Scott Foresman Science
... There are different kinds of root systems. Each system has its own structures. A taproot is one system. It is a large root that grows straight down. It remains the largest root structure as the plant grows. Taproots may store food for the plant. Smaller roots may grow sideways out of the main taproo ...
... There are different kinds of root systems. Each system has its own structures. A taproot is one system. It is a large root that grows straight down. It remains the largest root structure as the plant grows. Taproots may store food for the plant. Smaller roots may grow sideways out of the main taproo ...
Cell Structure
... • Water is split by an enzyme • Electrons extracted from water fill “hole”in chlorophyll A • H+ stay w/in thylakoid space • Oxygen released into atmosphere ...
... • Water is split by an enzyme • Electrons extracted from water fill “hole”in chlorophyll A • H+ stay w/in thylakoid space • Oxygen released into atmosphere ...
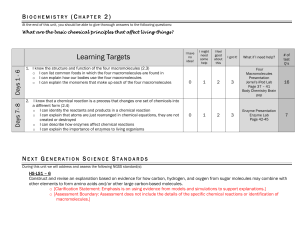
Macromolecule Packet
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
... 25. __________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings (cuticle) on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carb ...
Aerobic Respiration
... Reduced NAD and reduced FAD donate hydrogen atoms. The carriers become re oxidised in the process (due to loss of hydrogen) and return to glycolysis, link reaction or the krebs cycle to collect more hydrogen The hydrogen atoms split into protons (H+) and electrons. (occurs in the matrix) The electro ...
... Reduced NAD and reduced FAD donate hydrogen atoms. The carriers become re oxidised in the process (due to loss of hydrogen) and return to glycolysis, link reaction or the krebs cycle to collect more hydrogen The hydrogen atoms split into protons (H+) and electrons. (occurs in the matrix) The electro ...
PDF Datastream - Brown Digital Repository
... The slow muscles are more efficient at using oxygen to generate more fuel (known as ATP) for continuous, extended muscle contractions over a long time. They fire more slowly than fast twitch fibers and can go for a long time before they fatigue. Therefore, slow twitch fibers are great at helping ...
... The slow muscles are more efficient at using oxygen to generate more fuel (known as ATP) for continuous, extended muscle contractions over a long time. They fire more slowly than fast twitch fibers and can go for a long time before they fatigue. Therefore, slow twitch fibers are great at helping ...
Tropism
... respond to touch, light, and gravity because they have hormones. A hormone produced by a plant is a chemical that affects they way that they grow and develop. ...
... respond to touch, light, and gravity because they have hormones. A hormone produced by a plant is a chemical that affects they way that they grow and develop. ...
Lecture_3_17012017
... Oxidation of the carbon atom may form a compound with high phosphoryl-transfer potential that can then be used to synthesize ATP. The energy released when carbon 1 (shown in red) of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is oxidized can be captured first as1,3-bisphosphoglycerate and then as ATP. ...
... Oxidation of the carbon atom may form a compound with high phosphoryl-transfer potential that can then be used to synthesize ATP. The energy released when carbon 1 (shown in red) of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is oxidized can be captured first as1,3-bisphosphoglycerate and then as ATP. ...
Ch.9cellrespiration
... chain) is a series of reduction/oxidation reactions Enzymes embedded in mitochondrial membranes ...
... chain) is a series of reduction/oxidation reactions Enzymes embedded in mitochondrial membranes ...
Energy-FLow-and-Cycles1516-rev1
... Air is about 78% nitrogen gas (N2). That’s where most of the nitrogen hangs out. Most organisms can’t use atmospheric (free) nitrogen as is. They need it changed into nitrogen compounds. Plants need their nitrogen "fixed", which means as part of compounds such as: ammonia (NH3) urea (NH2)2CO nitrate ...
... Air is about 78% nitrogen gas (N2). That’s where most of the nitrogen hangs out. Most organisms can’t use atmospheric (free) nitrogen as is. They need it changed into nitrogen compounds. Plants need their nitrogen "fixed", which means as part of compounds such as: ammonia (NH3) urea (NH2)2CO nitrate ...
the chemical basis of the body
... The sugar portion of the molecule is a pentose sugar, ribose. ...
... The sugar portion of the molecule is a pentose sugar, ribose. ...
BSCA Questions: Biochemistry
... What would a DNA dependent RNA polymerase make? A. DNA from DNA B. DNA from RNA C. RNA from DNA D. RNA from RNA ...
... What would a DNA dependent RNA polymerase make? A. DNA from DNA B. DNA from RNA C. RNA from DNA D. RNA from RNA ...
3.7 Cell Respiration
... Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic molecules in cells to form ATP. 2. State the equation for the process of cell respiration. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy 3. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic in terms of cell respiration. Outline the general process of ...
... Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic molecules in cells to form ATP. 2. State the equation for the process of cell respiration. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy 3. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic in terms of cell respiration. Outline the general process of ...
Biology 4A Exam 2 Study Guide The exam will consist of multiple
... • How do plants capture light energy? Your answer should include the following terms: photon, antanna complex, reaction center, photosystem I & II, electrons, wavelengths, pigments • Compare photophosphorylation with oxidative phosphorylation (from cellular respiration). What are the similarities? ...
... • How do plants capture light energy? Your answer should include the following terms: photon, antanna complex, reaction center, photosystem I & II, electrons, wavelengths, pigments • Compare photophosphorylation with oxidative phosphorylation (from cellular respiration). What are the similarities? ...
Macromolecule Notes - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
... • By adding this group, a portion of the molecule becomes hydrophobic (the tails) and portion is now hydrophilic (the head). So what? Now this molecule can be used as a type of sack. When dropped in water, they form spheres with the heads facing the water and tails facing inside. ...
... • By adding this group, a portion of the molecule becomes hydrophobic (the tails) and portion is now hydrophilic (the head). So what? Now this molecule can be used as a type of sack. When dropped in water, they form spheres with the heads facing the water and tails facing inside. ...
Spotlight on Metabolism Ans
... First, triglycerides are separated into glycerol and three fatty acids. Glycerol forms pyruvate and can be broken down to yield a small amount of energy. Beta-oxidation breaks down fatty acid chains to two-carbon links that form acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. Beta-oxidation and the ...
... First, triglycerides are separated into glycerol and three fatty acids. Glycerol forms pyruvate and can be broken down to yield a small amount of energy. Beta-oxidation breaks down fatty acid chains to two-carbon links that form acetyl CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle. Beta-oxidation and the ...
protist-plankton-of-the-ocean
... • A group of dinoflagellates called zooxanthellae live in close association with animals such as coral, sea anenomes, sponges and giant clams • Symbiotic: zooxanthellae photosynthesize within the body of an animal host, releasing organic matter and receiving nutrients (in the form of waste products) ...
... • A group of dinoflagellates called zooxanthellae live in close association with animals such as coral, sea anenomes, sponges and giant clams • Symbiotic: zooxanthellae photosynthesize within the body of an animal host, releasing organic matter and receiving nutrients (in the form of waste products) ...
Macromolecule Notes Powerpoint
... • By adding this group, a portion of the molecule becomes hydrophobic (the tails) and portion is now hydrophilic (the head). So what? Now this molecule can be used as a type of sack. When dropped in water, they form spheres with the heads facing the water and tails facing inside. ...
... • By adding this group, a portion of the molecule becomes hydrophobic (the tails) and portion is now hydrophilic (the head). So what? Now this molecule can be used as a type of sack. When dropped in water, they form spheres with the heads facing the water and tails facing inside. ...
Physics 107 Exam #3 October 13, 1994 Your name: Multiple Choice
... 4. We cannot think of the electron as orbiting the nucleus in any conventional sense because (a) the Pauli exclusion principle prevents us from exactly specifying the electron's position, (b) the radial part of the electron's wave function is independent of the orbital angle, (c) the Heisenberg unce ...
... 4. We cannot think of the electron as orbiting the nucleus in any conventional sense because (a) the Pauli exclusion principle prevents us from exactly specifying the electron's position, (b) the radial part of the electron's wave function is independent of the orbital angle, (c) the Heisenberg unce ...
How many grams of oxygen are made if 3.75 moles of KClO 3
... 12. There is 3.61 X 10-2 g of caffeine in a shot of espresso. The chemical formula of caffeine is C8H1N4O2. Determine the moles of caffeine in a tall coffee that has 1 shot of espresso. Acetaminophen, the active ingredient in Tylenol, has the formula C8H9NO2. Determine the number of molecules of ace ...
... 12. There is 3.61 X 10-2 g of caffeine in a shot of espresso. The chemical formula of caffeine is C8H1N4O2. Determine the moles of caffeine in a tall coffee that has 1 shot of espresso. Acetaminophen, the active ingredient in Tylenol, has the formula C8H9NO2. Determine the number of molecules of ace ...
PRINCIPLES OF LIGHT
... Beginning to get good seedling growth when under bench lights are within inches of leaf tips (awkward watering) Possible unexpected negative or positivethree Odonts out of approx 20 in spike have apical spike from top of pseudobulb in contrast with previous experience of one of about 200 in 30 years ...
... Beginning to get good seedling growth when under bench lights are within inches of leaf tips (awkward watering) Possible unexpected negative or positivethree Odonts out of approx 20 in spike have apical spike from top of pseudobulb in contrast with previous experience of one of about 200 in 30 years ...
Notes
... Four pairs of hydrogen atoms are also produced by the reduction of 3 NAD and one FAD molecules. Some ATP is also produced NADH and FADH2 are eventually used in the electron transport chain to produce additional ATP. The electron transport chain is a series of electron transport molecules attached to ...
... Four pairs of hydrogen atoms are also produced by the reduction of 3 NAD and one FAD molecules. Some ATP is also produced NADH and FADH2 are eventually used in the electron transport chain to produce additional ATP. The electron transport chain is a series of electron transport molecules attached to ...
Principles of Ecology
... process of death and decay by bacteria. Lightning and certain bacteria convert the nitrogen in the air into more usable ...
... process of death and decay by bacteria. Lightning and certain bacteria convert the nitrogen in the air into more usable ...
energy flow
... Only plants, some algae and certain bacteria can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use that energy to produce food. These organisms are autotrophs (producers). called ___________ ...
... Only plants, some algae and certain bacteria can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use that energy to produce food. These organisms are autotrophs (producers). called ___________ ...
Ecosystems - St. Joan of Arc School
... An ecosystem is all living things from plants and animals to microscopic organisms that share an environment. It is formed by the interaction between biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) things. An ecosystem can be small, like a single log, or very large, like a forest. All living things in an ec ...
... An ecosystem is all living things from plants and animals to microscopic organisms that share an environment. It is formed by the interaction between biotic (living) and abiotic (nonliving) things. An ecosystem can be small, like a single log, or very large, like a forest. All living things in an ec ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.