Each football game begins with a coin toss in the presence of the
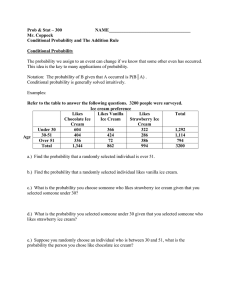
... 3. A breeder records probabilities for two variables in a population of animals using the two-way table given here. Given that an animal is brown-haired, what is the probability that it's short-haired? Brown-haired Short-haired Shaggy ...
... 3. A breeder records probabilities for two variables in a population of animals using the two-way table given here. Given that an animal is brown-haired, what is the probability that it's short-haired? Brown-haired Short-haired Shaggy ...
Notes on Special Discrete Distributions
... and var(X) = E(X 2 ) − [E(X)]2 works out to give var(X) = r(1 − p)/p2 . The cdf, F (x), can be obtained from p(x) in the usual way, as a summation, but has no nice closed formula. A NegBin(r, p) random variable X can be thought of as the number of trials until the rth success when independent trials ...
... and var(X) = E(X 2 ) − [E(X)]2 works out to give var(X) = r(1 − p)/p2 . The cdf, F (x), can be obtained from p(x) in the usual way, as a summation, but has no nice closed formula. A NegBin(r, p) random variable X can be thought of as the number of trials until the rth success when independent trials ...
Chapter 4: Probability Rare Event Rule for Inferential Statistics Rare
... • For the complete set of distinct possible outcomes of a random circumstance, the total of the assigned probabilities must equal 1. ...
... • For the complete set of distinct possible outcomes of a random circumstance, the total of the assigned probabilities must equal 1. ...
Conceptions of Determinism in Radical Behaviorism
... Nevin (1991) and Baum (1994) have also uttered statements that appear to be compatible with metaphysical determinism. Nevin (1991), for instance, has made clear: “According to the most central tenets of our creed, all behavior is determined by genetic and environmental processes” (p. 36). Similarly, ...
... Nevin (1991) and Baum (1994) have also uttered statements that appear to be compatible with metaphysical determinism. Nevin (1991), for instance, has made clear: “According to the most central tenets of our creed, all behavior is determined by genetic and environmental processes” (p. 36). Similarly, ...
Problem Sheet 6
... (d) [For further exploration! ] In lectures we considered a simple random walk, which at each step goes up with probability p and down with probability 1 − p. Suppose the walk starts from site 1. By taking limits in the gambler’s ruin model, we showed that the probability that the walk ever hits sit ...
... (d) [For further exploration! ] In lectures we considered a simple random walk, which at each step goes up with probability p and down with probability 1 − p. Suppose the walk starts from site 1. By taking limits in the gambler’s ruin model, we showed that the probability that the walk ever hits sit ...
Dane Rudhyar and Alan Leo Platonistic roots
... than the one fixed from eternity is impossible1. This definition of determinism is Laplacian (if all the laws of the universe are known and all the knowledge of the universe is known then all future events can also be known – the universe is complicated but ultimately understandable like a machine). ...
... than the one fixed from eternity is impossible1. This definition of determinism is Laplacian (if all the laws of the universe are known and all the knowledge of the universe is known then all future events can also be known – the universe is complicated but ultimately understandable like a machine). ...
Alliance Class
... • What are the chances of seeing an elephant a the zoo? Exploring the meaning of the probability of event A occurring • What’s in the Bag? Experimental probability vs. theoretical probability ...
... • What are the chances of seeing an elephant a the zoo? Exploring the meaning of the probability of event A occurring • What’s in the Bag? Experimental probability vs. theoretical probability ...
Introduction Introduction to probability theory
... Combinatorial results then helps us to derive the following probabilities for X. ...
... Combinatorial results then helps us to derive the following probabilities for X. ...
(1) Probability distribution: Consider the two probability density
... (8) Mortality is often highly age dependent. Suppose that the probability of dying at age x (in years) is p(x) = C(1 + (x − 20)2 ) where 0 < x < 100. (a) Find the constant C. (b) Find the fraction of the population that has died by age 20. (c) Find the fraction of the population that has died by age ...
... (8) Mortality is often highly age dependent. Suppose that the probability of dying at age x (in years) is p(x) = C(1 + (x − 20)2 ) where 0 < x < 100. (a) Find the constant C. (b) Find the fraction of the population that has died by age 20. (c) Find the fraction of the population that has died by age ...
Discrete Distributions
... 2. There are a fixed number of trials 3. Outcomes of different trials are independent 4. The probability that a trial results in success is the same for all trials The binomial random variable x is defined as the number of successes out of the fixed number ...
... 2. There are a fixed number of trials 3. Outcomes of different trials are independent 4. The probability that a trial results in success is the same for all trials The binomial random variable x is defined as the number of successes out of the fixed number ...