Class: 7 Subject: Biology Topic: Respiration in Organisms No. of
... little brown grains. The little brown grains of yeast may not seem to be alive, but if we put them in water with sugar, the yeast will carry out cellular respiration and grow. We can grow yeast in a test tube filled with water and sealed with a balloon. Under anaerobic conditions, yeast carries out ...
... little brown grains. The little brown grains of yeast may not seem to be alive, but if we put them in water with sugar, the yeast will carry out cellular respiration and grow. We can grow yeast in a test tube filled with water and sealed with a balloon. Under anaerobic conditions, yeast carries out ...
melgarejo richard
... one or more double bonds. Saturated fat produces atherosclerosis and can impede blood flow. I. Proteins account for 50% of the dry cells in cells and are in almost all of what organisms do, they are used for structural support, storage, transport of other substances, signaling from one part of the o ...
... one or more double bonds. Saturated fat produces atherosclerosis and can impede blood flow. I. Proteins account for 50% of the dry cells in cells and are in almost all of what organisms do, they are used for structural support, storage, transport of other substances, signaling from one part of the o ...
this lecture as PDF here - Development of e
... represented in a simplified manner as (CH 2 O). Photosynthesis fixes inorganic carbon as biological carbon, which is a constituent of all life molecules. An important aspect of the carbon cycle is that it is the cycle by which energy is transferred to biological systems. Organic or biological carbon ...
... represented in a simplified manner as (CH 2 O). Photosynthesis fixes inorganic carbon as biological carbon, which is a constituent of all life molecules. An important aspect of the carbon cycle is that it is the cycle by which energy is transferred to biological systems. Organic or biological carbon ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ (protons) into the space between the mitochondrial membranes • In chemiosmosis, the H+ ions diffuse back through the inner membrane through ATP synthase, which ...
... • The electrons from NADH and FADH2 travel down the electron transport chain to oxygen • Energy released by the electrons is used to pump H+ (protons) into the space between the mitochondrial membranes • In chemiosmosis, the H+ ions diffuse back through the inner membrane through ATP synthase, which ...
Unit 6 Homework
... 6. Identify two functions of gibberellins. 7. Identify a few plant responses to ethylene. 8. Are all wavelengths of light equal when it comes to phototropism? Explain. 9. What are the two forms of phytochrome and how are they switched? 10. When do short-day plants flower? Define photoperiodism. 11. ...
... 6. Identify two functions of gibberellins. 7. Identify a few plant responses to ethylene. 8. Are all wavelengths of light equal when it comes to phototropism? Explain. 9. What are the two forms of phytochrome and how are they switched? 10. When do short-day plants flower? Define photoperiodism. 11. ...
Metabolism without Oxygen
... to allow aerobic respiration to continue (that is, in muscles used to the point of fatigue). In muscles, lactic acid accumulation must be removed by the blood circulation and the lactate brought to the liver for further metabolism. The chemical reactions of lactic acid fermentation are the following ...
... to allow aerobic respiration to continue (that is, in muscles used to the point of fatigue). In muscles, lactic acid accumulation must be removed by the blood circulation and the lactate brought to the liver for further metabolism. The chemical reactions of lactic acid fermentation are the following ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 8 Outline Glycolysis Transition
... A cellular process that requires oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. – Most often involves complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. ! Energy within a glucose molecule is released slowly so that ATP can be produced gradually. ! NAD+ and FAD are oxidation-reduction enzymes active du ...
... A cellular process that requires oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. – Most often involves complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water. ! Energy within a glucose molecule is released slowly so that ATP can be produced gradually. ! NAD+ and FAD are oxidation-reduction enzymes active du ...
File
... Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food Respiration is not the same as breathing!! Respiration can be either aerobic or anaerobic. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic does not. Humans and all other animals carry out aerobic respiration while many micro-organisms lik ...
... Respiration is the controlled release of energy from food Respiration is not the same as breathing!! Respiration can be either aerobic or anaerobic. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen while anaerobic does not. Humans and all other animals carry out aerobic respiration while many micro-organisms lik ...
File
... B. Protein molecules are made up of strands of DNA joined together by amino acid sequences. C. The sequence of amino acids that make up a protein molecule do not affect its function. D. Protein molecules have many functions in the body, including the storage of genetic information. Question 11 Prote ...
... B. Protein molecules are made up of strands of DNA joined together by amino acid sequences. C. The sequence of amino acids that make up a protein molecule do not affect its function. D. Protein molecules have many functions in the body, including the storage of genetic information. Question 11 Prote ...
Capturing Energy from the Sun
... -Most wild plant species are adapted to thrive in the low levels if nitrogen usually found in soil and water -Once scientists developed a method to fix nitrogen, fertilizers were developed -This enabled farmers to increase their crop yields -By the end of the 20h century, the amount of nitrogen prov ...
... -Most wild plant species are adapted to thrive in the low levels if nitrogen usually found in soil and water -Once scientists developed a method to fix nitrogen, fertilizers were developed -This enabled farmers to increase their crop yields -By the end of the 20h century, the amount of nitrogen prov ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... Because of their strong, lignified cell walls, tracheids provide greater structure and support to plants, enabling plants to grow more erect. ...
... Because of their strong, lignified cell walls, tracheids provide greater structure and support to plants, enabling plants to grow more erect. ...
Opuntia phaeacantha Engelm., BROWN
... Opuntia phaeacantha Engelm., BROWN-SPINED PRICKLY PEAR. Shrub, stem succulent, spinescent, mostly individual plants but potentially clonal via rooted stem segments of broken branches, fibrous-rooted, green-stemmed, often with horizontal branches radiating from base but elevated above ground, in rang ...
... Opuntia phaeacantha Engelm., BROWN-SPINED PRICKLY PEAR. Shrub, stem succulent, spinescent, mostly individual plants but potentially clonal via rooted stem segments of broken branches, fibrous-rooted, green-stemmed, often with horizontal branches radiating from base but elevated above ground, in rang ...
Ecology Population Ecology Classwork Which level of organization
... 3. The Sargasso Sea is a gyre in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean that is created by the convergence of four different oceans currents. Although classified as the open ocean, the Sargasso Sea often is teeming with life. One important habitat in the Sargasso Sea is large floating mats of sargassum, a ...
... 3. The Sargasso Sea is a gyre in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean that is created by the convergence of four different oceans currents. Although classified as the open ocean, the Sargasso Sea often is teeming with life. One important habitat in the Sargasso Sea is large floating mats of sargassum, a ...
Respiration
... phosphate dehydrogenase to 1, 3 biphosphoglycerate, it is simultaneously phosphorylated by inorganic phosphate. Here 2NAD is changed to 2NADH. 7. 1,3, biphosphoglycerate is dephosphorylated in presence of enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase to 3 phosphoglycerate and ATP is changed to ADP. 8. Now the phos ...
... phosphate dehydrogenase to 1, 3 biphosphoglycerate, it is simultaneously phosphorylated by inorganic phosphate. Here 2NAD is changed to 2NADH. 7. 1,3, biphosphoglycerate is dephosphorylated in presence of enzyme phosphoglycerate kinase to 3 phosphoglycerate and ATP is changed to ADP. 8. Now the phos ...
A-level
... It displays a greater affinity for oxygen and its oxygen dissociation curve is displaced to the left of haemoglobin. It acts as a storage of oxygen in resting muscle They release oxygen when supplies of oxyhaemoglobin have been exhausted such as severe muscular exercies. ...
... It displays a greater affinity for oxygen and its oxygen dissociation curve is displaced to the left of haemoglobin. It acts as a storage of oxygen in resting muscle They release oxygen when supplies of oxyhaemoglobin have been exhausted such as severe muscular exercies. ...
Cell Energy
... • How the process of chemiosmosis utilizes the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP • How linear electron flow in the light reactions results in the formation of ATP, NADPH, and O2 • How chemiosmosis generates ATP in the light reactions ...
... • How the process of chemiosmosis utilizes the electrons from NADH and FADH2 to produce ATP • How linear electron flow in the light reactions results in the formation of ATP, NADPH, and O2 • How chemiosmosis generates ATP in the light reactions ...
Biology Review
... participants are all approximately the same age and weight; they have similar medical histories and similar habits in terms of diet and exercise. She randomly assigns 50 individuals to Group A and 50 to Group B. Group A receives one diet a pill a day for 30 days. Group B receives a placebo once a da ...
... participants are all approximately the same age and weight; they have similar medical histories and similar habits in terms of diet and exercise. She randomly assigns 50 individuals to Group A and 50 to Group B. Group A receives one diet a pill a day for 30 days. Group B receives a placebo once a da ...
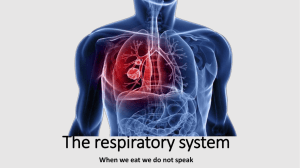
The respiratory system
... The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells. ...
... The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells. ...
BIO 15 SM 2016 FINAL EXAM 135 Q 160804.1rac
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes fr ...
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes fr ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the levels of organization
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes fr ...
... Carbon atoms are the most versatile building blocks of the molecules used by living organisms because _____. a. carbon is the central atom of carbon dioxide, a necessary molecule for photosynthesis b. carbon is the central atom in urea, a molecule used by many living organisms to transport wastes fr ...
PLANTS - Weebly
... process, osmotic pressure moves water out of the vascular tissue of the leaf. • The movement of water out of the leaf pulls water through the vascular system all the way from the roots. This is called transpiration pull. On a hot day, a small tree may lose as much as 100 liters of water to transpira ...
... process, osmotic pressure moves water out of the vascular tissue of the leaf. • The movement of water out of the leaf pulls water through the vascular system all the way from the roots. This is called transpiration pull. On a hot day, a small tree may lose as much as 100 liters of water to transpira ...
Document
... • Re-read the indicated pages where each reaction is described in Creighton. Look at related power point slides and examples discussed in class. • Put together a summary sheet with each reaction in as much detail as presented in Creighton or in class and explain how it is used. ...
... • Re-read the indicated pages where each reaction is described in Creighton. Look at related power point slides and examples discussed in class. • Put together a summary sheet with each reaction in as much detail as presented in Creighton or in class and explain how it is used. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.