Chapter 3: Chemical Reactions and the Earth`s Composition
... Example 2: Everclear is a brand of grain alcohol that can be as high as 190 proof (or 95% ethanol, C2H5OH, by volume). Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced upon complete combustion of the ethanol in a 750 mL bottle of Everclear. Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of eth ...
... Example 2: Everclear is a brand of grain alcohol that can be as high as 190 proof (or 95% ethanol, C2H5OH, by volume). Calculate the mass of carbon dioxide produced upon complete combustion of the ethanol in a 750 mL bottle of Everclear. Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of eth ...
Preview Sample 1
... C) may be held together by ionic bonds. D) can make up proteins. E) both A and C ...
... C) may be held together by ionic bonds. D) can make up proteins. E) both A and C ...
chapt08
... 1. The electron transport chain is located in the cristae of mitochondria and consists of carriers that pass electrons successively from one to another. 2. Some of the protein carriers are cytochrome molecules, complex carbon rings with a heme (iron) group in the center. 3. NADH and FADH2 carry the ...
... 1. The electron transport chain is located in the cristae of mitochondria and consists of carriers that pass electrons successively from one to another. 2. Some of the protein carriers are cytochrome molecules, complex carbon rings with a heme (iron) group in the center. 3. NADH and FADH2 carry the ...
Respiratory System - Fall River Public Schools
... into millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli • Alveoli is arranged in clusters similar to grapes • Capillaries surround each alveolus ...
... into millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli • Alveoli is arranged in clusters similar to grapes • Capillaries surround each alveolus ...
Ecology Crossword
... Ecosystem/collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving environment Biome/group of ecosystems that have the same climate and dominant communities Autotroph/organism that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food ...
... Ecosystem/collection of all the organisms that live in a particular place, together with their nonliving environment Biome/group of ecosystems that have the same climate and dominant communities Autotroph/organism that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food ...
Answer key Ws 17-1 Viruses
... What is photosynthetic? organisms that use the energy of sunlight to make their own food Why are cyanobacteria not called blue-green algae anymore? Algae are eukaryotic cells not prokaryotic cells What colour is chlorophyll a? green What causes other cyanobacteria to be yellow, brown, or red? Other ...
... What is photosynthetic? organisms that use the energy of sunlight to make their own food Why are cyanobacteria not called blue-green algae anymore? Algae are eukaryotic cells not prokaryotic cells What colour is chlorophyll a? green What causes other cyanobacteria to be yellow, brown, or red? Other ...
The Digestive System
... The produces digestive enzymes used in the small intestine. Bile is also produced which is used to break down fats in the small intestine. ...
... The produces digestive enzymes used in the small intestine. Bile is also produced which is used to break down fats in the small intestine. ...
First Homework Assignment
... reducing sugars and the beta linkages would be hydrolyzed by a beta-galactosidase. Similarly, connecting glucose as a glucopyranoside to galactose also gives 8 possible types of linkage. These are all reducing sugars and the alpha type of linkage would be cut by an alpha glucosidase. Finally, the tw ...
... reducing sugars and the beta linkages would be hydrolyzed by a beta-galactosidase. Similarly, connecting glucose as a glucopyranoside to galactose also gives 8 possible types of linkage. These are all reducing sugars and the alpha type of linkage would be cut by an alpha glucosidase. Finally, the tw ...
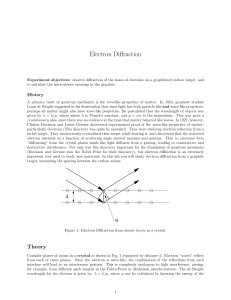
Electron Diffraction
... Louis de Broglie suggested in his dissertation that since light has both particle-like and wave-like properties, perhaps all matter might also have wave-like properties. He postulated that the wavelength of objects was given by λ = h/p, where where h is Planck’s constant, and p = mv is the momentum. ...
... Louis de Broglie suggested in his dissertation that since light has both particle-like and wave-like properties, perhaps all matter might also have wave-like properties. He postulated that the wavelength of objects was given by λ = h/p, where where h is Planck’s constant, and p = mv is the momentum. ...
State a significant event that occurs during each of the following
... Which phase of aerobic respiration occurs in cytosol? glycolysis What is consumed during this process? glucose What is produced during this process? 2ATP, 2NADH, 2 Pyruvate 4B (5 pts) Which phase of aerobic respiration occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion? Krebs cycle What is consumed during th ...
... Which phase of aerobic respiration occurs in cytosol? glycolysis What is consumed during this process? glucose What is produced during this process? 2ATP, 2NADH, 2 Pyruvate 4B (5 pts) Which phase of aerobic respiration occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion? Krebs cycle What is consumed during th ...
8.2 Cells and Energy
... oxygen and glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy (Figure 8.9). When you breathe in, you take in the oxygen your cells need for cellular respiration. When you breathe out, you get rid of the carbon dioxide that your cells produce during cellular respiration. Try breathing onto a mirror ...
... oxygen and glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy (Figure 8.9). When you breathe in, you take in the oxygen your cells need for cellular respiration. When you breathe out, you get rid of the carbon dioxide that your cells produce during cellular respiration. Try breathing onto a mirror ...
Exchange of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
... continually using oxygen, and the partial pressure of oxygen in active cells remains below 40 mmHg. Oxygen circulating in the systemic arterial blood readily diffuses across the membranes of the blood vessels into the tissues, replenishing the supply of oxygen in the cells. The final concentration o ...
... continually using oxygen, and the partial pressure of oxygen in active cells remains below 40 mmHg. Oxygen circulating in the systemic arterial blood readily diffuses across the membranes of the blood vessels into the tissues, replenishing the supply of oxygen in the cells. The final concentration o ...
Seed plants
... • Cooksonia, the first vascular land plant, appeared about 420 MYA – Only a few centimeters tall – No roots or leaves – Homosporous (spores are the same size and type) ...
... • Cooksonia, the first vascular land plant, appeared about 420 MYA – Only a few centimeters tall – No roots or leaves – Homosporous (spores are the same size and type) ...
Content of phloem and xylem exudates
... Respiration - the process of mobilizing organic compounds and oxidizing them. The released energy is transiently stored as ATP. The reduced carbon compounds that are substrates for respiration in plants include glucose, sucrose, fructose-containing polymers, lipids, and organic acids. ...
... Respiration - the process of mobilizing organic compounds and oxidizing them. The released energy is transiently stored as ATP. The reduced carbon compounds that are substrates for respiration in plants include glucose, sucrose, fructose-containing polymers, lipids, and organic acids. ...
Cell Respiration notes
... Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that generates ATP during fermentation. No O2 is required; it generates a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH Significantly less ATP is generated, but it is enough to keep your muscles contracting for a short while when the need for ATP outpaces the delivery of O2 via th ...
... Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that generates ATP during fermentation. No O2 is required; it generates a net gain of 2 ATP and 2 NADH Significantly less ATP is generated, but it is enough to keep your muscles contracting for a short while when the need for ATP outpaces the delivery of O2 via th ...
B3 - miss-lovell
... 6. Apical dominance is where the apical bud produces auxin in high concentrations. This causes cells to elongate and grow faster at the apex. The auxin diffuses down the plant and in high concentrations inhibits the growth in the lateral buds. When the apical bud is removed the dormant lateral buds ...
... 6. Apical dominance is where the apical bud produces auxin in high concentrations. This causes cells to elongate and grow faster at the apex. The auxin diffuses down the plant and in high concentrations inhibits the growth in the lateral buds. When the apical bud is removed the dormant lateral buds ...
Unit 7 Review
... 12. Ecologically diverse; some cause diseases and some are beneficial to humans. 13. Found in the most extreme environments like volcanoes, brine pools, and the guts of cows. Cell membranes contain unique lipids. 14. Most feed on dead or decaying organic matter. Also secrete digestive enzymes into t ...
... 12. Ecologically diverse; some cause diseases and some are beneficial to humans. 13. Found in the most extreme environments like volcanoes, brine pools, and the guts of cows. Cell membranes contain unique lipids. 14. Most feed on dead or decaying organic matter. Also secrete digestive enzymes into t ...
The biosphere - Hillpark Secondary School
... indicate the direction of energy flow. The arrows in a food web show the direction of energy flow. In a food web, energy is transferred from food to feeder. Living things can use this energy to move and grow. 10b. General: State two ways in which energy can be lost from a food web. There is ...
... indicate the direction of energy flow. The arrows in a food web show the direction of energy flow. In a food web, energy is transferred from food to feeder. Living things can use this energy to move and grow. 10b. General: State two ways in which energy can be lost from a food web. There is ...
Topic Three Chemistry of Life - MrsGorukhomework
... Topic Three Chemistry of Life Unicellular organisms must perform all cellular functions at the cellular level. Multicellular organism can differentiate or specialize and by doing this, there is a division of labor. This allows the cell to form tissues organs and organ systems. A cells job is determ ...
... Topic Three Chemistry of Life Unicellular organisms must perform all cellular functions at the cellular level. Multicellular organism can differentiate or specialize and by doing this, there is a division of labor. This allows the cell to form tissues organs and organ systems. A cells job is determ ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.