cellular respiration - Aurora City Schools
... How does energy flow through an ecosystem? Can energy be recycled? How do producers get their energy? In which cell organelle does most of this take place? Draw and label it. ...
... How does energy flow through an ecosystem? Can energy be recycled? How do producers get their energy? In which cell organelle does most of this take place? Draw and label it. ...
PHOTOSYNTHESIS & CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION • The process by which living organisms obtain energy from the bonds of food. • There are two important ways the cells can harvest energy from food….cellular respiration and fermentation ...
... CELLULAR RESPIRATION • The process by which living organisms obtain energy from the bonds of food. • There are two important ways the cells can harvest energy from food….cellular respiration and fermentation ...
Cytochromes
... food is called Cellular Respiration ► It is the process by which the chemical energy of "food“ molecules is released and captured in the form of ATP. ...
... food is called Cellular Respiration ► It is the process by which the chemical energy of "food“ molecules is released and captured in the form of ATP. ...
Chapter 6 and 17 notes
... Function of ATP The function of ATP is energy storage The bond linking the last phosphate group is a high-energy bond When the third phosphate is removed, it can attach to another compound and transfer the energy from that high-energy bond. This transfer of energy is phosphorylation Removi ...
... Function of ATP The function of ATP is energy storage The bond linking the last phosphate group is a high-energy bond When the third phosphate is removed, it can attach to another compound and transfer the energy from that high-energy bond. This transfer of energy is phosphorylation Removi ...
I. Introduction to class
... catabolism is available for work, the rest is lost as heat. Energy transformations are inefficient. ...
... catabolism is available for work, the rest is lost as heat. Energy transformations are inefficient. ...
Biochemistry notes (updated 10/26)
... muscles. It can also be broken down to monomers to release energy during cellular respiration. ONLY IN ANIMALS Cellulose – also made up of many glucose units. However, in this case the molecule is not easily broken down to its monomers. It is important for providing a rigid structure in plant cell ...
... muscles. It can also be broken down to monomers to release energy during cellular respiration. ONLY IN ANIMALS Cellulose – also made up of many glucose units. However, in this case the molecule is not easily broken down to its monomers. It is important for providing a rigid structure in plant cell ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
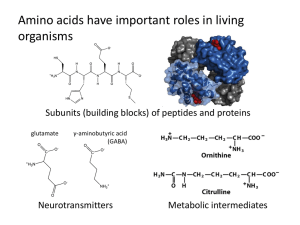
... 3. Why are humans unable to synthesis Vitamin C? 4. Give the structure of tocotrienol. 5. Why is HDL considered as good cholesterol? 6. What is physiological fuel value? Give the values for a. carbohydrates b. proteins c. fats 7. Give the specific functions of the following amino acids :a. glutamic ...
... 3. Why are humans unable to synthesis Vitamin C? 4. Give the structure of tocotrienol. 5. Why is HDL considered as good cholesterol? 6. What is physiological fuel value? Give the values for a. carbohydrates b. proteins c. fats 7. Give the specific functions of the following amino acids :a. glutamic ...
6O2 + C6H12O6 ------------------------
... a. Occurs in the _____________________________________ b. _____________________ is broken down in to 2 molecules of pyruvate c. Uses ________ ATP to start, then makes ______ ATP, so net gain= ____________ d. Many vitamins and minerals are necessary components of cellular respiration, such as vitamin ...
... a. Occurs in the _____________________________________ b. _____________________ is broken down in to 2 molecules of pyruvate c. Uses ________ ATP to start, then makes ______ ATP, so net gain= ____________ d. Many vitamins and minerals are necessary components of cellular respiration, such as vitamin ...
Organic/Bio Chemistry
... Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of cell membranes and waterproofing. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, in ...
... Living things use carbohydrates as their main source of energy. Plants and some animals also use carbohydrates for structural purposes. Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of cell membranes and waterproofing. Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic, in ...
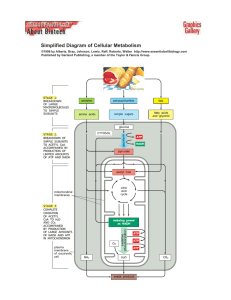
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Lab 8 – Analyzing Muscle Fatigue
... process is called aerobic metabolism or aerobic respiration. The skeletal muscles can also utilize glucose without oxygen, in a process called anaerobic metabolism or anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration can produce energy more quickly than aerobic respiration but, overall, the results are m ...
... process is called aerobic metabolism or aerobic respiration. The skeletal muscles can also utilize glucose without oxygen, in a process called anaerobic metabolism or anaerobic respiration. Anaerobic respiration can produce energy more quickly than aerobic respiration but, overall, the results are m ...
Diet for a person with a 10km run in a weeks time
... Bulk of chemical energy released = Carbohydrates The body’s principle fuel 75% of the body’s energy requirements The main and most efficient source of long lasting energy In the form of sugars and starches (simple or complex) Breakdown carbohydrates = Fuel for intensive exercise Stored in the mu ...
... Bulk of chemical energy released = Carbohydrates The body’s principle fuel 75% of the body’s energy requirements The main and most efficient source of long lasting energy In the form of sugars and starches (simple or complex) Breakdown carbohydrates = Fuel for intensive exercise Stored in the mu ...
Biomolecules
... Polysaccharide found in plant cell walls • For humans cellulose is indigestible and forms dietary fiber • Made up entirely of β glucoses – Structure is constrained into straight microfibrils ...
... Polysaccharide found in plant cell walls • For humans cellulose is indigestible and forms dietary fiber • Made up entirely of β glucoses – Structure is constrained into straight microfibrils ...
Energy Systems and Muscle Fibre Types
... The Chemistry of Energy Production • Energy in the human body is derived from the breakdown of complex nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. • The end result of this breakdown is production of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule. ...
... The Chemistry of Energy Production • Energy in the human body is derived from the breakdown of complex nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. • The end result of this breakdown is production of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule. ...
Second test - rci.rutgers.edu
... B. both form a Schiff base with substrate C. both use an aldose as a group donor D. both use a ketose as a group donor ...
... B. both form a Schiff base with substrate C. both use an aldose as a group donor D. both use a ketose as a group donor ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... waste products of carbon dioxide and and water. The chemical reaction is as follows: ...
... waste products of carbon dioxide and and water. The chemical reaction is as follows: ...
Chapter 2 - Clinton Public Schools
... Bonds break and form during chemical reactions. •Chemical reactions change substances into different ones by __________ and ___________ chemical bonds. –___________ are changed during a chemical reaction. –___________ are made by a chemical reaction. •Bond energy is the amount of energy that ______ ...
... Bonds break and form during chemical reactions. •Chemical reactions change substances into different ones by __________ and ___________ chemical bonds. –___________ are changed during a chemical reaction. –___________ are made by a chemical reaction. •Bond energy is the amount of energy that ______ ...
I. Background - Berks Catholic
... Oxygens are the final H acceptors at the end of electron transport. Carbon dioxide is released during the Kreb’s cycle Water is produced during the electron transport chain. It is a total of 12 water’s but 6 were put in during the Kreb’s cycle. 34 ATP’s as a result of electron transport: 3 for eve ...
... Oxygens are the final H acceptors at the end of electron transport. Carbon dioxide is released during the Kreb’s cycle Water is produced during the electron transport chain. It is a total of 12 water’s but 6 were put in during the Kreb’s cycle. 34 ATP’s as a result of electron transport: 3 for eve ...
Biology Chp 7 Notes
... a. ATP and NADH are made b. It is anaerobic 2. Aerobic Respiration: oxygen is used to break down pyruvic acid and make ATP c. Fermentation: glycolysis and anaerobic pathways occur when oxygen is not available d. Many of the reactions are REDOX reactions (Oxidized loses electrons, Reduced gains elect ...
... a. ATP and NADH are made b. It is anaerobic 2. Aerobic Respiration: oxygen is used to break down pyruvic acid and make ATP c. Fermentation: glycolysis and anaerobic pathways occur when oxygen is not available d. Many of the reactions are REDOX reactions (Oxidized loses electrons, Reduced gains elect ...
unit 2 – the chemistry of life
... 14. Explain the induced-fit model of enzyme function. 15. Describe the mechanisms by which enzymes lower activation energy. 16. Explain how substrate concentration affects the rate of an enzymecatalyzed reaction. 17. Explain how temperature, pH, cofactors, and enzyme inhibitors can affect enzyme act ...
... 14. Explain the induced-fit model of enzyme function. 15. Describe the mechanisms by which enzymes lower activation energy. 16. Explain how substrate concentration affects the rate of an enzymecatalyzed reaction. 17. Explain how temperature, pH, cofactors, and enzyme inhibitors can affect enzyme act ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.