The Chemical Basis of Life Atoms, Molecules, Ions, and Bonds
... • Thus, you will always see four lines connecting a carbon atom to other atoms, each line representing a pair of shared electrons (one electron from carbon and one from another atom). ...
... • Thus, you will always see four lines connecting a carbon atom to other atoms, each line representing a pair of shared electrons (one electron from carbon and one from another atom). ...
Ch 19 reading guide
... transformed into the high energy bond ____________________, which leads to phosphorylation of the enzyme on a ____________ residue, then finally to formation of ___________. 12. Draw the three-reaction transformation of succinate to oxaloacetate. (You need to know this basic pathway well because it ...
... transformed into the high energy bond ____________________, which leads to phosphorylation of the enzyme on a ____________ residue, then finally to formation of ___________. 12. Draw the three-reaction transformation of succinate to oxaloacetate. (You need to know this basic pathway well because it ...
File
... manipulate or move glucose and its breakdown products through the various steps of both fermentation and aerobic respiration. When you feel you have developed a good working model, demonstrate and explain it to another student. ...
... manipulate or move glucose and its breakdown products through the various steps of both fermentation and aerobic respiration. When you feel you have developed a good working model, demonstrate and explain it to another student. ...
Organic Molecules: The Molecules of Life
... Making molecules called synthesis, sometimes called dehydration reaction The equivalent of a water molecule is removed from the chemicals, so they are “dehydrated” Monomer- OH + H- Monomer polymer + H20 Taking molecules apart is called degradation of hydrolysis (water, splitting)Water is added to t ...
... Making molecules called synthesis, sometimes called dehydration reaction The equivalent of a water molecule is removed from the chemicals, so they are “dehydrated” Monomer- OH + H- Monomer polymer + H20 Taking molecules apart is called degradation of hydrolysis (water, splitting)Water is added to t ...
Chapter 39: Plant Responses to Internal and External Signals
... 5. What are the two second messengers in this pathway? The transduction of extremely weak signals involves second messengers – small molecules and ions in the cell that amplify the signal and transfer it from the receptor to other proteins that carry out the response. Calcium ions (Ca2+) and cyclic ...
... 5. What are the two second messengers in this pathway? The transduction of extremely weak signals involves second messengers – small molecules and ions in the cell that amplify the signal and transfer it from the receptor to other proteins that carry out the response. Calcium ions (Ca2+) and cyclic ...
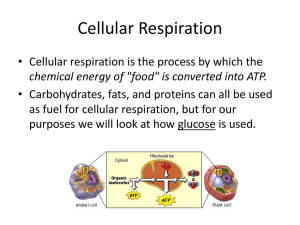
Cellular Respiration
... • The electron transport chain (ETC) consists of a series of molecules, mostly proteins, embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. • The electron transport chain captures the electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 and passes them along the membrane. – As the electrons move along the membrane H+ buil ...
... • The electron transport chain (ETC) consists of a series of molecules, mostly proteins, embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. • The electron transport chain captures the electrons stored in NADH and FADH2 and passes them along the membrane. – As the electrons move along the membrane H+ buil ...
Anaerobic Fermentation
... Your body doesn't always get enough oxygen during excercise... *Body compensates for the lack of oxygen by a process called Anaerobic fermentation that carries out a series of chemical reactions that produce ATP from glucose in the absence of O 2 *Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue maki ...
... Your body doesn't always get enough oxygen during excercise... *Body compensates for the lack of oxygen by a process called Anaerobic fermentation that carries out a series of chemical reactions that produce ATP from glucose in the absence of O 2 *Fermentation allows glycolysis to continue maki ...
Section 16.1 - CPO Science
... • Vascular plants are divided into two groups—those that produce seeds and those that do not. • Plants that produce seeds are divided into gymnosperms and angiosperms. • Examples of plants that have no seeds are ferns, mosses and horsetails. ...
... • Vascular plants are divided into two groups—those that produce seeds and those that do not. • Plants that produce seeds are divided into gymnosperms and angiosperms. • Examples of plants that have no seeds are ferns, mosses and horsetails. ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... When the first step occurs and 2 acetaldehyde is formed, 2 CO₂ is released Then acetaldehyde accepts hydrogen and electrons from the 2 NADH formed through Glycolysis With the combining of e-, H+, and 2 acetaldehyde, 2 NAD+ is regenerated and 2ethanol is created ...
... When the first step occurs and 2 acetaldehyde is formed, 2 CO₂ is released Then acetaldehyde accepts hydrogen and electrons from the 2 NADH formed through Glycolysis With the combining of e-, H+, and 2 acetaldehyde, 2 NAD+ is regenerated and 2ethanol is created ...
Mark scheme Outline the process of glycolysis. (5 marks) occurs in
... inner membrane contains ATP synthetase / ATPase / stalked particles that make ATP (narrow) gap between inner and outer membranes / inter-membrane space ( must be stated or labeled) pH / H+ / proton concentration gradient rapidly established / steeper chemiosmosis therefore more efficient / chemiosmo ...
... inner membrane contains ATP synthetase / ATPase / stalked particles that make ATP (narrow) gap between inner and outer membranes / inter-membrane space ( must be stated or labeled) pH / H+ / proton concentration gradient rapidly established / steeper chemiosmosis therefore more efficient / chemiosmo ...
Sample exam questions Chapter 11 Carbohydrates
... 24) All of the following statements concerning the citric acid cycle are true EXCEPT A. The cycle starts with the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate, adds two carbons from acetyl-CoA, stepwise loses two carbons as CO2, and regenerated the fourcarbon compound oxaloacetate. B. For each molecule of gluc ...
... 24) All of the following statements concerning the citric acid cycle are true EXCEPT A. The cycle starts with the four-carbon compound oxaloacetate, adds two carbons from acetyl-CoA, stepwise loses two carbons as CO2, and regenerated the fourcarbon compound oxaloacetate. B. For each molecule of gluc ...
The Human Respiratory System
... • Place where gas exchange occurs – Oxygen into blood, carbon dioxide into lung – Each is surrounded by capillaries • 300 million alveoli are in each healthy lung – Provides a large surface area for gas exchange ...
... • Place where gas exchange occurs – Oxygen into blood, carbon dioxide into lung – Each is surrounded by capillaries • 300 million alveoli are in each healthy lung – Provides a large surface area for gas exchange ...
FireWorks Glossary - Missoula Fire Lab
... organic matter: the material that comprises living and dead things; also the name for complex chemical compounds that contain carbon. Decaying organic matter is an important part of soil. oxygen: one of many gases in Earth’s atmosphere. Oxygen is produced by photosynthesis and is used in both combu ...
... organic matter: the material that comprises living and dead things; also the name for complex chemical compounds that contain carbon. Decaying organic matter is an important part of soil. oxygen: one of many gases in Earth’s atmosphere. Oxygen is produced by photosynthesis and is used in both combu ...
Biology Name_____________________________________
... 8. Put the following events of Glycolysis in order that they occur: a. Two 3-carbon molecules called PGAL are formed b. Two molecules of pyruvic acid are produced. c. An ADP is transformed into an ATP d. An ATP is used to provide energy. e. NAD+ is transformed into NADH 9. What is the difference be ...
... 8. Put the following events of Glycolysis in order that they occur: a. Two 3-carbon molecules called PGAL are formed b. Two molecules of pyruvic acid are produced. c. An ADP is transformed into an ATP d. An ATP is used to provide energy. e. NAD+ is transformed into NADH 9. What is the difference be ...
How Does Oxygen Get to Muscles?
... complete oxidation of carbohydrate and fat produces ATP, H2O, CO2, and The process by which carbohydrate and fat are oxidized to produce ATP is referred to as internal respiration because it occurs inside cells. The delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the cells is called external respiration. ...
... complete oxidation of carbohydrate and fat produces ATP, H2O, CO2, and The process by which carbohydrate and fat are oxidized to produce ATP is referred to as internal respiration because it occurs inside cells. The delivery of oxygen from the lungs to the cells is called external respiration. ...
The Citric Acid Cycle - Rubin Risto Gulaboski
... Regulation of Kreb’s Cycle • The regulation is mediated via allosteric inhibition by products on enzymes used previously in the cycle. • For example, an increase in Citrate will cause a decreased activity of Citrate Synthase • An increased NADH or Acetyl CoA will decrease Pyruvate Dehydrogenase act ...
... Regulation of Kreb’s Cycle • The regulation is mediated via allosteric inhibition by products on enzymes used previously in the cycle. • For example, an increase in Citrate will cause a decreased activity of Citrate Synthase • An increased NADH or Acetyl CoA will decrease Pyruvate Dehydrogenase act ...
MCAS and Final Review Packet 2014
... 9. What are the products? H2O + CO2 10. What kind of organisms carry out cellular respiration? All living things 11. Label this simple diagram to illustrate how carbon dioxide, water, glucose, and oxygen are used in the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in a plant. CO2 and H2O go in ...
... 9. What are the products? H2O + CO2 10. What kind of organisms carry out cellular respiration? All living things 11. Label this simple diagram to illustrate how carbon dioxide, water, glucose, and oxygen are used in the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in a plant. CO2 and H2O go in ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation and Electron Transport Chain(ETC)
... • Electrons stored in the form of the reduced coenzymes, NADH or [FADH2], are passed through an elaborate and highly organized chain of proteins and coenzymes, therefore called electron transport chain, finally reaching O2 (molecular oxygen) is the terminal electron acceptor. • Each component of th ...
... • Electrons stored in the form of the reduced coenzymes, NADH or [FADH2], are passed through an elaborate and highly organized chain of proteins and coenzymes, therefore called electron transport chain, finally reaching O2 (molecular oxygen) is the terminal electron acceptor. • Each component of th ...
Nitrogen cycle review - West Perry School District
... 3rd Idea: Energy from the sun flows through an ecosystem as it is passed from one organism to the next. With each transfer some energy is lost as heat. Use the diagrams of food chains below to answer the following questions. 4. The arrows in a food chain always point in the direction of ___the con ...
... 3rd Idea: Energy from the sun flows through an ecosystem as it is passed from one organism to the next. With each transfer some energy is lost as heat. Use the diagrams of food chains below to answer the following questions. 4. The arrows in a food chain always point in the direction of ___the con ...
The Biology Staff Handbook
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions in which plants are grown can be changed to promote growth. Photosynthesis Photo = light Synthesis = making of (glucose) Photosynt ...
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions in which plants are grown can be changed to promote growth. Photosynthesis Photo = light Synthesis = making of (glucose) Photosynt ...
Unit 2 summary notes
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions in which plants are grown can be changed to promote growth. Photosynthesis Photo = light Synthesis = making of (glucose) Photosynt ...
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions in which plants are grown can be changed to promote growth. Photosynthesis Photo = light Synthesis = making of (glucose) Photosynt ...
Anaerobic Pathways Lesson Plan
... o Misconceptions about lactic acid: muscle stiffness/soreness, acidosis; lactate production enables intense exercises and does not cause acidosis because it is deprotonated o lactate thought to be the cause of muscle stiffness and soreness, but lactate levels in muscles return to normal within an ho ...
... o Misconceptions about lactic acid: muscle stiffness/soreness, acidosis; lactate production enables intense exercises and does not cause acidosis because it is deprotonated o lactate thought to be the cause of muscle stiffness and soreness, but lactate levels in muscles return to normal within an ho ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.