AP bio fall 2014 final exam prep Multiple Choice Identify the choice
... ____ 35. If you were searching for anaerobic bacteria, you would NOT look for them in a. the guts of farm animals. b. swamps. c. shallow, running water. d. sediments of lakes and oceans. ____ 36. Which statement is true? a. High concentrations of ATP inhibit the formation of more ATP. b. The ATP co ...
... ____ 35. If you were searching for anaerobic bacteria, you would NOT look for them in a. the guts of farm animals. b. swamps. c. shallow, running water. d. sediments of lakes and oceans. ____ 36. Which statement is true? a. High concentrations of ATP inhibit the formation of more ATP. b. The ATP co ...
Chapter 9 PP - Jones-Bio
... Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis • Most of the ETC molecules are proteins containing chemical groups that facilitate redox reactions. All but one of these proteins are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. – In contrast, the lipid-soluble ubiquinone (Q) can move throughout the membrane. ...
... Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis • Most of the ETC molecules are proteins containing chemical groups that facilitate redox reactions. All but one of these proteins are embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane. – In contrast, the lipid-soluble ubiquinone (Q) can move throughout the membrane. ...
Photosynthesis_Cell Resp_Jeopardy
... You have a friend who lost 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of fat on a “low carb” diet. The fat ultimately left her body in this form. ...
... You have a friend who lost 7 kg (about 15 pounds) of fat on a “low carb” diet. The fat ultimately left her body in this form. ...
An Introduction to Metabolism
... resources of the cell. Some metabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. These degradative processes are called catabolic pathways, or breakdown pathways. A major pathway of catabolism is cellular respiration, in which the sugar glucose and other organic ...
... resources of the cell. Some metabolic pathways release energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds. These degradative processes are called catabolic pathways, or breakdown pathways. A major pathway of catabolism is cellular respiration, in which the sugar glucose and other organic ...
Lactic Acidosis - UNC School of Medicine
... An economic system in which the production and distribution of goods are controlled substantially by the government rather than by private enterprise, and in which cooperation rather than competition guides economic activity. There are many varieties of socialism. Some socialists tolerate capitalism ...
... An economic system in which the production and distribution of goods are controlled substantially by the government rather than by private enterprise, and in which cooperation rather than competition guides economic activity. There are many varieties of socialism. Some socialists tolerate capitalism ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... filamentous complexes. Transition to the inactive conformation is associated with dissociation to yield the monomeric form of the enzyme (protomer). ...
... filamentous complexes. Transition to the inactive conformation is associated with dissociation to yield the monomeric form of the enzyme (protomer). ...
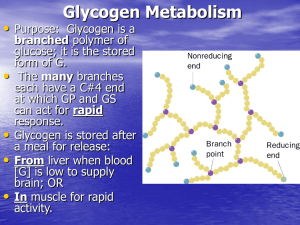
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... dephospho- state of GP, GPK, and GS cannot occur without the accumulation of glucose. It is said that “GP is the glucose sensor”: a) In the phospho (active) form, the P’s on GP are “buried” where PP1 can’t get at them. b) When G binds to active GP-P, its conformation changes, “exposing” the P’s so P ...
... dephospho- state of GP, GPK, and GS cannot occur without the accumulation of glucose. It is said that “GP is the glucose sensor”: a) In the phospho (active) form, the P’s on GP are “buried” where PP1 can’t get at them. b) When G binds to active GP-P, its conformation changes, “exposing” the P’s so P ...
The Stimulatory Effect of Globular Adiponectin on Insulin
... important role in regulating insulin sensitivity in rodents. However, little is known regarding the effect of adiponectin on metabolism in human skeletal muscle. Therefore, we examined whether the globular head of adiponectin, gAcrp30, acutely activates fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake in iso ...
... important role in regulating insulin sensitivity in rodents. However, little is known regarding the effect of adiponectin on metabolism in human skeletal muscle. Therefore, we examined whether the globular head of adiponectin, gAcrp30, acutely activates fatty acid oxidation and glucose uptake in iso ...
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism
... Energy that matter occupies because of it’s location, arrangement, or position. Energy of position. ...
... Energy that matter occupies because of it’s location, arrangement, or position. Energy of position. ...
Chapter 9
... Glycolysis (Figure 9.8) Citric Acid Cycle (Figure 9.11) Oxidative Phosphorylation: Electron Transport (Fig. 9.13 & 9.15) Oxidative Phosphorylation: Chemiosmosis (Figure 9.14 & 9.15) Anaerobic respiration (Figure 9.17) ...
... Glycolysis (Figure 9.8) Citric Acid Cycle (Figure 9.11) Oxidative Phosphorylation: Electron Transport (Fig. 9.13 & 9.15) Oxidative Phosphorylation: Chemiosmosis (Figure 9.14 & 9.15) Anaerobic respiration (Figure 9.17) ...
In vivo analysis of straight-chain and branched
... very high level of intact butyrate incorporation is, however, more consistent with the direct utilization of butyryl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis using either a Type I or Type II fatty acid synthase (Fig. 1). In contrast, a low level of intact hexanoate incorporation into the straight-chain fatty ...
... very high level of intact butyrate incorporation is, however, more consistent with the direct utilization of butyryl-CoA for fatty acid biosynthesis using either a Type I or Type II fatty acid synthase (Fig. 1). In contrast, a low level of intact hexanoate incorporation into the straight-chain fatty ...
Pancreas
... Increases production of glucose from amino acids (gluconeogenesis). Also increases lipolysis, to free fatty acids for metabolism. Result: maintenance of blood glucose levels ...
... Increases production of glucose from amino acids (gluconeogenesis). Also increases lipolysis, to free fatty acids for metabolism. Result: maintenance of blood glucose levels ...
The Effect of Oxygen on the Growth and Mannitol
... Growth of the eight strains under aerobic conditions yielded lactate as the main product, whether or not oxygen suppressed growth, although strains FIL, MT8148 and PK 1-M produced lower concentrations of lactate, as expected from their poor growth. In contrast, anaerobic growth led to heterolactic f ...
... Growth of the eight strains under aerobic conditions yielded lactate as the main product, whether or not oxygen suppressed growth, although strains FIL, MT8148 and PK 1-M produced lower concentrations of lactate, as expected from their poor growth. In contrast, anaerobic growth led to heterolactic f ...
Chapter 1 - Research Explorer
... biomolecules which play a vital role as building blocks in protein synthesis. These neutral aliphatic amino acids, containing methyl-branched side-chains are present in protein-containing food. BCAAs are metabolized predominantly in the skeletal muscle and the liver (>70%). Between 8 – 30% of the ox ...
... biomolecules which play a vital role as building blocks in protein synthesis. These neutral aliphatic amino acids, containing methyl-branched side-chains are present in protein-containing food. BCAAs are metabolized predominantly in the skeletal muscle and the liver (>70%). Between 8 – 30% of the ox ...
Dietary Supplementation With Lipoic Acid Inhibits Exercise
... Acute anaerobic exercise can promote oxidation of lipids. In rats, a single one-minute sprint at 45 m/min elevates lipid hydroperoxides and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in skeletal muscle, indicating significant lipid peroxidation (7). In mice, six 30 s sprints at a pace of 30 m/m ...
... Acute anaerobic exercise can promote oxidation of lipids. In rats, a single one-minute sprint at 45 m/min elevates lipid hydroperoxides and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) in skeletal muscle, indicating significant lipid peroxidation (7). In mice, six 30 s sprints at a pace of 30 m/m ...
Chapter 5
... reactions. Conversely, heterotrophic organisms such as animals ingest food made up of these large polymers, which, when broken down in the digestive process, release energy for maintaining and building that organism. Such chemical reactions, in which complex molecules are broken down to simpler comp ...
... reactions. Conversely, heterotrophic organisms such as animals ingest food made up of these large polymers, which, when broken down in the digestive process, release energy for maintaining and building that organism. Such chemical reactions, in which complex molecules are broken down to simpler comp ...
Gluconeogenesis
... This metabolic pathway is very important because glucose is the primary energy source for the brain. Erythrocytes do not have mitochondria and derive all of their energy by glycolysis converting glucose into two molecules of lactate. The daily requirement for glucose for a typical adult is around 16 ...
... This metabolic pathway is very important because glucose is the primary energy source for the brain. Erythrocytes do not have mitochondria and derive all of their energy by glycolysis converting glucose into two molecules of lactate. The daily requirement for glucose for a typical adult is around 16 ...
Carbohydrate Synthesis 1. Photosynthesis
... Up to this point in the course, the main focus has been the breakdown of metabolites, including carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. The primary purpose of these pathways is to extract energy in useable form with the common end product being ATP, the "energy currency" of the cell. In the case of g ...
... Up to this point in the course, the main focus has been the breakdown of metabolites, including carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids. The primary purpose of these pathways is to extract energy in useable form with the common end product being ATP, the "energy currency" of the cell. In the case of g ...
Stable Isotope Tracer Analysis in Isolated Mitochondria from
... incubation times of 3, 10 and 30 minutes. To evaluate the isotopic enrichment of metabolites generated upon incubation with respiratory substrates, we performed mass isotopomer distribution analyses (described in Section 3.7). As shown in Figure 3C–F, both the amount and isotopic enrichment of multi ...
... incubation times of 3, 10 and 30 minutes. To evaluate the isotopic enrichment of metabolites generated upon incubation with respiratory substrates, we performed mass isotopomer distribution analyses (described in Section 3.7). As shown in Figure 3C–F, both the amount and isotopic enrichment of multi ...
CELLULAR ENERGY METABOLISM DURING FETAL
... In view of the importance of fatty acids as substrates for the mature heart, fatty acid oxidation by fetal and calf heart mitochondria has been investigated . Free fatty acids of 10 carbon units or less which exhibit carnitine-independent transport into mitochondria were effective substrates for oxi ...
... In view of the importance of fatty acids as substrates for the mature heart, fatty acid oxidation by fetal and calf heart mitochondria has been investigated . Free fatty acids of 10 carbon units or less which exhibit carnitine-independent transport into mitochondria were effective substrates for oxi ...
... NAFLD is defined as an excess of fat in the liver in which at least 5% of hepatocytes display lipid droplets (Neuschwander-Tetri, 2005) that exceed 5%-10% of liver weight (Adams et al., 2005 and Browning & Horton, 2004) in patients who do not A currently favored hypothesis is that “two hits” are req ...
Biochimie
... by introducing constructs that express anti-sense or invertedrepeat-containing RNAs [19]. Diatom expression vectors for the validation of subcellular localization, immunodetection of proteins of interest and overexpression studies have also been developed [20]. Thus, the essential molecular and gene ...
... by introducing constructs that express anti-sense or invertedrepeat-containing RNAs [19]. Diatom expression vectors for the validation of subcellular localization, immunodetection of proteins of interest and overexpression studies have also been developed [20]. Thus, the essential molecular and gene ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.