Cellular Respiration - Labs - Department of Plant Biology, Cornell
... Each cell has the basic chemicals required for life, however, the precursors required by each cell, the rate of turnover of the chemicals, and the chemicals produced by each cell differ depending on cell type. The structure and chemical composition of a cell depends on the function of the cell in an ...
... Each cell has the basic chemicals required for life, however, the precursors required by each cell, the rate of turnover of the chemicals, and the chemicals produced by each cell differ depending on cell type. The structure and chemical composition of a cell depends on the function of the cell in an ...
Synthesis of Fats, Proteins, and Carbohydrates Lab
... d. When a fat is made, 3 water molecules are also made (this is called a condensation reaction). Make the 3 water molecules by cutting out and gluing together the one H-H-H piece with three O-H pieces. Make sure to glue this piece onto the same sheet as the fat. e. Label your paper “Fat or Lipid” 3. ...
... d. When a fat is made, 3 water molecules are also made (this is called a condensation reaction). Make the 3 water molecules by cutting out and gluing together the one H-H-H piece with three O-H pieces. Make sure to glue this piece onto the same sheet as the fat. e. Label your paper “Fat or Lipid” 3. ...
The Science of Energy Metabolism
... of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is an energy storage molecule which provides chemical energy to drive the energy demands of the body. ATP is produced by a number of chemical reactions which take place within the mitochondria, organelles which are present in all cells of the human body. Mitochon ...
... of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is an energy storage molecule which provides chemical energy to drive the energy demands of the body. ATP is produced by a number of chemical reactions which take place within the mitochondria, organelles which are present in all cells of the human body. Mitochon ...
الشريحة 1
... plasma from which the drug is completely removed per unit time. The amount eliminated is proportional to the concentration of the drug in the blood. A clearance of 100 mL/minute of a chemical means that 100 mL of blood/plasma is completely cleared of the compound in each ...
... plasma from which the drug is completely removed per unit time. The amount eliminated is proportional to the concentration of the drug in the blood. A clearance of 100 mL/minute of a chemical means that 100 mL of blood/plasma is completely cleared of the compound in each ...
Environmental Microbiology – Seminar 31.10
... 1) What is the difference between aerobic respiration and fermentation? Explain the mechanism and give examples. In fermentation, energy is gained via substrate level phosphorylation. E.g, Phosphoenolpyruvate reacts with ADP and Pi to Pyruvate and ATP. 2) What happens if there is no O2 in the body? ...
... 1) What is the difference between aerobic respiration and fermentation? Explain the mechanism and give examples. In fermentation, energy is gained via substrate level phosphorylation. E.g, Phosphoenolpyruvate reacts with ADP and Pi to Pyruvate and ATP. 2) What happens if there is no O2 in the body? ...
The Molecules of Cells
... – High energy molecule • Last 2 phosphate bonds are unstable and easily broken • Terminal phosphate bond is cleaved releasing energy • Leaves ADP and an inorganic phosphate ...
... – High energy molecule • Last 2 phosphate bonds are unstable and easily broken • Terminal phosphate bond is cleaved releasing energy • Leaves ADP and an inorganic phosphate ...
NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm
... NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm features pharmaceutical grade L-tryptophan, an essential amino acid which is converted to serotonin in the brain. In addition, the herbs ashwaganda, theanine and valerian root help soothe and relax naturally, effectively and safely. 1 Capsule ...
... NUTRICALM A Formula Designed to Calm and Sooth NutriCalm features pharmaceutical grade L-tryptophan, an essential amino acid which is converted to serotonin in the brain. In addition, the herbs ashwaganda, theanine and valerian root help soothe and relax naturally, effectively and safely. 1 Capsule ...
2 hours
... F. How are a change in conformation and mechanical energy related? (1 point) Answer: ATP may be bound to a protein, inducing a conformational change, which can store free energy. This change in conformation is actually the mechanical energy of movement such as muscle contraction. ...
... F. How are a change in conformation and mechanical energy related? (1 point) Answer: ATP may be bound to a protein, inducing a conformational change, which can store free energy. This change in conformation is actually the mechanical energy of movement such as muscle contraction. ...
Chapter 5b Cell Respiration
... 19. Two electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 are made in the Krebs cycle. These electron carriers store as much energy as glucose and Pyruvate. 20. The electron carriers, NADH and FADH 2, move from the Krebs cycle to the Electron Transport Chain, the third step of aerobic respiration. 21. Where does th ...
... 19. Two electron carriers NADH and FADH 2 are made in the Krebs cycle. These electron carriers store as much energy as glucose and Pyruvate. 20. The electron carriers, NADH and FADH 2, move from the Krebs cycle to the Electron Transport Chain, the third step of aerobic respiration. 21. Where does th ...
Function
... causes the birth canal to stretch beyond its setpoint amount of stretch, which is detected by sensors in the vaginal wall and fed back to hypothalamus of brain, which releases the hormone, oxytocin, which stimulates stronger and more frequent uterine contractions, which pushes the ...
... causes the birth canal to stretch beyond its setpoint amount of stretch, which is detected by sensors in the vaginal wall and fed back to hypothalamus of brain, which releases the hormone, oxytocin, which stimulates stronger and more frequent uterine contractions, which pushes the ...
Topic 4: BIOLOGICALLY IMPORTANT ORGANIC MOLECULES
... helps with this assembly. Fig. 5.26-chaperonins The local environment my influence protein structure and solubility: (1) heat denaturation- high temperatures break H- and ionic bonds causing folding to change. Hydrophobic amino acids normally buried in the interior may be forced to the surface causi ...
... helps with this assembly. Fig. 5.26-chaperonins The local environment my influence protein structure and solubility: (1) heat denaturation- high temperatures break H- and ionic bonds causing folding to change. Hydrophobic amino acids normally buried in the interior may be forced to the surface causi ...
Sentinel™ Performance LS Formula
... minerals, trace minerals and vitamins help build, strengthen and maintain all body tissues including bone and muscle. These nutrients also help regulate metabolic activities and help support the immune system to sustain overall health. The more biologically available chelated forms of zinc, copper a ...
... minerals, trace minerals and vitamins help build, strengthen and maintain all body tissues including bone and muscle. These nutrients also help regulate metabolic activities and help support the immune system to sustain overall health. The more biologically available chelated forms of zinc, copper a ...
PP Cellular Energy
... • Cellular respiration involves many different reactions, each controlled by its own enzyme. • Cellular respiration usually uses glucose however fats (fatty acids and glycerol) and amino acids can also be used. ...
... • Cellular respiration involves many different reactions, each controlled by its own enzyme. • Cellular respiration usually uses glucose however fats (fatty acids and glycerol) and amino acids can also be used. ...
Lecture 6
... generated and chemical energy will be stored in 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 • CO2 diffuses from the mitochondrial matrix into your blood where it is transported finally to your lungs ...
... generated and chemical energy will be stored in 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 • CO2 diffuses from the mitochondrial matrix into your blood where it is transported finally to your lungs ...
Test 2 - Lone Star College
... that cell damage is a product of aging, not the actual cause. “It’s like the sun coming up every morning—they can’t prove that it will,” he says in reference to free radical proponents. “But I have to prove that it won’t.” These modified worms are not healthy, though; they show evidence of oxidative ...
... that cell damage is a product of aging, not the actual cause. “It’s like the sun coming up every morning—they can’t prove that it will,” he says in reference to free radical proponents. “But I have to prove that it won’t.” These modified worms are not healthy, though; they show evidence of oxidative ...
Sylabus
... functions, as well as the biochemistry of the skeletal and smooth muscles, and biochemical functions of the blood; Knows biochemical mechanisms of hormones actions, and the consequences of disturbances in hormonal regulation; Knows the principles of the experimental biochemical investigations as wel ...
... functions, as well as the biochemistry of the skeletal and smooth muscles, and biochemical functions of the blood; Knows biochemical mechanisms of hormones actions, and the consequences of disturbances in hormonal regulation; Knows the principles of the experimental biochemical investigations as wel ...
Biochemistry and the Cell - Tanque Verde Unified District
... Water is not the only molecule that makes hydrogen bonds! They are important in DNA and other large molecules too. ...
... Water is not the only molecule that makes hydrogen bonds! They are important in DNA and other large molecules too. ...
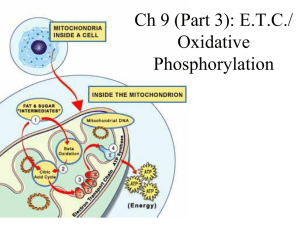
Ch 9: E.T.C./ Oxidative Phosphorylation
... they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
... they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration Cellular Energy •The Stages of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration has two stages. •Glycolysis The first stage of cellular respiration is called glycolysis. •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the p ...
... Cellular Respiration Cellular Energy •The Stages of Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration has two stages. •Glycolysis The first stage of cellular respiration is called glycolysis. •Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration The second stage of cellular respiration is either aerobic respiration (in the p ...
Basal metabolic rate

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the minimal rate of energy expenditure per unit time by endothermic animals at rest. (McNab, B. K. 1997). On the Utility of Uniformity in the Definition of Basal Rate of Metabolism. Physiol. Zool. Vol.70; Metabolism refers to the processes that the body needs to function. Basal Metabolic Rate is the amount of energy expressed in calories that a person needs to keep the body functioning at rest. Some of those processes are breathing, blood circulation, controlling body temperature, cell growth, brain and nerve function, and contraction of muscles. Basal metabolic rate (BMR) affects the rate that a person burns calories and ultimately whether you maintain, gain, or lose weight. Your basal metabolic rate accounts for about 60 to 75% of the calories you burn every day. It is influenced by several factors.