How Cells Release Chemical Energy
... • Cells take up glucose faster, more ATP is formed, glycogen and fatty-acid production increases ...
... • Cells take up glucose faster, more ATP is formed, glycogen and fatty-acid production increases ...
UNBREAKABLE! By the Training Research Group Cell volumizers
... able to absorb, utilize and convert protein into muscle mass. Basically, when you have greater nitrogen retention, your body is more anabolic. You’ll build muscle and increase strength faster. Nitroarginine works so well to improve nitrogen retention because once it enters the body it converts to ni ...
... able to absorb, utilize and convert protein into muscle mass. Basically, when you have greater nitrogen retention, your body is more anabolic. You’ll build muscle and increase strength faster. Nitroarginine works so well to improve nitrogen retention because once it enters the body it converts to ni ...
Agent-based Protein Structure Prediction
... process for reaching the native state is known as the protein folding. Currently, the native conformations of more than 30000 proteins are available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) [4]. In this work we concentrate on ab-initio modelling. These methods are based on the Anfinsen thermodynamic hypothesi ...
... process for reaching the native state is known as the protein folding. Currently, the native conformations of more than 30000 proteins are available in the Protein Data Bank (PDB) [4]. In this work we concentrate on ab-initio modelling. These methods are based on the Anfinsen thermodynamic hypothesi ...
Document
... • Cells take up glucose faster, more ATP is formed, glycogen and fatty-acid production increases ...
... • Cells take up glucose faster, more ATP is formed, glycogen and fatty-acid production increases ...
Chapter 16 The Citric Acid Cycle
... D) 1 mol of oxaloacetate. E) 7 mol of ATP. 8. The oxidative decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate proceeds by means of multistep reactions in which all but one of the following cofactors are required. Which one is not required? A) ATP B) Coenzyme A C) Lipoic acid D) NAD+ E) Thiamine pyrophosphate 9. Th ...
... D) 1 mol of oxaloacetate. E) 7 mol of ATP. 8. The oxidative decarboxylation of α-ketoglutarate proceeds by means of multistep reactions in which all but one of the following cofactors are required. Which one is not required? A) ATP B) Coenzyme A C) Lipoic acid D) NAD+ E) Thiamine pyrophosphate 9. Th ...
Chapter 6
... The evidence for chemiosmosis The processes by which ATP is made in photophosphorylation (in photosynthesis) and oxidative phosphorylation (in respiration) are very similar. In both cases, energy is used to pump hydrogen ions across a membrane, building up a gradient for them. They are then allowed ...
... The evidence for chemiosmosis The processes by which ATP is made in photophosphorylation (in photosynthesis) and oxidative phosphorylation (in respiration) are very similar. In both cases, energy is used to pump hydrogen ions across a membrane, building up a gradient for them. They are then allowed ...
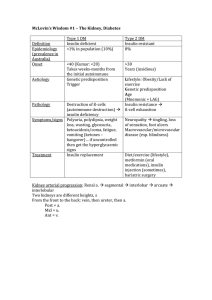
McLovin`s Wisdom #1 – The Kidney, Diabetes Type 1 DM Type 2
... Proteins in the body are not just “stored” – they are always doing something ...
... Proteins in the body are not just “stored” – they are always doing something ...
2 Organic Acidemias
... Many of the organic acidemias respond to treatment, and in the neonate especially, early diagnosis and prompt management are essential to a good outcome. The aim of therapy is to restore biochemical and physiologic homeostasis. The treatments, while similar in principle, depend on the specific bioch ...
... Many of the organic acidemias respond to treatment, and in the neonate especially, early diagnosis and prompt management are essential to a good outcome. The aim of therapy is to restore biochemical and physiologic homeostasis. The treatments, while similar in principle, depend on the specific bioch ...
14C2H4 : Distribution of 14G-labeled tissue metabolites
... acidic compounds while the neutral fraction comprised only 1% of the label. In contrast, the reverse was found for 14C2H4 incorporation (Table 1, columns 1-3). That is, the acid fraction contained 5 to 10% of the label while the neutral fraction represented 35-40% of the 14C water-soluble materials. ...
... acidic compounds while the neutral fraction comprised only 1% of the label. In contrast, the reverse was found for 14C2H4 incorporation (Table 1, columns 1-3). That is, the acid fraction contained 5 to 10% of the label while the neutral fraction represented 35-40% of the 14C water-soluble materials. ...
The RAVEN Toolbox and Its Use for Generating a Genome
... allows for semi-automated reconstruction of genome-scale models. It makes use of published models and/or the KEGG database, coupled with extensive gap-filling and quality control features. The software suite also contains methods for visualizing simulation results and omics data, as well as a range ...
... allows for semi-automated reconstruction of genome-scale models. It makes use of published models and/or the KEGG database, coupled with extensive gap-filling and quality control features. The software suite also contains methods for visualizing simulation results and omics data, as well as a range ...
Energy coupling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
... conservation of free energy (ATP) during product formation. Product pathways with a positive net ATP yield provide microorganisms with free energy for growth and maintenance processes. However, during industrial production of chemicals, excess microbial biomass constitutes an undesirable byproduct, ...
... conservation of free energy (ATP) during product formation. Product pathways with a positive net ATP yield provide microorganisms with free energy for growth and maintenance processes. However, during industrial production of chemicals, excess microbial biomass constitutes an undesirable byproduct, ...
Manganese orchestrates a metabolic shift leading to the increased
... cofactors. The activity of aconitase (ACN, EC 4.2.1.3) was determined in the soluble fractions of the CFE. Tricarballylic acid (10 mM), a citrate analogue was added to the whole cells prior to cellular disruption to ensure the stability of this enzyme (30). The assay consisted of activity buffer (25 ...
... cofactors. The activity of aconitase (ACN, EC 4.2.1.3) was determined in the soluble fractions of the CFE. Tricarballylic acid (10 mM), a citrate analogue was added to the whole cells prior to cellular disruption to ensure the stability of this enzyme (30). The assay consisted of activity buffer (25 ...
12918_2009_420_moesm5_esm - Springer Static Content Server
... A theoretical biomass reaction is generally accepted as a suitable objective function for predicting behavior in many growth conditions. This reaction necessitates the specification of all molar constituents of a "mole" of biomass, defined to be 1 g dry cell weight, along with an ATP maintenance cos ...
... A theoretical biomass reaction is generally accepted as a suitable objective function for predicting behavior in many growth conditions. This reaction necessitates the specification of all molar constituents of a "mole" of biomass, defined to be 1 g dry cell weight, along with an ATP maintenance cos ...
+ E A.
... The mental retardation is caused by the accumulation of phenylalanine, which becomes a major donor of amino groups in aminotransferase activity and depletes neural tissue of αketoglutarate. Absence of α-ketoglutarate in the brain shuts down the TCA cycle and the associated production of aerobic ener ...
... The mental retardation is caused by the accumulation of phenylalanine, which becomes a major donor of amino groups in aminotransferase activity and depletes neural tissue of αketoglutarate. Absence of α-ketoglutarate in the brain shuts down the TCA cycle and the associated production of aerobic ener ...
Metabolism in the pre-implantation oocyte and embryo
... mucification, nucleic acid synthesis and plays a major role as a stress/fuel sensing molecule (reviewed by Sutton-McDowall et al., 2010). With the progression of COC maturation, metabolism increases steadily, with increases in glucose, pyruvate and oxygen consumption observed (Sutton et al., 2003a). ...
... mucification, nucleic acid synthesis and plays a major role as a stress/fuel sensing molecule (reviewed by Sutton-McDowall et al., 2010). With the progression of COC maturation, metabolism increases steadily, with increases in glucose, pyruvate and oxygen consumption observed (Sutton et al., 2003a). ...
Fe-S
... finally electrons combine with O2 and protons to form H2O. • Associated with cell breath, also called respiratory chain. • Electron carriers located in mitochondria according to a order. ...
... finally electrons combine with O2 and protons to form H2O. • Associated with cell breath, also called respiratory chain. • Electron carriers located in mitochondria according to a order. ...
(enzyme).
... • Enzymes can either break up or put together substrates • Enzymes are specific – only work on certain substances. • Enzymes are catalysts that react on substrates • Enzymes are NOT CHANGED in the reaction Textbook ...
... • Enzymes can either break up or put together substrates • Enzymes are specific – only work on certain substances. • Enzymes are catalysts that react on substrates • Enzymes are NOT CHANGED in the reaction Textbook ...
PDF - American Academy of Family Physicians
... and mass. Another report9 of 19 women who took supplements for 10 weeks also described increases in strength and mass. Some researchers10,11 have seen strength gains with as little as five to seven days of supplementation.10,11 Studies12 examining the effects of creatine in older individuals (60 to ...
... and mass. Another report9 of 19 women who took supplements for 10 weeks also described increases in strength and mass. Some researchers10,11 have seen strength gains with as little as five to seven days of supplementation.10,11 Studies12 examining the effects of creatine in older individuals (60 to ...
07c_MuscularSys_PPT
... Muscle Fatigue—When a muscle loses ability to contract due to a low pH (lactic acid buildup), low ATP levels, or other problems Recovery Period—Time after muscle activity that it takes to restore preexertion conditions Oxygen Debt—Amount of excess oxygen used during the recovery period Copyright © 2 ...
... Muscle Fatigue—When a muscle loses ability to contract due to a low pH (lactic acid buildup), low ATP levels, or other problems Recovery Period—Time after muscle activity that it takes to restore preexertion conditions Oxygen Debt—Amount of excess oxygen used during the recovery period Copyright © 2 ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.