Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism
... Proteins are degraded into amino acids. Protein turnover is tightly regulated. First step in protein degradation is the removal of the nitrogen Ammonium ion is converted to urea in most ...
... Proteins are degraded into amino acids. Protein turnover is tightly regulated. First step in protein degradation is the removal of the nitrogen Ammonium ion is converted to urea in most ...
2nd bio1 exam sample
... 1) A cell lacking oligosaccharides on the external surface of its plasma membrane would likely be inefficient in cell-cell recognition. 2) The most accepted model of plasma membrane structure is the fluid mosaic model. 3) The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals enables th ...
... 1) A cell lacking oligosaccharides on the external surface of its plasma membrane would likely be inefficient in cell-cell recognition. 2) The most accepted model of plasma membrane structure is the fluid mosaic model. 3) The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals enables th ...
File
... Short Answer: Be concise, yet thorough in your answers. Include any relevant information. (5pts each) 31. After a biochemical analysis of the victim’s tissues, brilliant biologist/criminal investigator J.C. Mickleberry announced his findings, “Contrary to the conclusions of the police, the victim di ...
... Short Answer: Be concise, yet thorough in your answers. Include any relevant information. (5pts each) 31. After a biochemical analysis of the victim’s tissues, brilliant biologist/criminal investigator J.C. Mickleberry announced his findings, “Contrary to the conclusions of the police, the victim di ...
Chapter 4 Outline
... 3. Some enzymes are present in the cell’s cytoplasm, so those reactions occur in the cytosol, while other enzymes are present in the mitochondria of the cell, so those reactions occur in the mitochondria. 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy ...
... 3. Some enzymes are present in the cell’s cytoplasm, so those reactions occur in the cytosol, while other enzymes are present in the mitochondria of the cell, so those reactions occur in the mitochondria. 4. All organic molecules (carbohydrates, fats, and proteins) can be processed to release energy ...
metabolism - Farmasi Unand
... acetylated • Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase deficiency, approximately 10% of black Americans • Phenytoin, Efficient & Poor Metabolizer • Propranolol, difference among Chinese population ...
... acetylated • Glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase deficiency, approximately 10% of black Americans • Phenytoin, Efficient & Poor Metabolizer • Propranolol, difference among Chinese population ...
chapter-23
... a. breaking down of molecules for energy b. building up of large molecules from smaller ones c. sum total of all chemical reactions involved in maintaining the living cell d. series of consecutive biochemical reactions e. generation of cations by oxidation reactions 2. Which of the following stateme ...
... a. breaking down of molecules for energy b. building up of large molecules from smaller ones c. sum total of all chemical reactions involved in maintaining the living cell d. series of consecutive biochemical reactions e. generation of cations by oxidation reactions 2. Which of the following stateme ...
Recitation 4: glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, and the citric acid cycle
... • Review of metabolism thus far • Practice problems • Questions about Pset 4? ...
... • Review of metabolism thus far • Practice problems • Questions about Pset 4? ...
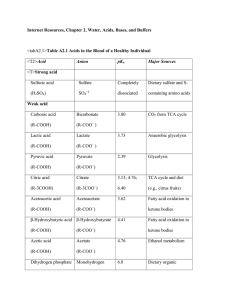
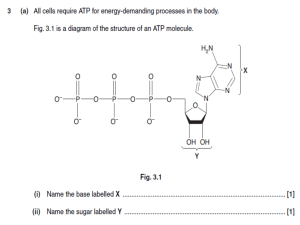
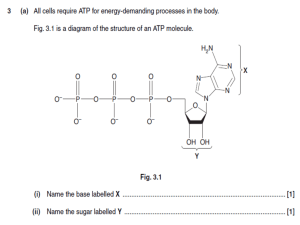
... Learning targets written in italics pertain to Honors Biology students. #1. How do cells use metabolic pathways to provide energy? ATP, Enzymes and Buffers A. I can list the basic components of an ATP molecule and draw them properly connected. I can demonstrate how an ATP molecule (serves as an ener ...
... Learning targets written in italics pertain to Honors Biology students. #1. How do cells use metabolic pathways to provide energy? ATP, Enzymes and Buffers A. I can list the basic components of an ATP molecule and draw them properly connected. I can demonstrate how an ATP molecule (serves as an ener ...
Molecular Principles of Bioactive Systems
... IV. Course objectives The ability to understand the relationship structure - function (reactivity, affinity, etc.), the main classes of biopolymers (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, polysaccharides) that provides the morphological structure and functions of cells and supra-cellular structures of ani ...
... IV. Course objectives The ability to understand the relationship structure - function (reactivity, affinity, etc.), the main classes of biopolymers (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, polysaccharides) that provides the morphological structure and functions of cells and supra-cellular structures of ani ...
Access the file
... Olfaction • SPME head space analysis showed compounds present in media after Brett growth • Are these major compounds the ones that are having the most odor impact? • SPME GC-Olfactory analysis attempted to answer that question. ...
... Olfaction • SPME head space analysis showed compounds present in media after Brett growth • Are these major compounds the ones that are having the most odor impact? • SPME GC-Olfactory analysis attempted to answer that question. ...
Biochemistry - Austin Community College
... • Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Be ...
... • Enzymes are proteins that carry out most catalysis in living organisms. • Unlike heat, enzymes are highly specific. Each enzyme typically speeds up only one or a few chemical reactions. • Unique three-dimensional shape enables an enzyme to stabilize a temporary association between substrates. • Be ...
Ch6PROTEIN
... • Albumin transports a variety of nutrients such as calcium, zinc, and Vitamin B6 • Transferrin transports iron (hemoglobin – a protein, contains iron, but it transports oxygen) • Proteins may also acts as channels or pumps across the cell membrane Energy Source • If the diet does not provide enough ...
... • Albumin transports a variety of nutrients such as calcium, zinc, and Vitamin B6 • Transferrin transports iron (hemoglobin – a protein, contains iron, but it transports oxygen) • Proteins may also acts as channels or pumps across the cell membrane Energy Source • If the diet does not provide enough ...
Chapter 04 - Lecture Outline
... Recall that glycolysis results in pyruvate. If oxygen is not present (i.e. under anaerobic conditions), pyruvate can ferment in one of two ways: ...
... Recall that glycolysis results in pyruvate. If oxygen is not present (i.e. under anaerobic conditions), pyruvate can ferment in one of two ways: ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • NAD can then be reused in glycolysis. • This production of lactate regenerates NAD. This means glycolysis can continue even when there is not much oxygen around, so a small amount of ATP can be produced to keep some biological ...
... • NAD can then be reused in glycolysis. • This production of lactate regenerates NAD. This means glycolysis can continue even when there is not much oxygen around, so a small amount of ATP can be produced to keep some biological ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • NAD can then be reused in glycolysis. • This production of lactate regenerates NAD. This means glycolysis can continue even when there is not much oxygen around, so a small amount of ATP can be produced to keep some biological ...
... • NAD can then be reused in glycolysis. • This production of lactate regenerates NAD. This means glycolysis can continue even when there is not much oxygen around, so a small amount of ATP can be produced to keep some biological ...
Cell Energy Part 3 – Respiration
... Metabolism – the set of chemical reactions that happen in an organism to maintain life Allow organisms to grow/reproduce, maintain structures, respond to environment Organized into pathways, where one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical Two categories: catab ...
... Metabolism – the set of chemical reactions that happen in an organism to maintain life Allow organisms to grow/reproduce, maintain structures, respond to environment Organized into pathways, where one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical Two categories: catab ...
BTEC First Principles Revision Tracker
... following eukaryotic cells: a. motor and sensory neurones b. red blood cell c. white blood cell d. egg cell e. sperm cell f. root hair cell g. xylem and phloem cells h. guard cell Describe the function of the following components of eukaryotic cells: a. nucleus b. cytoplasm c. cell membrane d. chlor ...
... following eukaryotic cells: a. motor and sensory neurones b. red blood cell c. white blood cell d. egg cell e. sperm cell f. root hair cell g. xylem and phloem cells h. guard cell Describe the function of the following components of eukaryotic cells: a. nucleus b. cytoplasm c. cell membrane d. chlor ...
KEY - chem.uwec.edu
... Assuming the oysters have a steady supply of oxaloacetate (from amino acids), how much energy could they derive from this process (per “cycle”)? One ATP “equivalent” is generated by succinyl CoA synthetase. The NADH used cancels the NADH produced and the second NADH can reduce FAD via the electron t ...
... Assuming the oysters have a steady supply of oxaloacetate (from amino acids), how much energy could they derive from this process (per “cycle”)? One ATP “equivalent” is generated by succinyl CoA synthetase. The NADH used cancels the NADH produced and the second NADH can reduce FAD via the electron t ...
Chapter 27 Bioenergetics: How the Body Converts Food to Energy
... potassium ATPase (see Chemical Connections 21C). When ATP is hydrolyzed, sodium ions are pumped out of a cell and potassium ions are pumped in. Because the charge concentration is now different outside and inside the cell there is an electrical gradient. This process is important in neurotransmissio ...
... potassium ATPase (see Chemical Connections 21C). When ATP is hydrolyzed, sodium ions are pumped out of a cell and potassium ions are pumped in. Because the charge concentration is now different outside and inside the cell there is an electrical gradient. This process is important in neurotransmissio ...
The Logic Linking Protein Acetylation and Metabolism
... biologically is an important topic for future studies. In the above framework, protein acetylation governs how cells choose glycolytic versus oxidative metabolism as a function of available energy and helps determine the storage or utilization of carbon energy. Because the substrates for protein ace ...
... biologically is an important topic for future studies. In the above framework, protein acetylation governs how cells choose glycolytic versus oxidative metabolism as a function of available energy and helps determine the storage or utilization of carbon energy. Because the substrates for protein ace ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.