Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
... Electrons transferred = maintain energy if stays in same energy level Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons (REDOX) o ...
... Electrons transferred = maintain energy if stays in same energy level Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons (REDOX) o ...
Ch16-1 Fatty-acid-and-triacylglycerol
... Carbohydrates, protein, and other molecules obtained from the diet in excess of the body's needs for these compounds can be converted to fatty acids, which are stored as triacylglycerols. In adult humans, fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the liver and lactating mammary glands and, to a l ...
... Carbohydrates, protein, and other molecules obtained from the diet in excess of the body's needs for these compounds can be converted to fatty acids, which are stored as triacylglycerols. In adult humans, fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the liver and lactating mammary glands and, to a l ...
Cellular respiration
... • The process that generates most of the ATP during cellular respiration is called oxidative phosphorylation because it is powered by redox reactions of an electron transport chain. • Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by cellular respiration. ...
... • The process that generates most of the ATP during cellular respiration is called oxidative phosphorylation because it is powered by redox reactions of an electron transport chain. • Oxidative phosphorylation accounts for almost 90% of the ATP generated by cellular respiration. ...
Answers - U of L Class Index
... When fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate splits, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate are formed. The dihydroxyacetone phosphate is converted to glyceraldehyde-3phosphate for subsequent reactions. ...
... When fructose-1, 6-bisphosphate splits, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate are formed. The dihydroxyacetone phosphate is converted to glyceraldehyde-3phosphate for subsequent reactions. ...
03-232 Biochemistry Exam III - S2014 Name:________________________
... 8. (6 pts) Please do one of the following choices. Choice A: What is the critical micelle concentration (CMC)? How does it depend on the number of carbons? Choice B: How does cholesterol affect the properties of membranes and why is this effect important for function? Choice C: In what way is the fu ...
... 8. (6 pts) Please do one of the following choices. Choice A: What is the critical micelle concentration (CMC)? How does it depend on the number of carbons? Choice B: How does cholesterol affect the properties of membranes and why is this effect important for function? Choice C: In what way is the fu ...
Regulation of Primary Metabolism in Response to
... Ala pathway provides a means for the role of Ala accumulation during hypoxia via reorganization of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Furthermore, given that the use of this strategy prevents pyruvate accumulation, the continued operation of glycolysis during waterlogging can occur. It should be noted, h ...
... Ala pathway provides a means for the role of Ala accumulation during hypoxia via reorganization of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Furthermore, given that the use of this strategy prevents pyruvate accumulation, the continued operation of glycolysis during waterlogging can occur. It should be noted, h ...
Enzyme Hydrolyzed Collagen Protein
... should intake 1 gram of protein for every 2.2 pounds of weight every day. Some people have a problem with digestion of protein and therefore are not assimilating the necessary amino acids because the protein molecules are too large for their stomach and small intestine to handle. When this happens, ...
... should intake 1 gram of protein for every 2.2 pounds of weight every day. Some people have a problem with digestion of protein and therefore are not assimilating the necessary amino acids because the protein molecules are too large for their stomach and small intestine to handle. When this happens, ...
enzymes - La Salle High School
... • Maximum activity at optimum pH • R groups of amino acids have proper charge • Tertiary structure of enzyme is correct • Narrow range of activity • Most lose activity in low or high pH ...
... • Maximum activity at optimum pH • R groups of amino acids have proper charge • Tertiary structure of enzyme is correct • Narrow range of activity • Most lose activity in low or high pH ...
Biochemistry - Bonham Chemistry
... Gluconeogenesis -Metabolic Pathways are Irreversible ∆G between the 1st & last metabolite is large & neg. - If 2 metabolites are interconvertible (metab 1 ...
... Gluconeogenesis -Metabolic Pathways are Irreversible ∆G between the 1st & last metabolite is large & neg. - If 2 metabolites are interconvertible (metab 1 ...
Untitled - Heart and Metabolism
... Decreased myocardial mechanical efficiency in the failing heart is a consistent and early finding both clinically and in experimental models. Assessment of myocardial mechanical efficiency is an important clinical tool for evaluation of the outcome of therapies. As illustrated in the Fig. 1, energy ...
... Decreased myocardial mechanical efficiency in the failing heart is a consistent and early finding both clinically and in experimental models. Assessment of myocardial mechanical efficiency is an important clinical tool for evaluation of the outcome of therapies. As illustrated in the Fig. 1, energy ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... • Maximum activity reached when all of enzyme combines with substrate ...
... • Maximum activity reached when all of enzyme combines with substrate ...
Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation
... hapters 3 and 4 contain many examples of an important principle: that a cell’s structure is intimately related to its function. In each instance one can readily relate an organelle’s construction to its function (and vice versa). A second unifying principle in biology is that life is sustained by th ...
... hapters 3 and 4 contain many examples of an important principle: that a cell’s structure is intimately related to its function. In each instance one can readily relate an organelle’s construction to its function (and vice versa). A second unifying principle in biology is that life is sustained by th ...
Metabolism of BCAAs
... However, this near equilibrium status also means that for the reaction to proceed, rather than cycle between BCAAs and BCKAs, BCKAs must be eliminated. This can occur via simple removal from the cell which is not typical as demonstrated by the exceptionally low circulating levels of BCKAs in the ser ...
... However, this near equilibrium status also means that for the reaction to proceed, rather than cycle between BCAAs and BCKAs, BCKAs must be eliminated. This can occur via simple removal from the cell which is not typical as demonstrated by the exceptionally low circulating levels of BCKAs in the ser ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... saturated, and which remains attached to the ACP. These seven steps are repeated, beginning with the transfer of the butyryl chain from the ACP to the Cys residue [2*], the attachment of a molecule of malonate to the ACP [3*], and the condensation of the two molecules liberating CO2 [4*]. The ca ...
... saturated, and which remains attached to the ACP. These seven steps are repeated, beginning with the transfer of the butyryl chain from the ACP to the Cys residue [2*], the attachment of a molecule of malonate to the ACP [3*], and the condensation of the two molecules liberating CO2 [4*]. The ca ...
Cellular Respiration Part V: Anaerobic Respiration and Fermentation
... to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
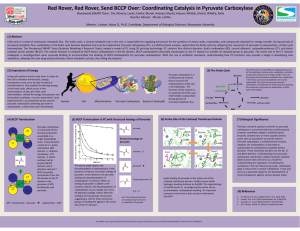
Poster
... increased metabolic flux, metabolites in the Krebs cycle become depleted and must be replenished. Pyruvate carboxylase (PC), a multifunctional enzyme, replenishes the Krebs cycle by catalyzing the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate, a Krebs cycle intermediate. The Shorewood SMART Team (Students ...
... increased metabolic flux, metabolites in the Krebs cycle become depleted and must be replenished. Pyruvate carboxylase (PC), a multifunctional enzyme, replenishes the Krebs cycle by catalyzing the conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate, a Krebs cycle intermediate. The Shorewood SMART Team (Students ...
Lecture Eighteen - Personal Webspace for QMUL
... Therefore __________ compartments in mitochondria The intermembrane space Between the OMM and IMM The __________ Surrounded by the IMM NOTE: Fatty acid oxidation, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, the citric acid cycle => located in the _________ NOTE: Respiratory electron transfer, oxid ...
... Therefore __________ compartments in mitochondria The intermembrane space Between the OMM and IMM The __________ Surrounded by the IMM NOTE: Fatty acid oxidation, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, the citric acid cycle => located in the _________ NOTE: Respiratory electron transfer, oxid ...
Abstract-- Lactic acid bacteria are characterized
... by numerous nutritional requirements. The influence of amino acids and peptides on the growth of Pediococcus pentosaceus c1 isolated from argentinean wines was determined. Cells were growth in synthetic media and in the same media added with the following dipeptides: leucine-leucine; leucine-proline ...
... by numerous nutritional requirements. The influence of amino acids and peptides on the growth of Pediococcus pentosaceus c1 isolated from argentinean wines was determined. Cells were growth in synthetic media and in the same media added with the following dipeptides: leucine-leucine; leucine-proline ...
video slide - Northwest Florida State College
... III. The Citric Acid Cycle • Citric Acid Cycle takes place in the MITOCHONDRION • Prior to entering Citric Acid Cycle, Acetyl CoA is added to the pyruvate molecule Addition of CoA group makes a ...
... III. The Citric Acid Cycle • Citric Acid Cycle takes place in the MITOCHONDRION • Prior to entering Citric Acid Cycle, Acetyl CoA is added to the pyruvate molecule Addition of CoA group makes a ...
Slide 1
... other mitochondrial uncoupling proteins) which are activated by calcium coming in through the calcium uniporter. Also note that electron carriers can autooxidize directly to oxygen, creating oxygen radicals (Co-Q is the major site of autooxidation) with as much as 5% of resting oxygen use due to thi ...
... other mitochondrial uncoupling proteins) which are activated by calcium coming in through the calcium uniporter. Also note that electron carriers can autooxidize directly to oxygen, creating oxygen radicals (Co-Q is the major site of autooxidation) with as much as 5% of resting oxygen use due to thi ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.