Cellular Respiration
... You can see that the two ATP molecules produced during glycolysis receive only a small percentage of the energy that could be released by the complete oxidation of each molecule of glucose. Much of the energy originally contained in glucose is still held in pyruvic acid. Even if pyruvic acid is conv ...
... You can see that the two ATP molecules produced during glycolysis receive only a small percentage of the energy that could be released by the complete oxidation of each molecule of glucose. Much of the energy originally contained in glucose is still held in pyruvic acid. Even if pyruvic acid is conv ...
Methylobacterium extorquens AM1
... cell extracts when cells were incubated overnight with methanol plus succinate [27]. An intermediate level of some of the enzymes activities compared to their levels under pure methanol or succinate conditions suggests the presence of a dedicated metabolism adapted to mixotrophic conditions. However ...
... cell extracts when cells were incubated overnight with methanol plus succinate [27]. An intermediate level of some of the enzymes activities compared to their levels under pure methanol or succinate conditions suggests the presence of a dedicated metabolism adapted to mixotrophic conditions. However ...
lecture7
... acid synthesis (Table 22.2). In fact, the reactions leading to fatty acid synthesis in higher organisms are very much like those of bacteria. The elongation phase of fatty acid synthesis starts with the formation of acetyl ACP and malonyl ACP. Acetyl transacylase and malonyl transacylase catalyze th ...
... acid synthesis (Table 22.2). In fact, the reactions leading to fatty acid synthesis in higher organisms are very much like those of bacteria. The elongation phase of fatty acid synthesis starts with the formation of acetyl ACP and malonyl ACP. Acetyl transacylase and malonyl transacylase catalyze th ...
A generalized stoichiometric model of C3, C2, C2
... calculates key reaction rates, and ATP and NADPH requirements, in the M and BS as well as fluxes between the BS and M when the following parameters are known: the locality of GDC and Rubisco, leaf-level Rubisco rates of carboxylation and oxygenation (VO, VC), and PEP carboxylation rate (VP). The ATP ...
... calculates key reaction rates, and ATP and NADPH requirements, in the M and BS as well as fluxes between the BS and M when the following parameters are known: the locality of GDC and Rubisco, leaf-level Rubisco rates of carboxylation and oxygenation (VO, VC), and PEP carboxylation rate (VP). The ATP ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... 1. Valine and isoleucine: These amino acids are branchedchain amino acids that generate propionyl CoA, which is converted to succinyl CoA by biotin- and vitamin B12– requiring reactions (Figure 20.10). 2. [Note: Propionyl CoA, then, is generated by the catabolism of certain amino acids and odd-numbe ...
... 1. Valine and isoleucine: These amino acids are branchedchain amino acids that generate propionyl CoA, which is converted to succinyl CoA by biotin- and vitamin B12– requiring reactions (Figure 20.10). 2. [Note: Propionyl CoA, then, is generated by the catabolism of certain amino acids and odd-numbe ...
The Metabolic Significance of the Citric Acid Cycle in
... (a) Isolation of gkutamic and aspartic acids. Each sample of extracted cells was hydrolysed in a sealed vessel at 105' for 18 hr. with a mixture of equal parts of lON-HC1 and glacial acetic acid. After evaporation to dryness, the residue was dissolved in water and a portion retained for chromatograp ...
... (a) Isolation of gkutamic and aspartic acids. Each sample of extracted cells was hydrolysed in a sealed vessel at 105' for 18 hr. with a mixture of equal parts of lON-HC1 and glacial acetic acid. After evaporation to dryness, the residue was dissolved in water and a portion retained for chromatograp ...
The urea cycle
... production (the total lack of any cycle enzyme results in death shortly after birth). Rather, the deficient enzyme's substrate builds up, increasing the rate of the deficient reaction to normal. The anomalous substrate buildup is not without cost, however. The substrate concentrations become elevate ...
... production (the total lack of any cycle enzyme results in death shortly after birth). Rather, the deficient enzyme's substrate builds up, increasing the rate of the deficient reaction to normal. The anomalous substrate buildup is not without cost, however. The substrate concentrations become elevate ...
lecture 6 ppt
... V. Anaerobic respiration VI. Respiration using other biomolecules VII. Lecture Concepts ...
... V. Anaerobic respiration VI. Respiration using other biomolecules VII. Lecture Concepts ...
Biochemical Screening of Pyrimidine
... In general, oxidative phosphorylation is perhaps not the energy source of choice in a biochemical-pharmacological screening system. This source of energy has certain disadvantages, Among these are the rigorous standards of cleanliness which must be observed and the instability of the enzyme system. ...
... In general, oxidative phosphorylation is perhaps not the energy source of choice in a biochemical-pharmacological screening system. This source of energy has certain disadvantages, Among these are the rigorous standards of cleanliness which must be observed and the instability of the enzyme system. ...
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts, and Peroxisomes
... Mitochondria contain their own genetic system, which is separate and distinct from the nuclear genome of the cell. Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship in which they lived within larger cells (endosymbiosis). This hypothesis has recently been ...
... Mitochondria contain their own genetic system, which is separate and distinct from the nuclear genome of the cell. Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship in which they lived within larger cells (endosymbiosis). This hypothesis has recently been ...
(pdf)
... aspartic acid racemization rate as a function of temperature is well known, the determination of the D/L-aspartic acid ratio of the amino acids from intact cells therefore should provide a direct measure of the in situ anabolic rate without relying upon any assumptions about the fraction of living b ...
... aspartic acid racemization rate as a function of temperature is well known, the determination of the D/L-aspartic acid ratio of the amino acids from intact cells therefore should provide a direct measure of the in situ anabolic rate without relying upon any assumptions about the fraction of living b ...
TCA (Krebs) Cycle
... ©Copyright 1999-2004 by Gene C. Lavers No part of this presentation may be reproduced by any mechanical, photographic, or electronic process, or in the form of a phonographic recording, nor may it be stored in a retrieval system, transmitted, or otherwise copied for public or private use, without wr ...
... ©Copyright 1999-2004 by Gene C. Lavers No part of this presentation may be reproduced by any mechanical, photographic, or electronic process, or in the form of a phonographic recording, nor may it be stored in a retrieval system, transmitted, or otherwise copied for public or private use, without wr ...
Energy for Cells
... Whether you go skiing, take an aerobics class, or just hang out, ATP molecules provide the energy needed for your muscles to contract. ATP molecules are produced during cellular respiration, a process that requires the participation of mitochondria. Cellular respiration is aptly named because just a ...
... Whether you go skiing, take an aerobics class, or just hang out, ATP molecules provide the energy needed for your muscles to contract. ATP molecules are produced during cellular respiration, a process that requires the participation of mitochondria. Cellular respiration is aptly named because just a ...
cellular respiration
... is then 2 phosphorylated 2-phosphoglycerate is transferred from (G3P) molecule, ATP are onproduced C1 •Creates a double bond PEP to ADP •The phospate source is between C1 ...
... is then 2 phosphorylated 2-phosphoglycerate is transferred from (G3P) molecule, ATP are onproduced C1 •Creates a double bond PEP to ADP •The phospate source is between C1 ...
Adjeitey_Cyril _Nii-Klu_2013_ thesis
... States (22, 107, 108). In addition, between 2007-2009 it was estimated that approximately 24.1% of Canadians are obese (143). Obesity is commonly assessed by measuring an individual’s body mass index (BMI) which is calculated by dividing mass measured in kilograms by height measured in meters square ...
... States (22, 107, 108). In addition, between 2007-2009 it was estimated that approximately 24.1% of Canadians are obese (143). Obesity is commonly assessed by measuring an individual’s body mass index (BMI) which is calculated by dividing mass measured in kilograms by height measured in meters square ...
Metabolomics Reveals New Mechanisms for Pathogenesis in Barth
... Barth Syndrome is the only known Mendelian disorder of cardiolipin remodeling, with characteristic clinical features of cardiomyopathy, skeletal myopathy, and neutropenia. While the primary biochemical defects of reduced mature cardiolipin and increased monolysocardiolipin are well-described, much o ...
... Barth Syndrome is the only known Mendelian disorder of cardiolipin remodeling, with characteristic clinical features of cardiomyopathy, skeletal myopathy, and neutropenia. While the primary biochemical defects of reduced mature cardiolipin and increased monolysocardiolipin are well-described, much o ...
Chapter 1 – Title of Chapter
... The B Vitamins are interdependent. The presence of one may affect the absorption, metabolism, and excretion of another. A deficiency of one may affect the functioning or deficiency of another. A variety of foods from each food group will provide an adequate supply of all the B vitamins. A. B Vitamin ...
... The B Vitamins are interdependent. The presence of one may affect the absorption, metabolism, and excretion of another. A deficiency of one may affect the functioning or deficiency of another. A variety of foods from each food group will provide an adequate supply of all the B vitamins. A. B Vitamin ...
Carbohydrate metabolism
... •In absence of O2 re-oxidation of NADH at glyceraldehyde-3-Pdehydrogenase stage cannot take place in electron-transport chain. But the cells have limited coenzyme. Hence to continue the glycolytic pathway NADH must be oxidized to NAD+. This is achieved by reoxidation of NADH by conversion of pyruvat ...
... •In absence of O2 re-oxidation of NADH at glyceraldehyde-3-Pdehydrogenase stage cannot take place in electron-transport chain. But the cells have limited coenzyme. Hence to continue the glycolytic pathway NADH must be oxidized to NAD+. This is achieved by reoxidation of NADH by conversion of pyruvat ...
File - myrnafoxsciencespot
... 2) Kreb’s cycle - completes oxidation process - in mitochondrial matrix. 3) Electron transport chain - step by step energy release for ATP ...
... 2) Kreb’s cycle - completes oxidation process - in mitochondrial matrix. 3) Electron transport chain - step by step energy release for ATP ...
Metabolism of ketonе bodies
... The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. The concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable (starvation) or improperly utilized (diabetes). Oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (anaplerot ...
... The entry of acetyl CoA into the citric acid cycle depends on the availability of oxaloacetate. The concentration of oxaloacetate is lowered if carbohydrate is unavailable (starvation) or improperly utilized (diabetes). Oxaloacetate is normally formed from pyruvate by pyruvate carboxylase (anaplerot ...
VITAMINS-5
... • B5 is an important component of coenzyme A (CoA) • Role of CoA • Required for chemical reactions that generate energy from food (fat, carbohydrates, and proteins) • Synthesis of essential fats, cholesterol, steroid hormones , acetylcholine, melatonin and Heme • Metabolism of a number of drugs and ...
... • B5 is an important component of coenzyme A (CoA) • Role of CoA • Required for chemical reactions that generate energy from food (fat, carbohydrates, and proteins) • Synthesis of essential fats, cholesterol, steroid hormones , acetylcholine, melatonin and Heme • Metabolism of a number of drugs and ...
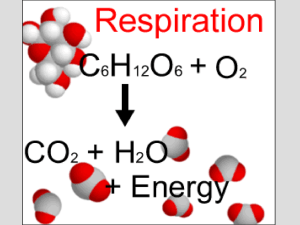
NVC Bio 120 lect 9 cell respiration
... Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy ( ...
... Cellular respiration includes both aerobic and anaerobic respiration but is often used to refer to aerobic respiration Although carbohydrates, fats, and proteins are all consumed as fuel, it is helpful to trace cellular respiration with the sugar glucose C6H12O6 + 6 O2 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Energy ( ...
Biochemistry Lecture 16
... Catabolism/Anabolism Balanced through Kreb’s Cycle • Amphibolic – Impt to both catabolism (breakdown) and anabolism (build-up) of cell’s molecules – Catabolism of carbohydrates, FA’s, aa’s through pyruvate, acetylCoA Kreb’s ATP ...
... Catabolism/Anabolism Balanced through Kreb’s Cycle • Amphibolic – Impt to both catabolism (breakdown) and anabolism (build-up) of cell’s molecules – Catabolism of carbohydrates, FA’s, aa’s through pyruvate, acetylCoA Kreb’s ATP ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.