CHAPTER 4: CELLULAR METABOLISM
... 3. Some enzymes are present in the cell’s cytoplasm, so those reactions occur in the cytosol, while other enzymes are present in the mitochondria of the cell, so those reactions occur in the mitochondria. 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy ...
... 3. Some enzymes are present in the cell’s cytoplasm, so those reactions occur in the cytosol, while other enzymes are present in the mitochondria of the cell, so those reactions occur in the mitochondria. 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy ...
Cellular Metabolism
... Oxygen – (like “burning of gasoline that make a engine run) many metabolic processes require oxygen to take place (breathing) ...
... Oxygen – (like “burning of gasoline that make a engine run) many metabolic processes require oxygen to take place (breathing) ...
Harvesting Energy
... transport chain, use the donated energy from the electron carriers to pump protons into the intermembrane space, forming a concentration gradient of protons across the membrane. The protons flow down their concentration gradient through the enzyme ATP synthase, which is a membrane protein. ATP synth ...
... transport chain, use the donated energy from the electron carriers to pump protons into the intermembrane space, forming a concentration gradient of protons across the membrane. The protons flow down their concentration gradient through the enzyme ATP synthase, which is a membrane protein. ATP synth ...
Modeling of CHO Metabolism and Krebs Cycle Using Petri
... For instance if energy is required by the body, glucose would undergo process of glycolysis and generate energy, however if the body do not utilize the glucose as an immediate energy, then glucose would undergo process of glycogen synthesis to produce glycogen. So, based on the above information, we ...
... For instance if energy is required by the body, glucose would undergo process of glycolysis and generate energy, however if the body do not utilize the glucose as an immediate energy, then glucose would undergo process of glycogen synthesis to produce glycogen. So, based on the above information, we ...
Station 1: Carbon Compounds
... Station 1: Carbon Compounds- Close Reading/ Annotate: Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon compounds are also called organic compounds. Many of the molecules in living things are so large that they are known as macromolecules. Macromolecules ...
... Station 1: Carbon Compounds- Close Reading/ Annotate: Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon compounds are also called organic compounds. Many of the molecules in living things are so large that they are known as macromolecules. Macromolecules ...
The Energy of Life The living cell Is a miniature factory where
... (a) Allosteric activators and inhibitors. In the cell, activators and inhibitors dissociate when at low concentrations. The enzyme can then oscillate again. ...
... (a) Allosteric activators and inhibitors. In the cell, activators and inhibitors dissociate when at low concentrations. The enzyme can then oscillate again. ...
Pantothenic Acid - Pure Encapsulations
... At this time, there are no known adverse reactions when taken in conjunction with medications. Consult your physician for more information. Pantothenic Acid each capsule contains ...
... At this time, there are no known adverse reactions when taken in conjunction with medications. Consult your physician for more information. Pantothenic Acid each capsule contains ...
Enzymes
... 1.the concentration of the enzyme. If the enzyme is diluted, its concentration is lowered, which slows the reaction rate. • If the enzyme concentration remains constant as the substrate concentration increases, the rate of the reaction increases until the rate of reaction approaches the maximum velo ...
... 1.the concentration of the enzyme. If the enzyme is diluted, its concentration is lowered, which slows the reaction rate. • If the enzyme concentration remains constant as the substrate concentration increases, the rate of the reaction increases until the rate of reaction approaches the maximum velo ...
Quiz SBI 4UI - Waterloo Region District School Board
... Increasing electronegativity of the molecules ...
... Increasing electronegativity of the molecules ...
Slide 1
... 2-D cross-sectional view of glycogen. A core protein of glycogenin is surrounded by branches of glucose units. The entire globular granule may contain approximately 30,000 glucose units.[1] ...
... 2-D cross-sectional view of glycogen. A core protein of glycogenin is surrounded by branches of glucose units. The entire globular granule may contain approximately 30,000 glucose units.[1] ...
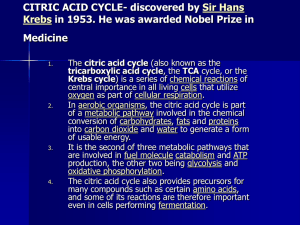
CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... tricarboxylic acid cycle, the TCA cycle, or the Krebs cycle) is a series of chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion ...
... tricarboxylic acid cycle, the TCA cycle, or the Krebs cycle) is a series of chemical reactions of central importance in all living cells that utilize oxygen as part of cellular respiration. In aerobic organisms, the citric acid cycle is part of a metabolic pathway involved in the chemical conversion ...
Amino acids: fed or fasted?
... Gln readily synthesised from glutamate Can be degraded back to glutamate Gut – gln converted to & released as ala – fuel for cells lining gut and available to liver Kidney: Gln derived NH3+ control urinary pH Gln nitrogen waste excretory molecule for muscle ...
... Gln readily synthesised from glutamate Can be degraded back to glutamate Gut – gln converted to & released as ala – fuel for cells lining gut and available to liver Kidney: Gln derived NH3+ control urinary pH Gln nitrogen waste excretory molecule for muscle ...
Glycolysis, Krebs cycle and Cytochrome chain
... At this stage high energy electrons are passed stepwise down an energy gradient enabling the formation of ATP molecules ie. Oxidative phosphorylation. This is a multi-stage pathway and for each NADH molecule that is oxidised to NAD + three x ATP form and for each FADH2 two x ATP form. ie. The total ...
... At this stage high energy electrons are passed stepwise down an energy gradient enabling the formation of ATP molecules ie. Oxidative phosphorylation. This is a multi-stage pathway and for each NADH molecule that is oxidised to NAD + three x ATP form and for each FADH2 two x ATP form. ie. The total ...
26.5 Cotobolism of smino ocids
... metabolism and the economy of nature. By using a single, central pathway for the metabolism of sugars, fats, and amino acids, the cell greatly decreasesthe number of enzymes and chemical steps that otherwise might be required to accomplishthe sametask. Cells have priorities for the utilization of am ...
... metabolism and the economy of nature. By using a single, central pathway for the metabolism of sugars, fats, and amino acids, the cell greatly decreasesthe number of enzymes and chemical steps that otherwise might be required to accomplishthe sametask. Cells have priorities for the utilization of am ...
2 Molecular - bloodhounds Incorporated
... chain on either side of the double bond are either both “up” or both “down,” such that both are on the same side of the molecule. • In trans bonds, the two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other. • Naturally-occurring ...
... chain on either side of the double bond are either both “up” or both “down,” such that both are on the same side of the molecule. • In trans bonds, the two pieces of the molecule are on opposite sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other. • Naturally-occurring ...
Biochemistry with Elements of Chemistry
... essay, matching and formulas may be included. The grade obtained from the final exam may be increased for students who are very active during seminars, labs and have got high grades from intermediate tests by the head of the Department. Academic honesty: Cheating will not be tolerated! The minimum p ...
... essay, matching and formulas may be included. The grade obtained from the final exam may be increased for students who are very active during seminars, labs and have got high grades from intermediate tests by the head of the Department. Academic honesty: Cheating will not be tolerated! The minimum p ...
Name 1 Bio 451 12th November, 1999 EXAM III This
... c) The additionof ubiquitin protects segments of a protein from proteolysis. d) Lysosomal proteases degrade only extracellular proteins that enter the cell by endocytosis. e) The ubiquitin-transfer reactions catalyzed by E2 and E3 do not require the input of free energy in the form of ATP. ...
... c) The additionof ubiquitin protects segments of a protein from proteolysis. d) Lysosomal proteases degrade only extracellular proteins that enter the cell by endocytosis. e) The ubiquitin-transfer reactions catalyzed by E2 and E3 do not require the input of free energy in the form of ATP. ...
here
... behind your answers. Turn in to my Inbox on the front desk. Write your name, the date you turn it in (honor system) and the period of your class at the top. Each day late is penalized 10 pts. If you are out of school, it can be submitted via e-mail. ...
... behind your answers. Turn in to my Inbox on the front desk. Write your name, the date you turn it in (honor system) and the period of your class at the top. Each day late is penalized 10 pts. If you are out of school, it can be submitted via e-mail. ...
Editorial Comment
... failure patients of Sullivan et al,' the Vo2 was unexpectedly low. It can be calculated from either total body Vo2 or by oxygen consumption calculated from leg blood flow and arteriovenous oxygen difference, that the exercising muscles of the heart failure group had an oxygen consumption of only abo ...
... failure patients of Sullivan et al,' the Vo2 was unexpectedly low. It can be calculated from either total body Vo2 or by oxygen consumption calculated from leg blood flow and arteriovenous oxygen difference, that the exercising muscles of the heart failure group had an oxygen consumption of only abo ...
File
... Building Blocks: Containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Function: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic information. Examples: There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. ...
... Building Blocks: Containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Function: Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary, or genetic information. Examples: There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. ...
File - Mr. Shanks` Class
... A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of chemical bonds with the release or absorption of energy ...
... A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of chemical bonds with the release or absorption of energy ...
File
... (or vice versa) (this is mainly true for both high and low levels of iron); this increase in cellular iron could be due to increased numbers of chloroplasts / an increase in photosynthesis / an increase in the concentration of photosynthetic molecules when light is limiting; this could be due to the ...
... (or vice versa) (this is mainly true for both high and low levels of iron); this increase in cellular iron could be due to increased numbers of chloroplasts / an increase in photosynthesis / an increase in the concentration of photosynthetic molecules when light is limiting; this could be due to the ...
Oxidations – loss of electrons
... • Reduces organic molecules in order to regenerate NAD+ 1.Ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast – CO2, ethanol, and NAD+ are produced ...
... • Reduces organic molecules in order to regenerate NAD+ 1.Ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast – CO2, ethanol, and NAD+ are produced ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.