* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 ~ Learning Guide Name
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
History of phycology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
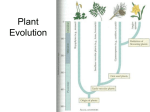
BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Unit 6 ~ Learning Guide Name: _______________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. 6.1 NOTES: DIVERSITY OF ALGAE General Characteristics of Algae Most algae are traditionally considered as _____________________________ within the 5-kingdom classification. The diagnostic characters of the algal group as a whole were ill-defined, but nevertheless vastly different from the well-defined traits of the other two plant subkingdoms, namely the bryophytes and vascular land plants. Other biologists who were convinced that _______________________________________ _______________________ revised the classification, ______________________ ____________________________________________, with only some multicellular phyla, particularly the ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________, remaining as plants. ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________. The result was, and still is confusion. All algae are ________________________________________________________. The various types contain ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. Most algae are _________________________________________________________________. The only algae that does not fall into these three classifications are those that are unicellular in all life stages and can move on their own. ________________________ __________________________________________________________________. While these algae reproduce by mitosis (__________________________), the green, brown, and red algae reproduce _____________________________ similar to higher plants. The generalized life cycle of these sexual algae is termed _________________ _______________________________________________________. To have an _________________________________________________, an organism ________________________________________ that are _____________ Page 1 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 _________________________________________________. An organism can spend equal time as each generation or it can spend most of its life as either the haploid or diploid form. Phylum Chlorophyta - Green Algae Green algae possess the pigments __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ ____________________________. Green algae are considered closely related to plants. All members of this phylum have a cell wall made of cellulose and store food in vacuoles which are characteristics of plants. _____________________________ __________________________________ __________________________________ __________________. Green algae can be unicellular, colonial, filamentous, or multicellular giving them a wide diversity of structure. __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________. Unicellular Green Algae Chlamydomonas is a ____________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________. It usually reproduces asexually by binary fission, but when faced with unfavorable conditions it will reproduce sexually in a haplontic life cycle. This method of reproduction is used in unfavorable conditions because the zygospore has a heavy protective wall. When faced with unfavorable conditions the Chlamydomonas _________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________. It is important to note that since all gametes are the same (no male or female) they are said to have isogametes. Page 2 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Colonial, filamentous and Multicellular Green Algae A colonial organism is __________________________ _______________________________________________. They are not independent, but have all the capabilities of being independent. For example, ___________is a colonial organism composed of thousands of cells that very closely resemble Chlamydomonas. Each cell would be capable of independent life, but they are arranged to work in a coordinated fashion. The Volvox resembles a sphere with a watery inside. The wall of the sphere is made up of Chlamydomonas-like cells. __________________________ _____________________________________________ making this one of the simplest organisms to produce heterogametes (sperm and egg). A filamentous organism is ______________________. The difference is that all cells are aligned in a one cell thick strand of filaments. An example of a filamentous algae is ___________________________, which gets its name from the shape of the chloroplasts in the cell. Spirogyra ________ ________________________________. If the strand breaks then both strands will grow as new algae. In sexual reproduction the contents of one strand will empty into another so there are no gametes involved. As with Chlamydomonas, sexual reproduction produces a diploid zygote that may be more resistant to unfavourable conditions. Spirogyra will often spend the winter as a diploid zygote and undergo meiosis in the spring when the weather warms again producing the haploid filament. Page 3 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 These Green algae look like plants to the untrained eye. However, there is no cellular differentiation and there is no protection of the zygote or embryo. _____________________________________________ _______________________________. The green algae ___________ so closely resembles a plant that its common name is sea lettuce. Ulva ______________________________________________ _____________________________. It spends equal time as a haploid and diploid organism. Isogametes produced by the gametophyte combine (fertilization) to form a zygote (2n) which grows to a sporophyte (2n). The sporophyte will undergo meiosis to produce spores (n) which will grow to a gametophyte and the cycle repeats. The adult stages, sporophyte and gametophyte, are the stages that resemble lettuce. The leafy structure is called a thallus. Red and Brown Algae - Phylum Rhodophyta _______________________________________ _________________________, but some species are filamentous. Most red algae are complex, branched multicellular algae which look like a bunch of ribbons. Red algae has an economic importance as the main constituent in agar. Check if it is in your favourite ice cream. Phylum Phaeophyta The ___________________________________ ____________________________________. It is the pigment fucoxanthin that gives this phylum its golden brown colour. Like red algae, ______ ______________________________________ _________________________. There are some filamentous representatives as well. __________ _______________________________________ _______________________________________ ______________________________________. They often have specialized structures. At one end you will find _________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Most brown _______________________________________________________. algae undergo an alternation of generations life cycle, but species such as Fucus reproduce via a diplontic life cycle meaning that the adult is the sporophyte and diploid. Page 4 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Diatoms and Dinoflagellates Phylum Chrysophyta Often called brown algae, _____________________________________________ _________________________________. They have a very unique unicellular structure that reproduces asexually. They are of economic importance as well since their __________________________________________ ______________________________________________. Their empty shells are also mined for use in gardening (diatomaceous earth), filters and polishes. Phylum Pyrrophyta Dinoflagellates are unique in that they ________________ _________________________________________________ ____________. They have ___________________________ __________________________________________________ ____________________________________. Dinoflagellates are an ___________________________________________ __________________________________________. This is of concern to humans because when consumed in large amounts they can make the shellfish toxic enough to paralyze whoever eats them. _______________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________. Euglenoids Phylum Euglenophyta Euglena are _____________________________________ for taxonomists because only a third of euglena are photosynthetic. The rest are more like a protozoan as they are heterotrophs and ingest their food. The typical euglena is depicted _________________________________________ _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________. Photosynthetic euglena can be easily found in bright aquatic locations and are often observed live under a microscope. Page 5 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 6.1 PRACTICE: DIVERSITY OF ALGAE 1. Distinguish between the terms diploid and haploid. (2 marks) 2. Alternation of Generation is an important concept in many organisms' life cycles. Describe what alternation of generation means. (2 marks) 3. The classification scheme of algae can be quite confusing and takes considerable practice to master. However, there are some key concepts that even the beginning biologist should be able to master: a. What two characteristics do all algae have in common? (2 marks) b. Most algae classified and named based on what characteristic? (1mark) Page 6 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 4. Some algae reproduce asexually, some reproduce asexually and some reproduce using both methods. Using your understanding of evolution and thinking critically: a. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of reproducing sexually. (2 marks) b. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of reproducing asexually. (2 marks) Page 7 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 6.2 NOTES: INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS Interesting Facts about Plants Bamboo is the fastest growing plant and has been observed to grow over 1 meter in a 24 hr. period The largest bloom (flower) is the stinking lily of Southeast Asia which measures 90 cm across The Welwitschia (wellWITCH-ee-a) plant grows in desert areas of Namibia and Angola. It has only two leaves that shred into many long, leathery pieces as they grow. This plant provides shelter for small desert animals and are an important part of the web of life in the desert. Cinnamon is from the bark of the Cinnamomum zeylandicum tree. The bark is peeled from the sprouts of these trees, then set out to dry and rolled up into quills The Largest living organism is the California Redwood at 111.6 m high with a 24 m circumference. A single coffee tree yields only one pound of roasted, ground coffee annually. The squirting cucumber (Ecballium elaterium), when brushed by a passerby, emits its seeds along with stream of poisonous juice that stings the skin. The oldest plant is the bristlecone pine which is 4900 years old. Page 8 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Interesting Facts about Plants Continued • ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ • every plant in Tomorrowland _______________________. • Trees in the arctic grow very slowly. • ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ • The ____________________________________________________. Fires that occur in a redwood forest take place inside the trees. at Disneyland in Anaheim, CA is Kingdom Plantae Why are plants so important? If plants hadn’t evolved to photosynthesize, life on this planet would be very different. _________________________________________ _________________________________________________________, and the most important waste product of this process is _________________ - something that most of the animal life on this planet can’t live without! As the first plants began photosynthesizing, ___ __________________________________________________ _________________________________________. Some of the oxygen in the outer layer of the atmosphere was converted to ozone. Eventually there was enough ozone in the upper atmosphere to effectively filter out the harmful ultraviolet rays that are highly destructive to living organisms. This allowed organisms to survive in the surface layers of water and on land. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ________________________________. This yields much more energy than can be obtained in an atmosphere without oxygen. Plants are also critical to other life on this planet because ______________________ ________________________________. Most plants are ______________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________. Some of the earliest fossils found have been aged at 3.8 billion years. These fossil deposits show evidence of photosynthesis, so plants, or the plant-like ancestors of plants, have lived on this planet longer than most other groups of organisms. Page 9 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 The fossil record for plants is spottier than animals as they lack hard parts that produce fossils but there is enough to show an evolutionary trend. _____________________ _________________ were the first to appear ______________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________. The fossil records, DNA, and other molecular evidence has traced the origin of plants to fresh water algae, however, __________________________________________________ Here is a proposed evolutionary tree for plant General Characteristics of Plants 1. 2. 3. 4. Plants make food by photosynthesis. Plants have cell walls made of cellulose. Plants stay put = Sessile. Plants show an Alternation of Generations in their life cycles (sporophyte and gametophyte). Plants, like green algae, __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ so it is said that they share a common ancestor. However, plants possess many differences in comparison to green algae, because they have to be able to survive in a much drier environment on land. One of the main ________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________________________. The cuticle is a waxy substance covering the leaves. With this waxy cuticle present _________________________________________ Page 10 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 ________________________________________________________ in and out of the leaves. ___________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________. Those plants that don't must live in a moist environment. _______________________________________ _________________________________________ and will be discussed in more detail later. Plants, like algae, ______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________. There are differences to accommodate the lack of water. For example, plants must protect the embryo from drying out during reproduction. Classifying Plants The 12 Phyla of plants can be _________________________________________ ___________________________ based on the presence of vascular tissue: 1. ____________________________________ 2. ____________________________________ Nonvascular Plants such as Bryophyta (mosses), Hepatophyta (liver warts), and Anthocerophyta (hornworts) __________________________________________ _________________________________________________________ (more on plant anatomy later…). Page 11 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Vascular Plants ______________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________. • Vascular plants can be further divided into 2 groups: i. Seedless Plants - _____________________________________________________ __________________________, and three other phyla closely associated with ferns: a. Psilotophyta (whisk Ferns) b. Lycophyta (club Mosses) c. Sphenophyta (Horsetails) d. Pterophyta (Ferns) ii. Seed Plants - that produce seeds for reproduction including ________________ _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________ - Gymnosperm produce __________________________________ _____________________________________ (i.e., pine trees) and include: a. Cycadophyta (i.e. Cycads) b. Ginkgophyta (i.e. Ginkgoes) c. Coniferophyta (i.e. Conifers) d. Gnetophyta (i.e. Gnetophytes) - Angiosperm produce __________________________________ _____________________________________ (i.e., apple and orange trees). Angiosperms are ________________________ _________________________ and include: a. Anthophyta (i.e. flowering plants). Class Monocotyledons (monocots) and Class Dicotyledons (dicots) We will study each of these groups as we move through the plant module. Page 12 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Review of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis _______________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ _________________. In plants, this process _________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________. Photosynthesis is the process that provides all of the energy made by producers that is the base of the energy pyramid. Without plants and autotrophs we would have no food to eat or oxygen to breath. Plants absorb a common gas called carbon dioxide, pull water up through their roots and use light to make sugar. Plants use the sugar to grow and give off oxygen as a byproduct. The chemical reaction that takes place in chloroplasts (say inside a tree leaf) uses the _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________. Page 13 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Review of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ __________________________________ that can do work inside cells. This process _____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________. Both plants and animals use the products of photosynthesis (glucose) for metabolic fuel. The chemical reaction that takes place in mitochondria (say inside a muscle cell) _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ ________________ currency of cells. Comparing Photosynthesis to Cellular Respiration It is important to note that ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________. The reactants and products are reversed. They are the same reaction running in two directions. Page 14 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Life Cycle of Plants Plants use an _________________________________________________________ ______________________. In the plant's cycle, the __________________________ ______________________________________________________________ and the ________________________________________________________________. The life cycles of each type of plant are dominant in one stage or the other. ____________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________. Within the cycle, the ___________________________ _____ (2n) undergoes meiosis to ___________________________ _________ (n) which will typically disperse. It will then divide and grow into a _______________________ (n). Two gametes will combine (fertilization) to form a zygote (2n), which will develop into a sporophyte (2n) to complete the cycle. Although the main difference between the life cycles of different plants is the structure that disperses the species, other differences between the cycles will be discussed in further lessons. 6.2 PRACTICE: INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS 1. State two reasons why plants are critical to life on Earth as we know it. (2 marks) Page 15 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 2. Identify 4 key characteristics of plants. (4 marks) 3. Photosynthesis is key to survival of life on Earth as we know it: a. Write the balanced equation for photosynthesis. (4 marks) b. Identify which organelle photosynthesis occurs in. (1 mark) c. Photosynthetic organisms that are capable of creating their own organic molecules are known as _______________________________. (1 mark) 4. Cellular respiration is also key to survival of life on Earth as we know it: a. Write the balanced equation for cellular respiration. (4 marks) b. Identify which organelle cellular respiration occurs in. (1 mark) Page 16 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 6.3 NOTES: NON-VASCULAR PLANTS Types of Non-vascular Plants ________________________ plants belong to the division ______________________, which includes _______________________ ______________________________. These plants have ___________________________ _______________________, so the plants ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ________________________________. The bryophytes __________________________ _____________________________________________________, although the plant body is differentiated into leaflike and stemlike parts. In some species, _____________ _________________________________________________________. With no vascular tissue, the bryophytes cannot retain water for long periods of time. Consequently, ________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________. This explains the presence of mosses in moist areas, such as swamps and bogs, and on the shaded sides of trees. ______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________ generation. Therefore, they are primarily haploid. Their only diploid stage is the zygote which grows to the sporophyte. Both the zygote and sporophyte are parasitic on the gametophyte since they do not have any photosynthetic tissue. The function of the sporophyte is simply to disperse the spores so it grows above the plant to reach the wind. • Hornworts - Division Anthocerotaceae Hornworts are described as a slimy looking photosynthetic substance in the gametophyte generation. It is the sporophyte which gives this division its name. It grows up like a spike from the gametophyte and continues to grow for the life of the plant. Page 17 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 • Liverworts - Division Hepatophyta Liverworts are a _____________________________ in the gametophyte generation _________________ ________________________________. The thallus has ____________________________________ ____________________________ growing down into the soil. Liverworts undergo both sexual and asexual reproduction. During asexual reproduction a gemmae will break out of the gemmae cup to form a new plant. Sexual reproduction occurs similarly to mosses in that they have _____________ _______________________________________________________________ which fertilize to form a sporophyte. The sporophyte releases spores that will grow to form a new liverwort. • Mosses _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ _________________________ ________________________. Mosses do have ______________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ____________________________ ___________________________. Food molecules produced by photosynthesis within the leaf-like structures cannot be distributed very far. As a result the mosses are generally limited in size. Mosses will typically grow as a mat of _____________________________________. To summarize: 1. __________________________________________________________ 2. __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 3. __________________________________________________________ 4. Mosses are small due to their lack of vascular tissue. 5. They depend on diffusion and osmosis for the movement of materials throughout the plant. Page 18 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Life Cycle of the Mosses The life cycle of the moss is typical of the bryophytes. Flask-shaped _____________________, located among the top leaves of the __________________ ______________________________________________________________, located similarly on the ________________________________________________________ __________________________________ that swim in drops of rainwater or dew into the neck of the archegonium to fertilize the egg cell. The zygote that results from the fertilization develops into a young sporophyte within the archegonium. The sporophyte grows out of the archegonium, taking its nourishment from the gametophyte, and differentiates into a slender stalk with a spore capsule near the tip. Haploid spores are produced by meiosis in this capsule, and when the tip of the capsule opens, the spores are freed. _______________________ _______________________________________________________________, which represent the next stage in the alternation of generations. Page 19 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Review ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________and is the form we recognize as ‘mosses.’ At the tip of the gametophyte are reproductive structures called the ____________________ ___________________________________________________________________. When sperm swims to the egg fertilization produces a zygote. When the zygote germinates it produces a diploid sporophyte. The sporophyte is totally dependent on the gametophyte for food and water as it grows on top of the gametophyte. The sporophyte has a capsule on top that contains haploid spores (produced by meiosis). Once a spore is released and it lands, it germinates into a mass of green filaments called a Protanema. This protanema develops shoots and rhizoids and becomes the dominant haploid gametophyte. Evolutionary Importance Nonvascular plants are important to evolutionary biologists because they __________ ____________________________________. They have some tissue differentiation but are obviously not as advanced as vascular plants. They are dependent on a nearly aquatic lifestyle for part of their life cycle. They are considered the most primitive of the plant kingdom and they are also known as great __________________ __________________. Bryophytes are also important ________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________. . 6.3 PRACTICE: NON-VASCULAR PLANTS 1. Identify 3 key differences between non-vascular plants and algae. (3 marks) Page 20 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 2. Define and explain the functions of the antheridia and archegonia. (4 marks) 6.4 NOTES: SEEDLESS PLANTS Types of Seedless Vascular Plants Vascular plants are divided into two main groups, seedless and seed. While _________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________. The seedless divisions include ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________. The structure of the vascular tissue is common to all vascular plants. _______________ ______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________. It is the xylem that enables vascular plants to be tall. Not only is the xylem capable of transporting water to the leaves of tall plants but the xylem is also responsible for stability in woody tissues. These tissues help the plant fight gravity and the wind. ______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________ generation. It is beneficial to be diploid because a faulty gene can be masked by its duplicate if it is normal reducing the Page 21 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 chance of mutation. _____________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ if a genetic change does occur. ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________. However, they ___________________ ______________________________________________________________________ _________________________________. They can live in dry environments in the sporophyte generation because the gametophyte is independent. • Whisk Ferns - Division Psilophyta Whisk ferns are an interesting group of plants because they have no leaves. Instead, the branches of the plant carry on photosynthesis and hold the sporangia which produce the spores. • Club Mosses - Division Lycopodophyta Club mosses are composed of a ______________________ ____________________________________ with small roots branching from it. They look like a more complexly branched whiskfern, but they actually have leaves. The small scale-like leaves branch off of the stem. The sporangia are held by specialized leaf clusters called strobili. • Horse Tails - Division Equisetophyta This division is made up of only 15 species, all of which are in the same genus. However, they are still found worldwide in moist habitats. Horsetails have a single stem growing up from a rhizome and whorled (circular arrangement) branches off of the stem. The horsetails also have a specialized leaf arrangement for holding the sporangia. It is called a strobilus because there is only one. Page 22 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 • Ferns - Division Pteridophyta Most ferns ________________________________________ ________________________________________. They range from less than 1cm to 25 m tall. Ferns live in all climates, on forest floors, as epiphytes (survive by living off of other plants), in full sun. Some ferns are aquatic. The ____________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________. The stems contain specialized vascular tissues for transporting water and dissolved substances from one part of the plant to another. Strong stems containing this vascular tissue allow plants to grow tall. Fern Life Cycle Like other seedless vascular plants, _________________________________ ________________________________________. However, ferns vary in size and shape much more than the other divisions. Typically, the ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ _________________________________. After the sperm swim to the ____________________________________ they fertilize the egg forming a zygote. The ___________________________________________________ ____________________________ that is a small curled stem with leaves. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Page 23 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Diagram of Fern Life cycle Page 24 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 6.4 PRACTICE: SEEDLESS PLANTS 1. Define vascular tissue with respect to plants. (1 mark) 2. Explain how vascular tissue enables a plant to grow larger. (2 marks) 3. Some plants are non-vascular while others are vascular. Using your understanding of evolution and thinking critically: a. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of being nonvascular. (2 marks) Page 25 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 b. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of being vascular. (2 marks) ~ END OF BIOLOGY 11 UNIT 6 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 26 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 UNIT 6 ANSWER KEY 6.1 PRACTICE: DIVERSITY OF ALGAE 1. Distinguish between the terms diploid and haploid. (2 marks) - diploid cells = 2n meaning they have two identical (barring mutation) copies of each chromosome - haploid cells = n meaning they have one copy of each chromosome 2. Alternation of Generation is an important concept in many organisms' life cycles. Describe what alternation of generation means. (2 marks) An organism that has an alternation of generation life cycle will alternate between a haploid stage and a diploid stage, although the length of time the organism spends in each stage can vary greatly depending on the species. In plants the sporophyte is diploid (2n) while the gametophyte is haploid (n). 3. The classification scheme of algae can be quite confusing and takes considerable practice to master. However, there are some key concepts that even the beginning biologist should be able to master: a. What two characteristics do all algae have in common? (2 marks) - aquatic and photosynthetic b. Most algae classified and named based on what characteristic? (1mark) - the type of pigments they contain 4. Some algae reproduce asexually, some reproduce asexually and some reproduce using both methods. Using your understanding of evolution and thinking critically: a. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of reproducing sexually. (2 marks) - advantage = greater genetic diversity = greater chance of surviving natural selection as a species - disadvantage = must find a "partner" to reproduce with Page 27 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 b. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of reproducing asexually. (2 marks) - advantage = rapids, no partner necessary so can occur anywhere, anytime - disadvantage = generally less genetic diversity = less chance of surviving natural selection as a species 6.2 PRACTICE: INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS 1. State two reasons why plants are critical to life on Earth as we know it. (2 marks) - animals are obligate aerobes meaning they require oxygen to live, without photosynthetic organisms like plants the Earth would lack oxygen and therefore animal life as we know it - plants are producers (autotrophs) that can convert water, carbon dioxide and solar energy into carbohydrates that are used to support all of Earth's consumers (heterotrophs) including humans 2. Identify 4 key characteristics of plants. (4 marks) - Photosynthesis…ability to produce own food from water, carbon dioxide and solar energy Cell walls that contain cellulose – affording structure and protection Sessile – do not move throughout their life cycle Alternation of Generations – switch between diploid sporophyte and haploid gametophyte throughout their life cycle 3. Photosynthesis is key to survival of life on Earth as we know it: a. Write the balanced equation for photosynthesis. (4 marks) 6 H 2 O + 6 CO 2 + Solar Energy C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 b. Identify which organelle photosynthesis occurs in. (1 mark) - chloroplasts c. Photosynthetic organisms that are capable of creating their own organic molecules are known as _______________________________. (1 mark) Page 28 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 4. Cellular respiration is also key to survival of life on Earth as we know it: a. Write the balanced equation for cellular respiration. (4 marks) C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 6 H 2 O + 6 CO 2 + Energy (in form of ATP) b. Identify which organelle cellular respiration occurs in. (1 mark) - mitochondria 6.3 PRACTICE: NON-VASCULAR PLANTS 1. Identify 3 key differences between non-vascular plants and algae. (3 marks) - cuticle = waxy outer layer to protect plant from drying out - stomata = pores for gas exchange - adaptations to prevent embryos from drying out 2. Define and explain the functions of the antheridia and archegonia. (4 marks) - Archegonia are found in the female gametophyte and produce eggs - Antheridia are found in the male gametophyte and produce sperm 6.4 PRACTICE: SEEDLESS PLANTS 1. Define vascular tissue with respect to plants. (1 mark) - Vascular tissue refers to vessel systems used to move substances throughout the plants. There are two main types of tissues namely xylem and phloem. - Xylem = transports water and minerals from roots, upwards throughout the plant - Phloem = transports nutrients produced in the leaves by photosynthesis to all other parts of the plant Page 29 of 30 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 2. Explain how vascular tissue enables a plant to grow larger. (2 marks) Vascular tissue enables a plant to grow larger as water, minerals and nutrients can be delivered over a greater area/volume than in non-vascular plants. Most material can diffuse effectively through tissues about 1 – 2mm thick (such as found in non-vascular plants) but once tissues exceed this thickness (such as in vascular plants) they must be supported by vascular tissue to ensure all the cells receive the resources necessary for survival. 3. Some plants are non-vascular while others are vascular. Using your understanding of evolution and thinking critically: a. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of being non-vascular. (2 marks) - advantage = less complex = potentially more efficient - disadvantage = must have regular, easy access to water such as in swamps and bogs b. Identify and explain a selective advantage and disadvantage of being vascular. (2 marks) - advantage = ability to survive in more diverse environments (with limited water) - disadvantage = more complex, potentially less efficient Page 30 of 30