There were several limitations to our study. The sample consisted of mainly 18-22 year old college studen ...
Interpretive Information
... This is a nonlinguistic task of visual attention and perception. It also offers information regarding the integrity of the upper and lower quadrants of left and right visual fields. Observe examinees’ scanning strategies. Are they searching laterally from left to right, down and up, or scanning unsy ...
... This is a nonlinguistic task of visual attention and perception. It also offers information regarding the integrity of the upper and lower quadrants of left and right visual fields. Observe examinees’ scanning strategies. Are they searching laterally from left to right, down and up, or scanning unsy ...
Chapter 6: Summary and Discussion
... meaningful concepts of our surroundings and act towards our goals. All our actions are motivated by obtaining reward, be it on the short or longer term, in one form or the other. During this process, through repeated trials and errors, we refine our methods and become more effective in what we do. I ...
... meaningful concepts of our surroundings and act towards our goals. All our actions are motivated by obtaining reward, be it on the short or longer term, in one form or the other. During this process, through repeated trials and errors, we refine our methods and become more effective in what we do. I ...
Serial position effect
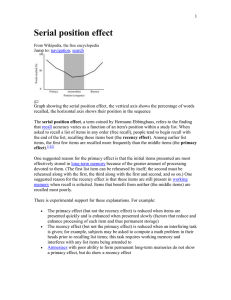
... The primacy effect, in psychology and sociology, is a cognitive bias that results from disproportionate salience of initial stimuli or observations. For example, a subject who reads a sufficiently long list of words is more likely to remember words toward the beginning than words in the middle. The ...
... The primacy effect, in psychology and sociology, is a cognitive bias that results from disproportionate salience of initial stimuli or observations. For example, a subject who reads a sufficiently long list of words is more likely to remember words toward the beginning than words in the middle. The ...
More is more: The relationship between vocabulary size and word
... learn some word types than others. Heibeck and Markman (1987) found that children did not learn as much about color or texture words as they learned about shape words when given the same amount of exposure to each word type. Similarly, O’Hanlon and Roberson (2007) found that 3-yearolds learned shape ...
... learn some word types than others. Heibeck and Markman (1987) found that children did not learn as much about color or texture words as they learned about shape words when given the same amount of exposure to each word type. Similarly, O’Hanlon and Roberson (2007) found that 3-yearolds learned shape ...
improving memory
... their colors. • Don’t read the words, just say the colors they’re printed in and as fast as you can • This is called the stroop effect – interference in the reaction time of a task. ...
... their colors. • Don’t read the words, just say the colors they’re printed in and as fast as you can • This is called the stroop effect – interference in the reaction time of a task. ...
TP_2005FK
... must suggest that this color preference must be innate (Kinoshita et al., 1998).1 After training the butterflies the results showed clearly that butterflies were attracted more to their respective trained color. The study also tested if the swallowtail butterfly would respond to the same color stimu ...
... must suggest that this color preference must be innate (Kinoshita et al., 1998).1 After training the butterflies the results showed clearly that butterflies were attracted more to their respective trained color. The study also tested if the swallowtail butterfly would respond to the same color stimu ...
Prefrontal cortex and diverse functions Keiji Tanaka The prefrontal
... have problems in planning (e.g., in the tower of London task) and in reasoning (e.g., in the Raven’s progressive matrices test). Because the planning and reasoning require working memory, the problems in planning and reasoning may be due to their weaker working memory capacity. Patients with damage ...
... have problems in planning (e.g., in the tower of London task) and in reasoning (e.g., in the Raven’s progressive matrices test). Because the planning and reasoning require working memory, the problems in planning and reasoning may be due to their weaker working memory capacity. Patients with damage ...
Paper Template for Pre
... The French physicians of XIX century Poeg and Plezanton have found out, that blue and violet beams render analgesic effect and can be applied as treatment of neuralgic diseases. Color is defined by wavelength of EM radiation. Color can be perceived not only cells of a retina of an eye, but also a su ...
... The French physicians of XIX century Poeg and Plezanton have found out, that blue and violet beams render analgesic effect and can be applied as treatment of neuralgic diseases. Color is defined by wavelength of EM radiation. Color can be perceived not only cells of a retina of an eye, but also a su ...
Sensation
... • Transduction – process by which sensory information is transformed into neural impulses. • Adaptation – the decreasing response of a sense when they are exposed to continuous stimulation. • Opponent-process theory – The thalamus of the brain responds to two pairs of colors (red/green and blue/yell ...
... • Transduction – process by which sensory information is transformed into neural impulses. • Adaptation – the decreasing response of a sense when they are exposed to continuous stimulation. • Opponent-process theory – The thalamus of the brain responds to two pairs of colors (red/green and blue/yell ...
Lecture S&P
... “on” and “off” regions Complex – also rectangular, larger receptive fields, respond best to a particular stimulus anywhere in its receptive field ...
... “on” and “off” regions Complex – also rectangular, larger receptive fields, respond best to a particular stimulus anywhere in its receptive field ...
Sussillo, David Recurrent Neural Network Dynamics Mar
... see big evidence of color representation on the color trials... (but irrelevant stim is ALSO repres (to our surprise)) irrelevant dimension IS repres in this population despite the fact that it is irelevant... context is a 4th dimension the first 3 Ds are motion, color, and choice... according to an ...
... see big evidence of color representation on the color trials... (but irrelevant stim is ALSO repres (to our surprise)) irrelevant dimension IS repres in this population despite the fact that it is irelevant... context is a 4th dimension the first 3 Ds are motion, color, and choice... according to an ...
Summary
... meaningful concepts of our surroundings and act towards our goals. All our actions are motivated by obtaining reward, be it on the short or longer term, in one form or the other. During this process, through repeated trials and errors, we refine our methods and become more effective in what we do. I ...
... meaningful concepts of our surroundings and act towards our goals. All our actions are motivated by obtaining reward, be it on the short or longer term, in one form or the other. During this process, through repeated trials and errors, we refine our methods and become more effective in what we do. I ...
Coding of Visual Information in the Retina Coding of Light d D k and
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
Poster
... The history of prior action in the human motor system is known to influence not only future performance through memory, but also the capacity for future learning. Interference and savings are two oppositelydirected phenomena that produce this effect. Interference describes the ability of one task t ...
... The history of prior action in the human motor system is known to influence not only future performance through memory, but also the capacity for future learning. Interference and savings are two oppositelydirected phenomena that produce this effect. Interference describes the ability of one task t ...
Process Dissociation, Cognitive Architecture, and Response Time
... specific context conditions in which the experiment was run. Process dissociation is typically embedded in two or more sets of context conditions to test how changes in context affect the relationship between Process 1 and Process 2. For instance, Jacoby et al. (1993) dissociated retrieval processes ...
... specific context conditions in which the experiment was run. Process dissociation is typically embedded in two or more sets of context conditions to test how changes in context affect the relationship between Process 1 and Process 2. For instance, Jacoby et al. (1993) dissociated retrieval processes ...
Perspectives on Cognitive Neuroscience
... The third example of a link between brain and cognition comes from research on how form, motion, and color information are processed in the visual system. If different parts of the system are specialized for different tasks, for example, for motion or color, then there should be conditions under whi ...
... The third example of a link between brain and cognition comes from research on how form, motion, and color information are processed in the visual system. If different parts of the system are specialized for different tasks, for example, for motion or color, then there should be conditions under whi ...
Hearing (sound waves)
... before being transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. • The opponent process theory explains perception within the ganglion cells, thalamus and visual cortex. ...
... before being transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. • The opponent process theory explains perception within the ganglion cells, thalamus and visual cortex. ...
Stroop effect

In psychology, the Stroop effect is a demonstration of interference in the reaction time of a task. When the name of a color (e.g., ""blue"", ""green"", or ""red"") is printed in a color not denoted by the name (e.g., the word ""red"" printed in blue ink instead of red ink), naming the color of the word takes longer and is more prone to errors than when the color of the ink matches the name of the color. The effect is named after John Ridley Stroop, who first published the effect in English in 1935. The effect had previously been published in Germany in 1929. The original paper has been one of the most cited papers in the history of experimental psychology, leading to more than 701 replications. The effect has been used to create a psychological test (Stroop test) that is widely used in clinical practice and investigation.