Structure and Function of Plants Review
... 2. When you eat the following, what plant structure are you consuming? Brussels sprouts, celery sticks, onions, and carrot sticks. 3. Characterize the role of each of the three tissue systems in a leaf. 4. Describe at least three specializations in plant organs and plant cells that are adaptations t ...
... 2. When you eat the following, what plant structure are you consuming? Brussels sprouts, celery sticks, onions, and carrot sticks. 3. Characterize the role of each of the three tissue systems in a leaf. 4. Describe at least three specializations in plant organs and plant cells that are adaptations t ...
Chapter 8 - Energy and Enzymes
... A hydrogen ion gradient is also used to produce ATP in the chloroplast (diagram below). In this case, sunlight provides energy to pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid. The energy of their movement back into the stroma by osmotic pressure is used to produce ATP. The enzyme that uses a hydrogen ion ...
... A hydrogen ion gradient is also used to produce ATP in the chloroplast (diagram below). In this case, sunlight provides energy to pump hydrogen ions into the thylakoid. The energy of their movement back into the stroma by osmotic pressure is used to produce ATP. The enzyme that uses a hydrogen ion ...
word - marric
... converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Glucose is a monomer (single unit) which when bonded with other glucose monomers form polymers of glucose such as starch, cellulose, glycogen (short term energy in animal cells). The next energy converting process that is used by cells involves ...
... converted into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Glucose is a monomer (single unit) which when bonded with other glucose monomers form polymers of glucose such as starch, cellulose, glycogen (short term energy in animal cells). The next energy converting process that is used by cells involves ...
Fungi and plants practice
... 33. The mycorrhizae found interacting with the roots of land plants are A. pathogens, feeding on plant tissue they have damaged with toxins. B. parasites, draining sugar from the plant's vascular system. C. saprophytes, stripping dead tissue from the root. D. symbionts, facilitating the plant's ...
... 33. The mycorrhizae found interacting with the roots of land plants are A. pathogens, feeding on plant tissue they have damaged with toxins. B. parasites, draining sugar from the plant's vascular system. C. saprophytes, stripping dead tissue from the root. D. symbionts, facilitating the plant's ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... of removing an irritant from the sensitive mucous membranes of the nose. Many things can irritate the mucous membranes. Dust, pollen, pepper or even a cold blast of air are just some of the many things that may cause you to ...
... of removing an irritant from the sensitive mucous membranes of the nose. Many things can irritate the mucous membranes. Dust, pollen, pepper or even a cold blast of air are just some of the many things that may cause you to ...
GLOSSARY
... *Niche: the ecological role of an organism in a community especially in regard to food consumption. ...
... *Niche: the ecological role of an organism in a community especially in regard to food consumption. ...
BIO 330 Cell Biology Lecture Outline Spring 2011 Chapter 10
... Creates water Releases free energy Electron transfer occurs in stepwise fashion to maximize efficiency B. Five kinds of electron carriers are parts of respiratory complexes Flavoproteins Carry electrons and protons together Iron-sulfur proteins Carry only one electron by redox of iron ions Cytochrom ...
... Creates water Releases free energy Electron transfer occurs in stepwise fashion to maximize efficiency B. Five kinds of electron carriers are parts of respiratory complexes Flavoproteins Carry electrons and protons together Iron-sulfur proteins Carry only one electron by redox of iron ions Cytochrom ...
The Effect of Nitrates on Water Quality
... • Nitrogen is essential for all living things, this includes both plants and animals. If you look at what makes up DNA in cells and what is found in proteins, you will find the presence of nitrogen. Animals get nitrogen by eating plants and other animals. • Plants need nitrogen for growth. Unlike an ...
... • Nitrogen is essential for all living things, this includes both plants and animals. If you look at what makes up DNA in cells and what is found in proteins, you will find the presence of nitrogen. Animals get nitrogen by eating plants and other animals. • Plants need nitrogen for growth. Unlike an ...
Exam Two Review Guide Chapter Five Anabolism vs. Catabolism
... 16. Account for all the ATP, CO2, H2O NADH+H+ and FADH2 generated by one glucose molecule, then again for one G3P molecule. 17. G3P separates the energy investment phase from the energy payoff stage of glycolysis. Why are these phases named as such? 18. We generate between 36-38 ATP in cellular resp ...
... 16. Account for all the ATP, CO2, H2O NADH+H+ and FADH2 generated by one glucose molecule, then again for one G3P molecule. 17. G3P separates the energy investment phase from the energy payoff stage of glycolysis. Why are these phases named as such? 18. We generate between 36-38 ATP in cellular resp ...
Photosynthesis
... Plentiful light for photosynthesis Carbon dioxide is present in higher concentrations and diffuses more readily in air than in water. ...
... Plentiful light for photosynthesis Carbon dioxide is present in higher concentrations and diffuses more readily in air than in water. ...
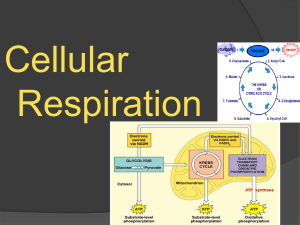
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration - Chemistry
... lactic acid. For example, during exercise, pyruvate in muscles is converted to lactate when muscles must operate without enough oxygen. ...
... lactic acid. For example, during exercise, pyruvate in muscles is converted to lactate when muscles must operate without enough oxygen. ...
Citric Acid Cycle Overview of Cycle Fate of Acetyl CoA
... • Some amino acids can also serve if in high concentration ...
... • Some amino acids can also serve if in high concentration ...
wild edible plants
... 3. Fat: Fats and oils. Seeds are a good source. Vegetable fat is healthier than animal fat. (9 cal. / gram). ...
... 3. Fat: Fats and oils. Seeds are a good source. Vegetable fat is healthier than animal fat. (9 cal. / gram). ...
plant adaptation
... Plants are often consumed by other living organisms, so they have developed many strategies to reduce the level of predation. Some plants produce lots of nasty chemicals that make them taste bad or that are poisonous. A great example of this is tobacco. Tobacco leaves are loaded with noxious chemica ...
... Plants are often consumed by other living organisms, so they have developed many strategies to reduce the level of predation. Some plants produce lots of nasty chemicals that make them taste bad or that are poisonous. A great example of this is tobacco. Tobacco leaves are loaded with noxious chemica ...
1 - Manabadi
... 1. after photosynthesis Glucose in plants gets converted to.....................in the leaves. 2. In submerged plants CO2 reaches the cells in the form of....................... 3. Ferredoxin is a.............................. 4. ADP Stands for.................................. 5. In Krebs’s cycle a ...
... 1. after photosynthesis Glucose in plants gets converted to.....................in the leaves. 2. In submerged plants CO2 reaches the cells in the form of....................... 3. Ferredoxin is a.............................. 4. ADP Stands for.................................. 5. In Krebs’s cycle a ...
3.DCP I Year BCP Metabolism Notes
... Ammonia and this ammonia is toxic to our body cells. This should be excrete from body this is happen by the urea cycle in this cycle the ammonia from amino acid metabolism converted into urea and this urea will be excrete trough kidneys from our body. Catabolism of Amino acids takes place by followi ...
... Ammonia and this ammonia is toxic to our body cells. This should be excrete from body this is happen by the urea cycle in this cycle the ammonia from amino acid metabolism converted into urea and this urea will be excrete trough kidneys from our body. Catabolism of Amino acids takes place by followi ...
Readiness— Knowledge and Skills Science 8— STAAR Review
... Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. They are dull and don’t conduct a current. Many of them are gasses. The group that is along the diagonal and is between the two main groups are called metalloids. These elements have properties of both metals and not metals. ...
... Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. They are dull and don’t conduct a current. Many of them are gasses. The group that is along the diagonal and is between the two main groups are called metalloids. These elements have properties of both metals and not metals. ...
Cellular Respirationn Review Answers
... 19. (a) A pH meter could be placed into the mitochondrial matrix and intermembrane space to test Peter Mitchell’s chemiosmotic theory. The pH of the intermembrane space should be significantly lower than the matrix. (b) A voltmeter could be used since an electric gradient is formed between the inter ...
... 19. (a) A pH meter could be placed into the mitochondrial matrix and intermembrane space to test Peter Mitchell’s chemiosmotic theory. The pH of the intermembrane space should be significantly lower than the matrix. (b) A voltmeter could be used since an electric gradient is formed between the inter ...
Growth final1 - TOP Recommended Websites
... Generation time • time for bacterial mass to double ...
... Generation time • time for bacterial mass to double ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.