recommendedBooks
... Nate Silver, The Signal and the Noise: Why So Many Predictions Fail – but Some Don’t, Penguin Press (2012) Nassim Nicholas Taleb, The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable, 2nd edition, Random House (2010) http://www.wimp.com/hilarious-probability/ Bangkok insurance ...
... Nate Silver, The Signal and the Noise: Why So Many Predictions Fail – but Some Don’t, Penguin Press (2012) Nassim Nicholas Taleb, The Black Swan: The Impact of the Highly Improbable, 2nd edition, Random House (2010) http://www.wimp.com/hilarious-probability/ Bangkok insurance ...
Probability - s3.amazonaws.com
... A score of two can only be obtained in one way – a 1 on each dice. A score of three can be obtained in two ways – 1 and 2 or 2 and 1, so the three is twice as likely. ...
... A score of two can only be obtained in one way – a 1 on each dice. A score of three can be obtained in two ways – 1 and 2 or 2 and 1, so the three is twice as likely. ...
Fun Facts about discrete random variables and logs
... RANDOM VARIABLES. A random variable is a variable whose value is determined by random chance (often denoted by a capital letter). A discrete random variable can assume one of only a discrete set of values (e.g., X = "the outcome of the roll of a die" or Y = "the number of A1 alleles found at locus A ...
... RANDOM VARIABLES. A random variable is a variable whose value is determined by random chance (often denoted by a capital letter). A discrete random variable can assume one of only a discrete set of values (e.g., X = "the outcome of the roll of a die" or Y = "the number of A1 alleles found at locus A ...
Probability of Independent Events
... • Independent event - two events whose occurrence of one event DOES NOT affect the likelihood that the other event will occur • Examples: – Fliping a coin and spinning a spinner – drawling a marble, replacing it, and then drawling another marble – a girl puppy is born first and a boy puppy is born s ...
... • Independent event - two events whose occurrence of one event DOES NOT affect the likelihood that the other event will occur • Examples: – Fliping a coin and spinning a spinner – drawling a marble, replacing it, and then drawling another marble – a girl puppy is born first and a boy puppy is born s ...
Probability Unit
... A game consists of rolling a colored die with three red sides, two green sides, and one blue side. A roll of red loses. A role of green pays $2.00. A roll of blue pays $5.00. The charge to play the game is $2.00. Would you play the game? Why or why not? ...
... A game consists of rolling a colored die with three red sides, two green sides, and one blue side. A roll of red loses. A role of green pays $2.00. A roll of blue pays $5.00. The charge to play the game is $2.00. Would you play the game? Why or why not? ...
union
... selected household is prosperous and B the event that it is educated. According to the Current Population Survey, P(A) = 0.138, P(B) = 0.261, and the probability that a household is both prosperous and educated is P(A and B) = 0.082. 1) What is the conditional probability that the household selected ...
... selected household is prosperous and B the event that it is educated. According to the Current Population Survey, P(A) = 0.138, P(B) = 0.261, and the probability that a household is both prosperous and educated is P(A and B) = 0.082. 1) What is the conditional probability that the household selected ...
Review for the Final
... The following questions are a sample exam similar to the content and length of the actual exam. (Note that this sample exam does not cover every possible topic listed above.) 1. A die is rolled 5 times. How many different sequences of rolls are possible if: (a) the die never lands on 4? (b) the die ...
... The following questions are a sample exam similar to the content and length of the actual exam. (Note that this sample exam does not cover every possible topic listed above.) 1. A die is rolled 5 times. How many different sequences of rolls are possible if: (a) the die never lands on 4? (b) the die ...
00i_GEOCRMC13_890522.indd
... Events Events If two events cannot happen at the same time, and Mutually Exclusive therefore have no common outcomes, they are said to be mutually exclusive. The following are the Addition Rules for Probability: Probability of Mutually Exclusive Events ...
... Events Events If two events cannot happen at the same time, and Mutually Exclusive therefore have no common outcomes, they are said to be mutually exclusive. The following are the Addition Rules for Probability: Probability of Mutually Exclusive Events ...
Probability in the many-worlds interpretation
... 2. As noted above, decision theory does not usually fix a unique probability measure over the set of States; it is usually possible for two ideally rational agents to have different probability measures. To obtain this feature in the Everettian case, Deutsch and Wallace must therefore be adding some ...
... 2. As noted above, decision theory does not usually fix a unique probability measure over the set of States; it is usually possible for two ideally rational agents to have different probability measures. To obtain this feature in the Everettian case, Deutsch and Wallace must therefore be adding some ...
Private-Key Quantum Money
... public-key quantum money, to go back and solve open problems about private-key quantum money “Open problems? About private-key quantum money?” 1. Are the Wiesner and BBBW schemes really secure? 2. Does every private-key money scheme require either a giant database, or else a computational assumption ...
... public-key quantum money, to go back and solve open problems about private-key quantum money “Open problems? About private-key quantum money?” 1. Are the Wiesner and BBBW schemes really secure? 2. Does every private-key money scheme require either a giant database, or else a computational assumption ...
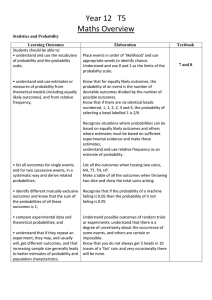
T5 Statistics and Probability
... • identify different mutually exclusive outcomes and know that the sum of the probabilities of all these outcomes is 1; ...
... • identify different mutually exclusive outcomes and know that the sum of the probabilities of all these outcomes is 1; ...
PowerPoint
... Dealing with Random Phenomena • A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen, but we don’t know which particular outcome did or will happen. • When dealing with probability, we will be dealing with many random phenomena. • Examples:: Die, Coin, Cards, Survey, Experi ...
... Dealing with Random Phenomena • A random phenomenon is a situation in which we know what outcomes could happen, but we don’t know which particular outcome did or will happen. • When dealing with probability, we will be dealing with many random phenomena. • Examples:: Die, Coin, Cards, Survey, Experi ...
Statistics (Data) and Probability (Chance)
... If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well enough. ...
... If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well enough. ...